Abstract
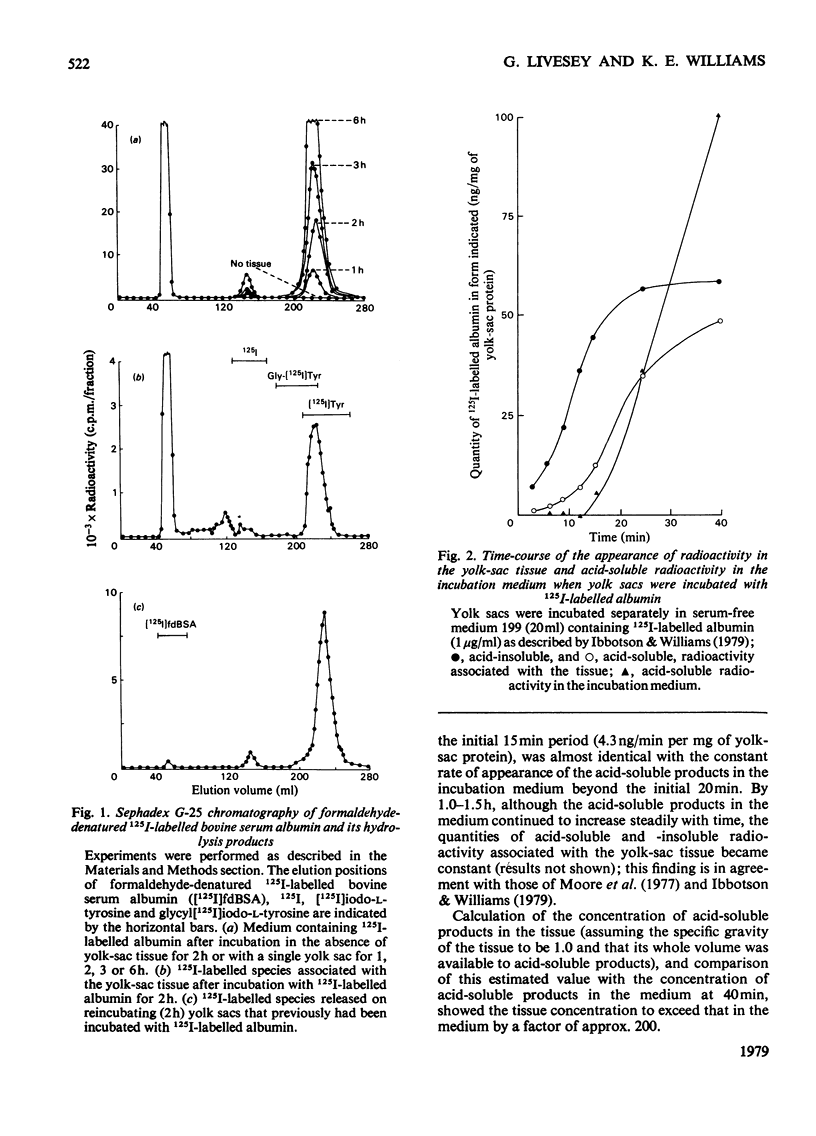
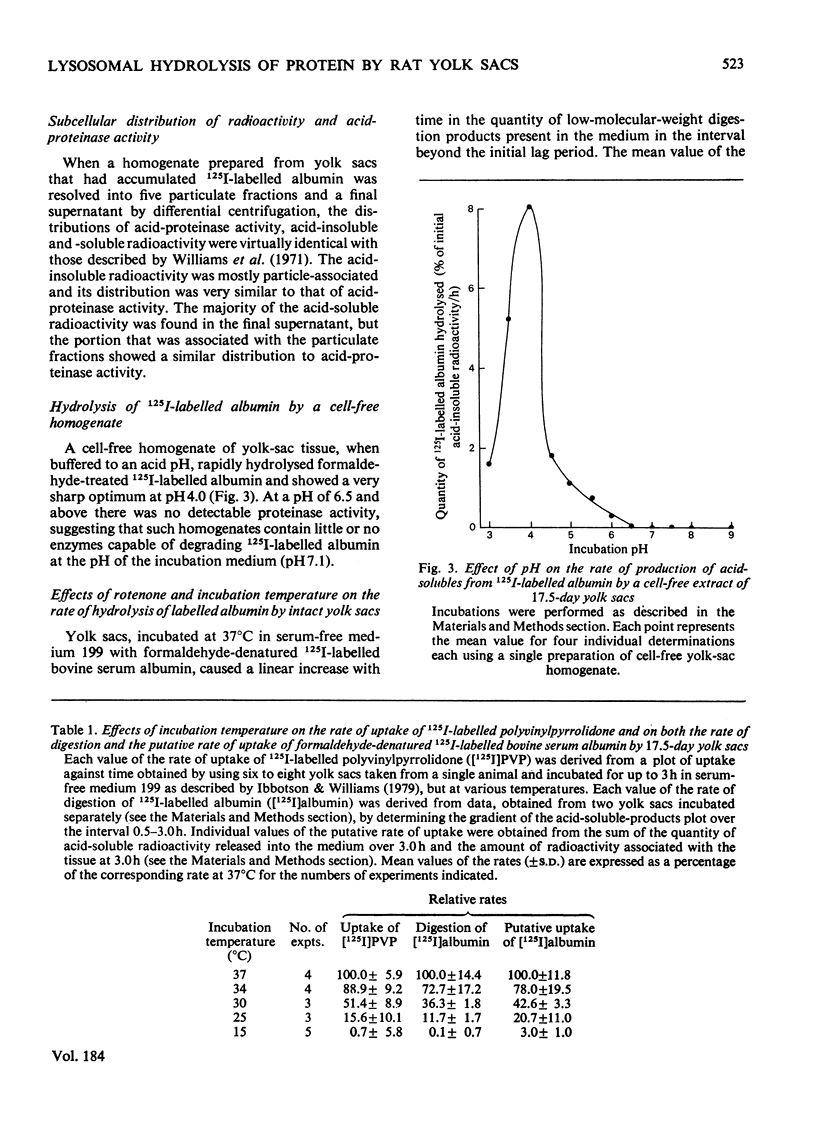
When added to the serum-free medium in which 17.5-day rat yolk sacs were incubated, formaldehyde-denatured 125I-labelled bovine serum albumin was rapidly degraded. More than 80% of the radiolabelled digestion products appearing in the incubation medium consisted of [125I]iodo-L-tyrosine; larger digestion products were found only in association with the yolk-sac tissue. In the early stages of an incubation, low-molecular-weight digestion products began to appear in the incubation medium only after they could be detected within the tissue, and progressive association of trichloroacetic acid-insoluble radioactivity with the tissue preceded both these events. None of the observed proteolysis could be attributed to proteinases released into the incubation medium. Tissue-associated acid-insoluble radioactivity showed a lysosomal distribution on sub-cellular fractionation, and cell-free homogenates of yolk sacs degraded albumin only at acid pH values. Progressively decreasing the rat of pinosome formation (either by progressively lowering the incubation temperature or by the use of increasing concentrations of the metabolic inhibitor rotenone) caused a corresponding decrease in the rate of degradation of albumin. These findings indicate that, in vitro, formaldehyde-denatured 125I-labelled bovine serum albumin is digested by rat yolk sacs exclusively intracellularly, within lysosomes.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Duncan R., Lloyd J. B. Pinocytosis in the rat visceral yolk sac. Effects of temperature, metabolic inhibitors and some other modifiers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 18;544(3):647–655. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90339-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenreich B. A., Cohn Z. A. The uptake and digestion of iodinated human serum albumin by macrophages in vitro. J Exp Med. 1967 Nov 1;126(5):941–958. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.5.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAZAKERLEY S., BEST D. R. SEPARATION OF AMINO ACIDS, AS COPPER CHELATES, FROM AMINO ACID, PROTEIN AND PEPTIDE MIXTURES. Anal Biochem. 1965 Aug;12:290–295. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Kahn R., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin interactions with liver plasma membranes. Independence of binding of the hormone and its degradation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3953–3961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabathuler M. P., Ryser H. J. The digestive function of lysosomes as studies by the turnover of ingested foreign macromolecules. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1969 Apr 15;173(1030):95–98. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1969.0041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brunschede G. Y., Brown M. S. Inhibition of proteolytic degradation of low density lipoprotein in human fibroblasts by chloroquine, concanavalin A, and Triton WR 1339. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7854–7862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibbotson G. E., Williams K. E. Rate of pinocytic capture of macromolecular substrates by rat yolk sac incubated in serum-free culture medium. Biochem J. 1979 Mar 15;178(3):785–792. doi: 10.1042/bj1780785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr M. A., Kenny A. J. The purification and specificity of a neutral endopeptidase from rabbit kidney brush border. Biochem J. 1974 Mar;137(3):477–488. doi: 10.1042/bj1370477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch R. E., Frith L. O., Saunders S. J. Albumin catabolism in vitro by cultured peritoneal and pulmonary mononuclear phagocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 18;279(1):87–91. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90243-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx S. J., Woodward C., Aurbach G. D., Glossmann H., Keutmann H. T. Renal receptors for calcitonin. Binding and degradation of hormone. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 10;248(13):4797–4802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore A. T., Williams K. E., Lloyd J. B. The effect of chemical treatments of albumin and orosomucoid on rate of clearance from the rat bloodstream and rate of pinocytic capture of rat yolk sac cultured in vitro. Biochem J. 1977 Jun 15;164(3):607–616. doi: 10.1042/bj1640607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson M., Berg T. Uptake and degradation of formaldehyde-treated 125I-labelled human serum albumin in rat liver cells in vivo and in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 29;497(1):171–182. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90150-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl S. L., Krans H. M., Birnbaumer L., Rodbell M. Inactivation of glucagon by plasma membranes of rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 25;247(8):2295–2301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reijngoud D. J., Tager J. M. The permeability properties of the lysosomal membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 14;472(3-4):419–449. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(77)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. V., Nicholls S. E., Griffiths P. A., Williams K. E., Lloyd J. B. A quantitative study of pinocytosis and lysosome function in experimentally induced lysosomal storage. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 15;160(3):621–629. doi: 10.1042/bj1600621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saez J. M., Dazord A., Morera A. M., Bataille P. Interactions of adrenocorticotropic hormone with its adrenal receptors. Degradation of ACTH-1-24 and ACTH-11-24. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1683–1689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein O., Weinstein D. B., Stein Y., Steinberg D. Binding, internalization, and degradation of low density lipoprotein by normal human fibroblasts and by fibroblasts from a case of homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):14–18. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terris S., Steiner D. F. Binding and degradation of 125I-insulin by rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 10;250(21):8389–8398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolleshaug H., Berg T., Nilsson M., Norum K. R. Uptake and degradation of 125I-labelled asialo-fetuin by isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 25;499(1):73–84. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90230-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tökés Z. A., Sorgente N. Cell surface-associated and released proteolytic activities of bovine aorta endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Dec 20;73(4):965–971. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90216-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. E., Kidston E. M., Beck F., Lloyd J. B. Quantitative studies of pinocytosis. I. Kinetics of uptake of (125I)polyvinylpyrrolidone by rat yolk sac cultured in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1975 Jan;64(1):113–122. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.1.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. E., Kidston E. M., Beck F., Lloyd J. B. Quantitative studies of pinocytosis. II. Kinetics of protein uptake and digestion by rat yolk sac cultured in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1975 Jan;64(1):123–134. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. E., Lloyd J. B., Davies M., Beck F. Digestion of an exogenous protein by rat yolk-sac cultured in vitro. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(1):303–308. doi: 10.1042/bj1250303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Duve C., de Barsy T., Poole B., Trouet A., Tulkens P., Van Hoof F. Commentary. Lysosomotropic agents. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Sep 15;23(18):2495–2531. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90174-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


