Abstract
Sodium pseudomonate was shown to be a powerful competitive inhibitor of Escherichia coli B isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase (Ile-tRNA synthetase). The antibiotic competitively inhibits (Ki 6 nM; cf. Km 6.3 microM), with respect top isoleucine, the formation of the enzyme . Ile approximately AMP complex as measured by the pyrophosphate-exchange reaction, and has no effect on the transfer of [14C]isoleucine from the enzyme . [14C]Ile approximately AMP complex to tRNAIle. The inhibitory constant for the pyrophosphate-exchange reaction was of the same order as that determined for the inhibition of the overall aminoacylation reaction (Ki 2.5 nM; cf. Km 11.1 microM). Sodium [9'-3H]pseudomonate forms a stable complex with Ile-tRNA synthetase. Gel-filtration and gel-electrophoresis studies showed that the antibiotic is only fully released from the complex by 5 M-urea treatment or boiling in 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulphate. The molar binding ratio of sodium [9'-3H]pseudomonate to Ile-tRNA synthetase was found to be 0.85:1 by equilibrium dialysis. Aminoacylation of yeast tRNAIle by rat liver Ile-tRNA synthetase was also competitively inhibited with respect to isoleucine, Ki 20 microM (cf. Km 5.4 microM). The Km values for the rat liver and E. coli B enzymes were of the same order, but the Ki for the rat liver enzyme was 8000 times the Ki for the E. coli B enzyme. This presumably explains the low toxicity of the antibiotic in mammals.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arndt D. J., Berg P. Isoleucyl transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase is a single polypeptide chain. J Biol Chem. 1970 Feb 10;245(3):665–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
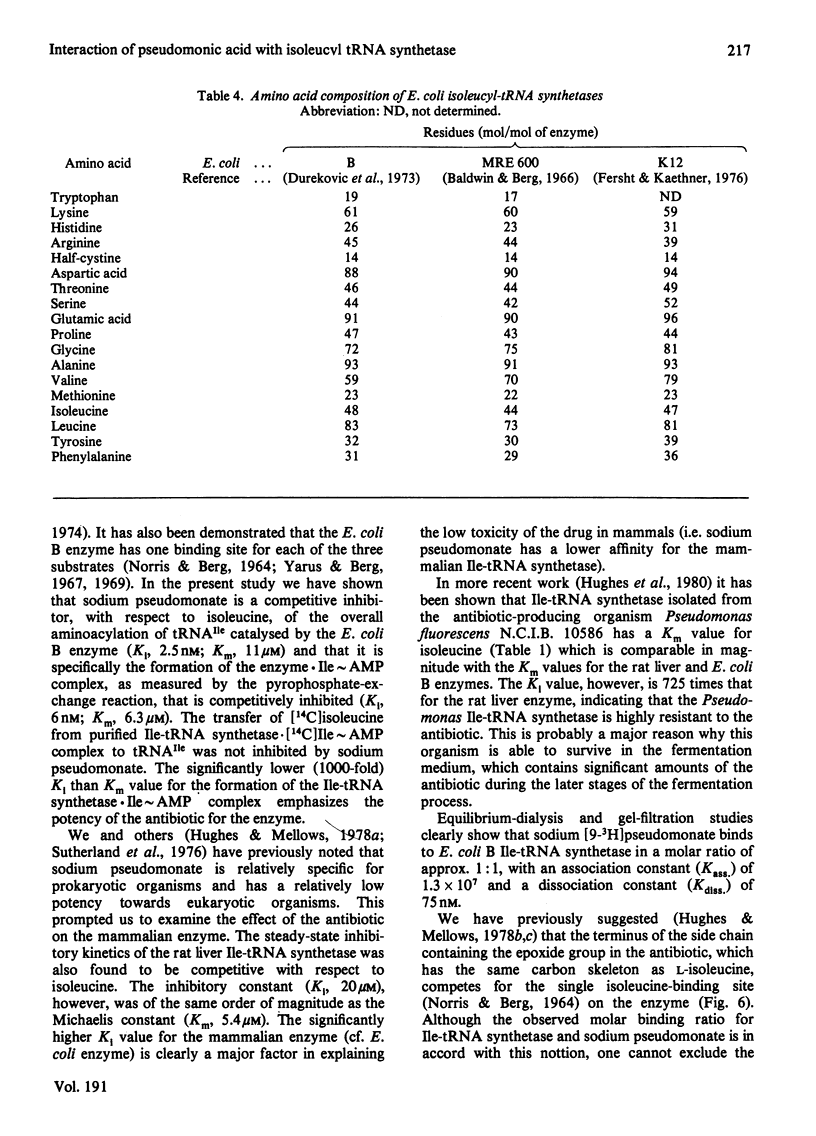
- Baldwin A. N., Berg P. Transfer ribonucleic acid-induced hydrolysis of valyladenylate bound to isoleucyl ribonucleic acid synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Feb 25;241(4):839–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole F. X., Schimmel P. R. On the rate law and mechanism of the adenosine triphosphate--pyrophosphate isotope exchange reaction of amino acyl transfer ribonucleic acid synthetases. Biochemistry. 1970 Feb 3;9(3):480–489. doi: 10.1021/bi00805a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dureković A., Flossdorf J., Kula M. R. Isolation and properties of isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase from Escherichia coli MRE 600. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 16;36(2):528–533. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02939.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldred E. W., Schimmel P. R. Investigation of the transfer of amino acid from a transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase-aminoacyl adenylate complex to transfer ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1972 Jan 4;11(1):17–23. doi: 10.1021/bi00751a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fersht A. R., Kaethner M. M. Mechanism of aminoacylation of tRNA. Proof of the aminoacyl adenylate pathway for the isoleucyl- and tyrosyl-tRNA synthetases from Escherichia coli K12. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 24;15(4):818–823. doi: 10.1021/bi00649a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flossdorf J., Prätorius H. J., Kula M. R. Influence of side-chain structure of aliphatic amino acids on binding to isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase from Escherichia coli MRE 600. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jun 15;66(1):147–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10435.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holler E., Bennett E. L., Calvin M. 2-p-Toluidinylnaphthalene-6-sulfonate, a fluorescent reporter group for L-isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Oct 15;45(2):409–415. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90834-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holler E., Calvin M. Isoleucyl transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase of Escherichia coli B. A rapid kinetic investigation of the L-isoleucine-activating reaction. Biochemistry. 1972 Sep 26;11(20):3741–3752. doi: 10.1021/bi00770a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holler E., Rainey P., Orme A., Bennett E. L., Calvin M. On the active site topography of isoleucyl transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase of Escherichia coli B. Biochemistry. 1973 Mar 13;12(6):1150–1159. doi: 10.1021/bi00730a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Mellows G. Inhibition of isoleucyl-transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase in Escherichia coli by pseudomonic acid. Biochem J. 1978 Oct 15;176(1):305–318. doi: 10.1042/bj1760305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Mellows G. On the mode of action of pseudomonic acid: inhibition of protein synthesis in Staphylococcus aureus. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1978 Apr;31(4):330–335. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.31.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iaccarino M., Berg P. Requirement of sulfhydryl groups for the catalytic and tRNA recognition functions of isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jun 14;42(2):151–169. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kula M. R. Structural studies on isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase from E. coli--identification of the cysteine residue modified specifically with N-ethylmaleimide. FEBS Lett. 1974 Sep 15;46(1):130–133. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80351-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lövgren T. N., Pastuszyn A., Loftfield R. B. The mechanism of the aminoacylation of transfer ribonucleic acid: enzyme-product dissociation is not rate limiting. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 15;15(12):2533–2540. doi: 10.1021/bi00657a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S. A colorimetric method for the determination of submicrogram quantities of protein. Anal Biochem. 1977 Mar;78(1):86–92. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORRIS A. T., BERG P. MECHANISM OF AMINOACYL RNA SYNTHESIS: STUDIES WITH ISOLATED AMINOACYL ADENYLATE COMPLEXES OF ISOLEUCYL RNA SYNTHETASE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Aug;52:330–337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.2.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rainey P., Hammer-Raber B., Kula M. R., Holler E. Modification of L-isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase with L-isoleucyl-bromomethyl ketone. The effect of the catalytic steps. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Aug 15;78(1):239–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11735.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santi D. V., Webster R. W., Jr Phenylalanyl transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase from rat liver. Analysis of phenylalanine and adenosine 5'-triphosphate binding sites and comparison to the enzyme from Escherichia coli. J Med Chem. 1976 Nov;19(11):1276–1279. doi: 10.1021/jm00233a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarus M., Berg P. Recognition of tRNA by aminoacyl tRNA synthetases. J Mol Biol. 1967 Sep 28;28(3):479–490. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80098-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarus M., Berg P. Recognition of tRNA by isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase. Effect of substrates on the dynamics of tRNA-enzyme interaction. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jun 14;42(2):171–189. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


