Abstract
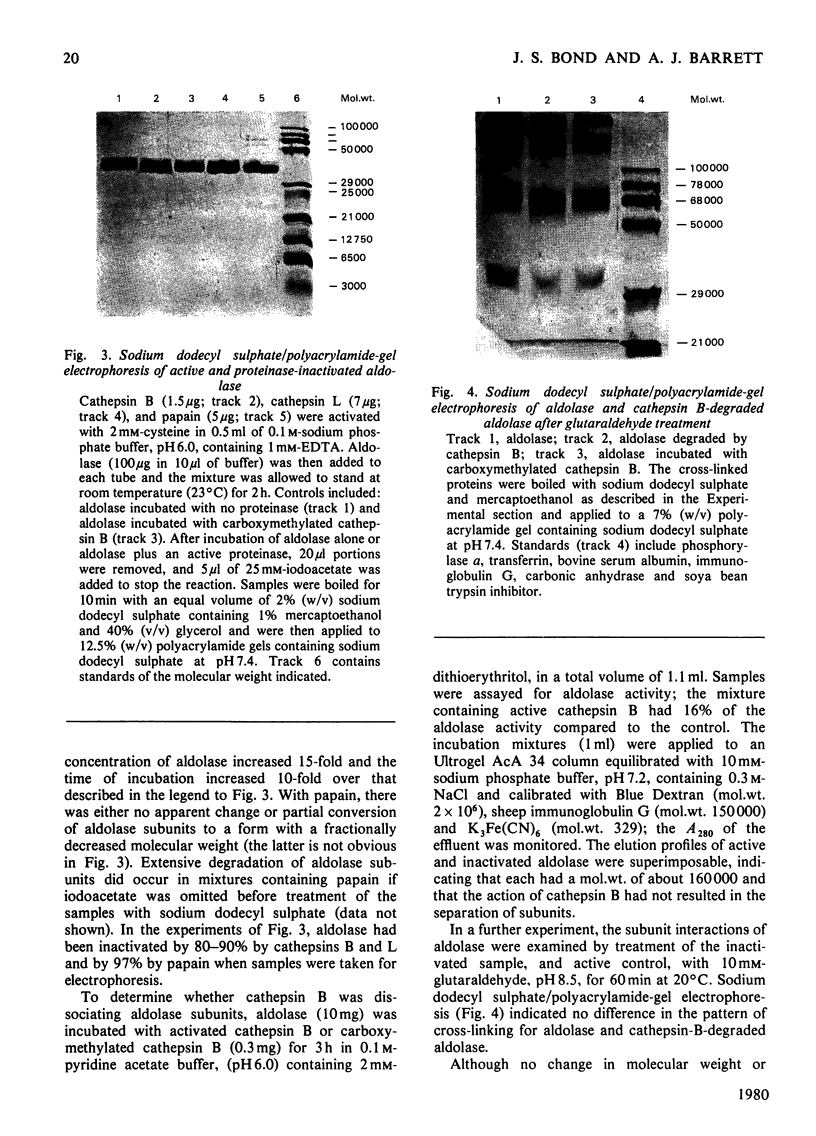
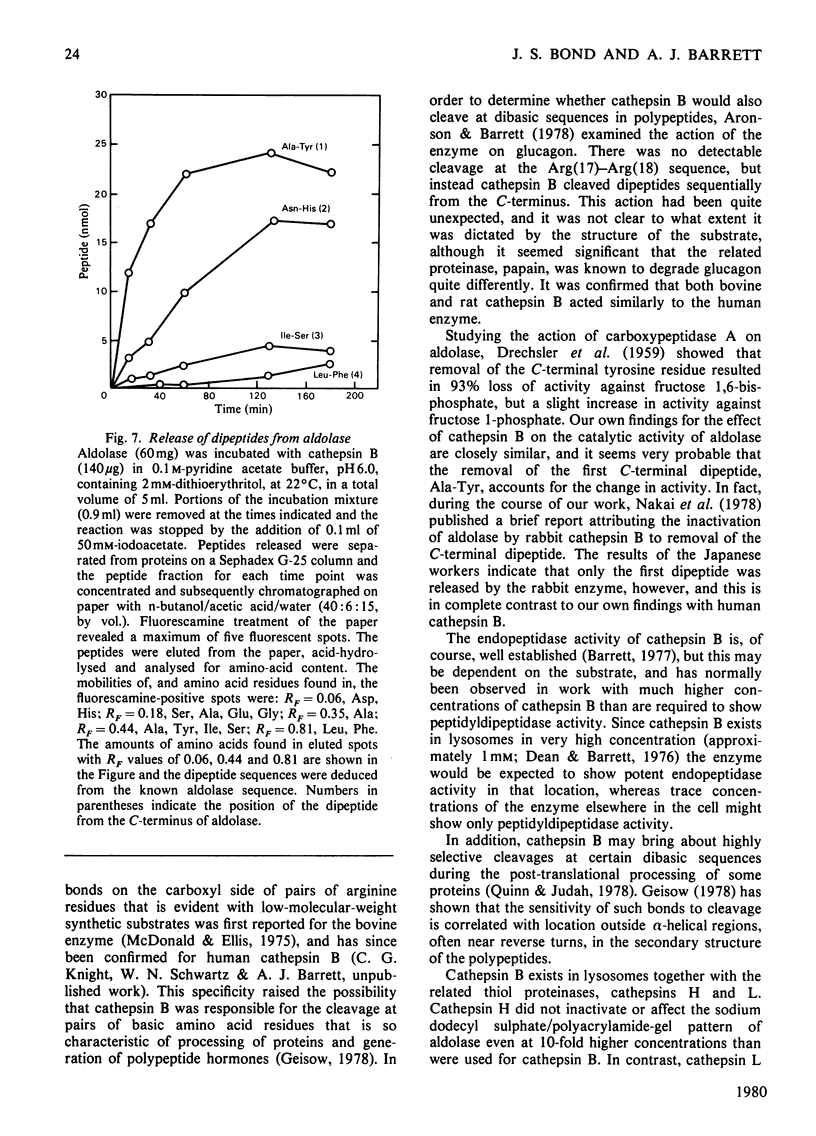
The mechanism of degradation of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase from rabbit muscle by the lysosomal proteinase cathepsin B was determined. Treatment of aldolase with cathepsin B destroys up to 90% of activity with fructose 1,6-bisphosphate as substrate, but activity with fructose 1-phosphate is slightly increased. Cathepsin L, another lysosomal thiol proteinase, and papain are also potent inactivators of aldolase, whereas inactivation is not caused by cathepsins D or H even at high concentrations, or by cathepsin B inhibited by leupeptin or iodoacetate. The cathepsin-B-treated aldolase shows no detectable change in subunit molecular weight, oligomer molecular weight or subunit interactions. Cathepsin B cleaves dipeptides from the C-terminus of th aldolase subunits. Four dipeptides are released sequentially: Ala-Tyr, Asn-His, Ile-Ser and Leu-Phe, and a maximum of five additional dipeptides may be released. There are indications that this peptidyldipeptidase activity of cathepsin B may be an important aspect of its action on protein substrates generally.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronson N. N., Jr, Barrett A. J. The specificity of cathepsin B. Hydrolysis of glucagon at the C-terminus by a peptidyldipeptidase mechanism. Biochem J. 1978 Jun 1;171(3):759–765. doi: 10.1042/bj1710759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J. Intracellular protein degradation. Essays Biochem. 1977;13:1–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J., Brown M. A., Sayers C. A. The electrophoretically 'slow' and 'fast' forms of the alpha 2-macroglobulin molecule. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 1;181(2):401–418. doi: 10.1042/bj1810401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. Human cathepsin B1. Purification and some properties of the enzyme. Biochem J. 1973 Apr;131(4):809–822. doi: 10.1042/bj1310809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRECHSLER E. R., BOYER P. D., KOWALSKY A. G. The catalytic activity of carboxypeptidase-degraded aldolase. J Biol Chem. 1959 Oct;234:2627–2634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E., Poole B. Fractionation of the rat liver enzymes that hydrolyze benzoyl-arginine-2-naphthylamide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 26;397(2):437–442. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90133-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean R. T., Barrett A. J. Lysosomes. Essays Biochem. 1976;12:1–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean R. T. Direct evidence of importance of lysosomes in degradation of intracellular proteins. Nature. 1975 Oct 2;257(5525):414–416. doi: 10.1038/257414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisow M. J. Polypeptide secondary structure may direct the specificity of prohormone conversion. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 1;87(1):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80146-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon H., Gershon D. Inactive enzyme molecules in aging mice: liver aldolase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):909–913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman W., Lanting L., Doddema H. J., Bouma J. M., Gruber M. Role of individual cathepsins in lysosomal protein digestion as tested by specific inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 25;370(1):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90054-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. W., Velick S. F. The synthesis and degradation of fructose diphosphate-aldolase and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase in rabbit liver. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 10;247(13):4138–4143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschke H., Langner J., Wiederanders B., Ansorge S., Bohley P. Cathepsin L. A new proteinase from rat-liver lysosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Apr 1;74(2):293–301. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschke H., Langner J., Wiederanders B., Ansorge S., Bohley P., Hanson H. Cathepsin H: an endoaminopeptidase from rat liver lysosomes. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1977;36(2):185–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. Y. Studies on the structure of rabbit muscle aldolase. Determination of the primary structure of the COOH-terminal BrCN peptide; the complete sequence of the subunit polypeptide chain. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jan;166(1):358–368. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90398-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. K., Ellis S. On the substrate specificity of cathepsins B1 and B2 including a new fluorogenic substrate for cathepsin B1. Life Sci. 1975 Oct 15;17(8):1269–1276. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90137-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai N., Wada K., Kobashi K., Hase J. The limited proteolysis of rabbit muscle aldolase by cathepsin B1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Aug 14;83(3):881–885. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91477-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petell J. K., Lebherz H. G. Properties and metabolism of fructose diphosphate aldolase in livers of "old" and "young" mice. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8179–8184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn P. S., Judah J. D. Calcium-dependent Golgi-vesicle fusion and cathepsin B in the conversion of proalbumin into albumin in rat liver. Biochem J. 1978 May 15;172(2):301–309. doi: 10.1042/bj1720301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSEN H. A modified ninhydrin colorimetric analysis for amino acids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Mar;67(1):10–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz W., Bird J. W. Degradation of myofibrillar proteins by cathepsins B and D. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 1;167(3):811–820. doi: 10.1042/bj1670811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyckoff M., Rodbard D., Chrambach A. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate-containing buffers using multiphasic buffer systems: properties of the stack, valid Rf- measurement, and optimized procedure. Anal Biochem. 1977 Apr;78(2):459–482. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]