Abstract
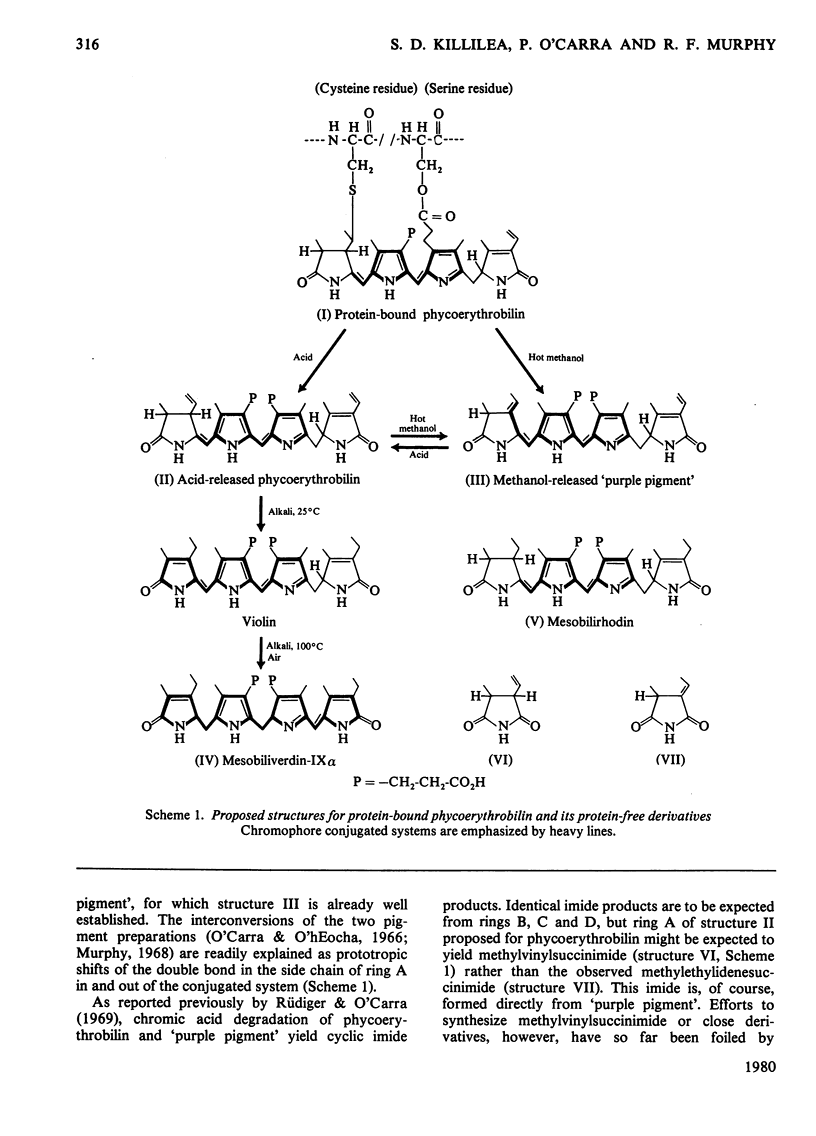
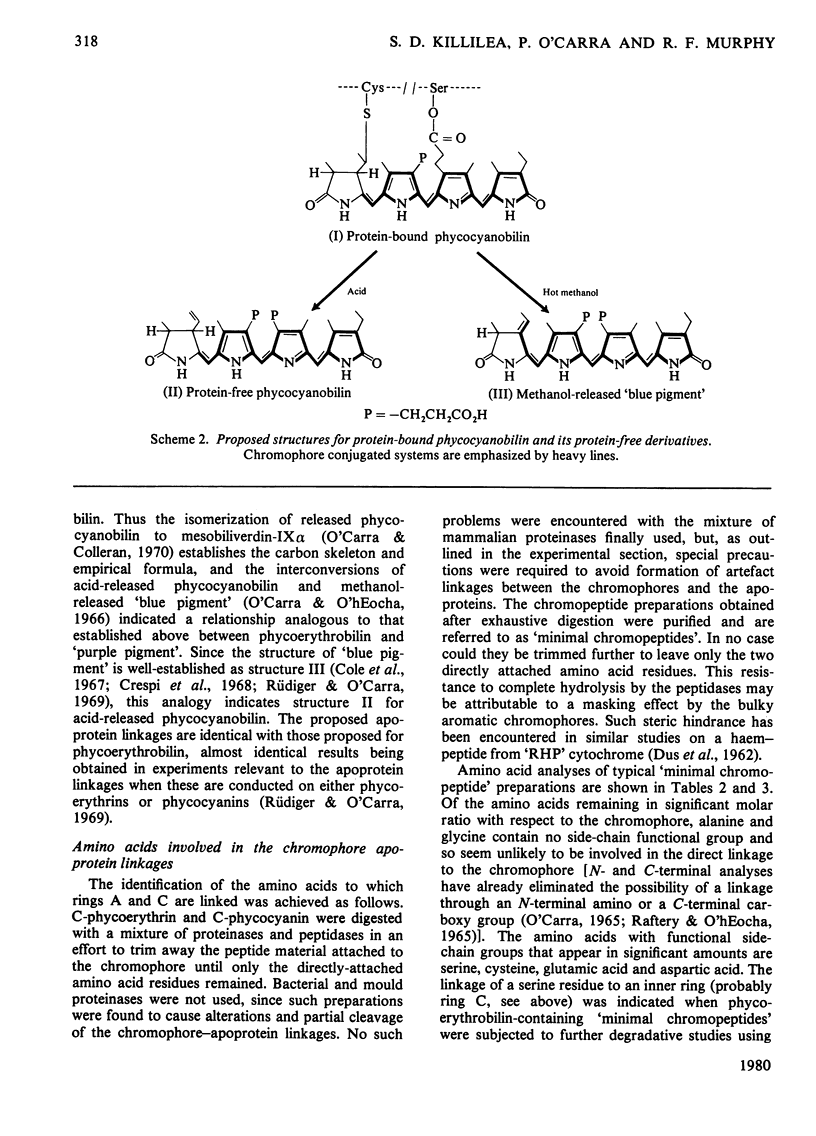
Phycoerythrobilin and phycocyanobilin are covalently attached to the apoproteins of phycoerythrins and phycocyanins. One linkage consists of an ester bond between the hydroxy group of a serine residue and the propionate side chain on one of the inner pyrrole rings (probably ring C). The other linkage is a labile thioether bond between a cysteine residue and the two-carbon side chain on pyrrole ring A. This side chain and both of the α-positions of the ring A are in the reduced state. This constitutes an important structural revision, since, in the structures currently accepted for the phycobilins, the two-carbon side chain on ring A is depicted as an ethylidene grouping and this has been regarded not only as a very characteristic feature of the phycobilins, but also as a probable structural feature of the chromophore of phytochrome, largely on the basis of other analogies with the phycobilins. The ethylidene-containing structures apply instead to artefact forms of the pigments released from the apoproteins by treatment with hot methanol. Cleavage of the ring-A linkage involves an elimination reaction releasing the cysteine residue and generating a double bond in the ring-A side chain. During cleavage in methanol the direction of the elimination is towards the ring, generating the ethylidene double bond. Since this is linked to the conjugated system, the methanol-released pigments differ spectrally from the native phycobilins. During acid-catalysed release of the pigments, the elimination apparently goes in the opposite direction, generating a double bond at the outer position of the side chain. Since this double bond is not linked to the conjugated system, the acid-released pigments remain spectrally identical with their protein-bound counterparts.
Full text
PDF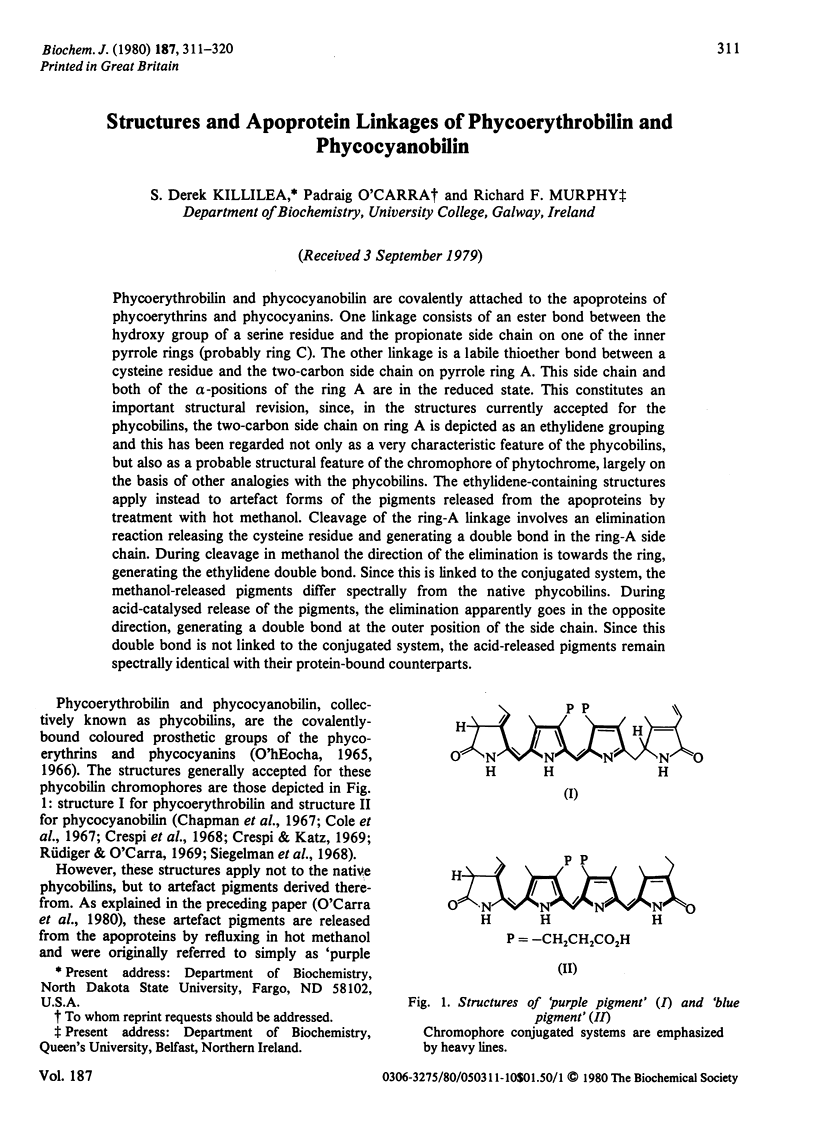







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLACKBURN S., LOWTHER A. G. The separation of N-2:4-dinitrophenly amino-acids on paper chromatograms. Biochem J. 1951 Jan;48(1):126–128. doi: 10.1042/bj0480126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. S., Troxler R. F. Bilin--apoprotein linkages in rhodophytan phycobiliproteins: the role of cysteine. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80585-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant D. A., Hixson C. S., Glazer A. N. Structural studies on phycobiliproteins III. Comparison of bilin-containing peptides from the beta subunits of C-phycocyanin, R-phycocyanin, and phycoerythrocyanin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 10;253(1):220–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byfield P. G., Zuber H. Chromophore-containing peptide sequences in C-phycocyanin from Mastigocladus laminosus. FEBS Lett. 1972 Nov 15;28(1):36–40. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80671-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman D. J., Budzikiewicz H., Siegelman H. W. The structure of mesobilirhodin. Experientia. 1972 Aug 15;28(8):876–878. doi: 10.1007/BF01924915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crespi H. L., Smith U., Katz J. J. Phycocyanobilin. Structure and exchange studies by nuclear magnetic resonance and its mode of attachment in phycocyanin. A model for phytochrome. Biochemistry. 1968 Jun;7(6):2232–2242. doi: 10.1021/bi00846a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazer A. N., Hixson C. S., DeLange R. J. Determination of the number of thioether-linked cysteine residues in cytochromes c and phycobiliproteins. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jan 15;92(2):489–496. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90689-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HULTQUIST D. E., MORRISON M. LACTOPEROXIDASE. I. THE PROSTHETIC GROUP OF LACTOPEROXIDASE. J Biol Chem. 1963 Aug;238:2843–2846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATHESON N. A. The quantitative isolation of valine from amino acid mixtures as its dinitrophenyl derivative. Biochem J. 1963 Jul;88:152–155. doi: 10.1042/bj0880152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLS G. L. Observations on the application of fluorodinitrobenzene to the quantitative analysis of proteins. Biochem J. 1952 Mar;50(5):707–712. doi: 10.1042/bj0500707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Carra P., Colleran E. Separation and identification of biliverdin isomers and isomer analysis of phycobilins and bilirubin. J Chromatogr. 1970 Aug 12;50(3):458–468. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)97973-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Carra P., Murphy R. F., Killilea S. D. The native forms of the phycobilin chromophores of algal biliproteins. A clarification. Biochem J. 1980 May 1;187(2):303–309. doi: 10.1042/bj1870303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OCARRA P. PURIFICATION AND N-TERMINAL ANALYSES OF ALGAL BILIPROTEINS. Biochem J. 1965 Jan;94:171–174. doi: 10.1042/bj0940171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAFTERY M. A., OHEOCHA C. AMINO ACID COMPOSITION AND C-TERMINAL RESIDUES OF ALGAL BILIPROTEINS. Biochem J. 1965 Jan;94:166–170. doi: 10.1042/bj0940166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery M. A., Cole R. D. On the aminoethylation of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 10;241(15):3457–3461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüdiger W., Carra P. O. Studies on the structures and apoprotein linkages of the phycobilins. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Feb;7(4):509–516. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb19637.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüdiger W. Recent chemistry and biochemistry of bile pigments. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1970 Jul;9(7):473–480. doi: 10.1002/anie.197004731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelman H. W., Chapman D. J., Cole W. J. Enzymatic cleavage of phycocyanobilin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Oct;122(1):261–261. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90152-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRISTRAM G. R., SMITH R. H. THE AMINO ACID COMPOSITION OF SOME PURIFIED PROTEINS. Adv Protein Chem. 1963;18:227–318. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams V. P., Glazer A. N. Structural studies on phycobiliproteins. I. Bilin-containing peptides of C-phycocyanin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 10;253(1):202–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


