Abstract
Cell-free extracts of antibiotic-negative mutants of Cephalosporium acremonium converted delta-(L-alpha-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine (LLD-tripeptide) into an antibiotic that was destroyed by penicillinase. The enzymic activity of the extracts was destroyed by boiling, but was not inhibited by cycloheximide. LLL-Tripeptide was totally inactive as substrate. The product resembled isopenicillin N, but not penicillin N, in its antibacterial spectrum. We propose that isopenicillin N is the first product of cyclization of LLD-tripeptide.
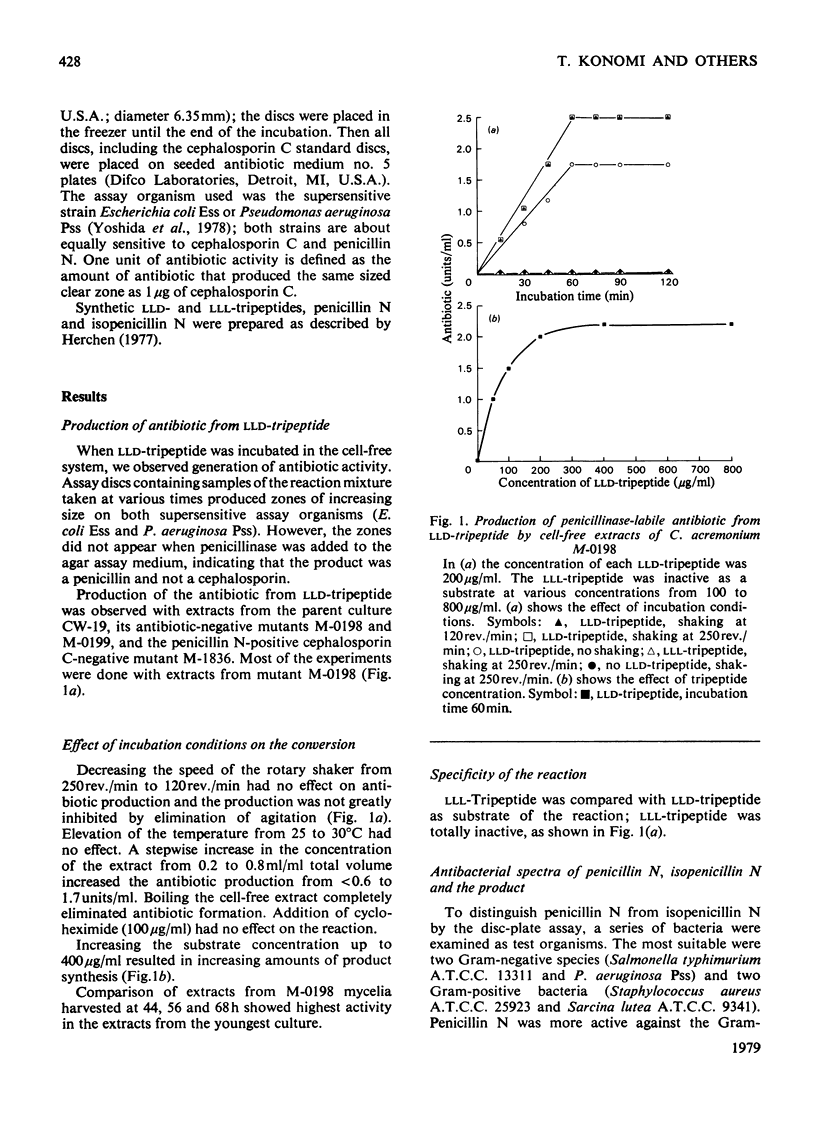
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bost P. E., Demain A. L. Studies on the cell-free biosynthesis of beta-lactam antibiotics. Biochem J. 1977 Mar 15;162(3):681–687. doi: 10.1042/bj1620681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLE M., BATCHELOR F. R. Aminoadipylpenicillin in penicillin fermentations. Nature. 1963;198:383–384. doi: 10.1038/198383a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett P. A., Loder P. B., Duncan M. J., Beesley T. J., Abraham E. P. Formation and properties of protoplasts from antibiotic-producing strains of Penicillium chrysogenum and Cephalosporium acremonium. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Dec;79(2):293–309. doi: 10.1099/00221287-79-2-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett P. A., Usher J. J., Huddleston J. A., Bleaney R. C., Nisbet J. J., Abraham E. P. Synthesis of delta-(alpha-aminoadipyl)cysteinylvaline and its role in penicillin biosynthesis. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 1;157(3):651–660. doi: 10.1042/bj1570651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohsaka M., Demain A. L. Conversion of penicillin N to cephalosporin(s) by cell-free extracts of Cephalosporium acremonium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 17;70(2):465–473. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91069-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan J., Bleaney R. C., Huddleston J. A., Abraham E. P. Incorporation of 3H from delta-(L-alpha-amino (4,5-3H)adipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-(4,4-3H)valine into isopenicillin N. Biochem J. 1979 Nov 15;184(2):421–426. doi: 10.1042/bj1840421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usher J. J., Loder B., Abraham E. P. Synthesis of tritium-labelled isopenicillin N, penicillin N and 6-aminopenicillanic acid. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;151(3):729–739. doi: 10.1042/bj1510729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderhaeghe H., Vlietinck A., Claesen M., Parmentier G. Preparation of penicillin N and isopenicillin N. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1974 Mar;27(3):169–177. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.27.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M., Konomi T., Kohsaka M., Baldwin J. E., Herchen S., Singh P., Hunt N. A., Demain A. L. Cell-free ring expansion of penicillin N to deacetoxycephalosporin C by Cephalosporium acremonium CW-19 and its mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6253–6257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


