Abstract
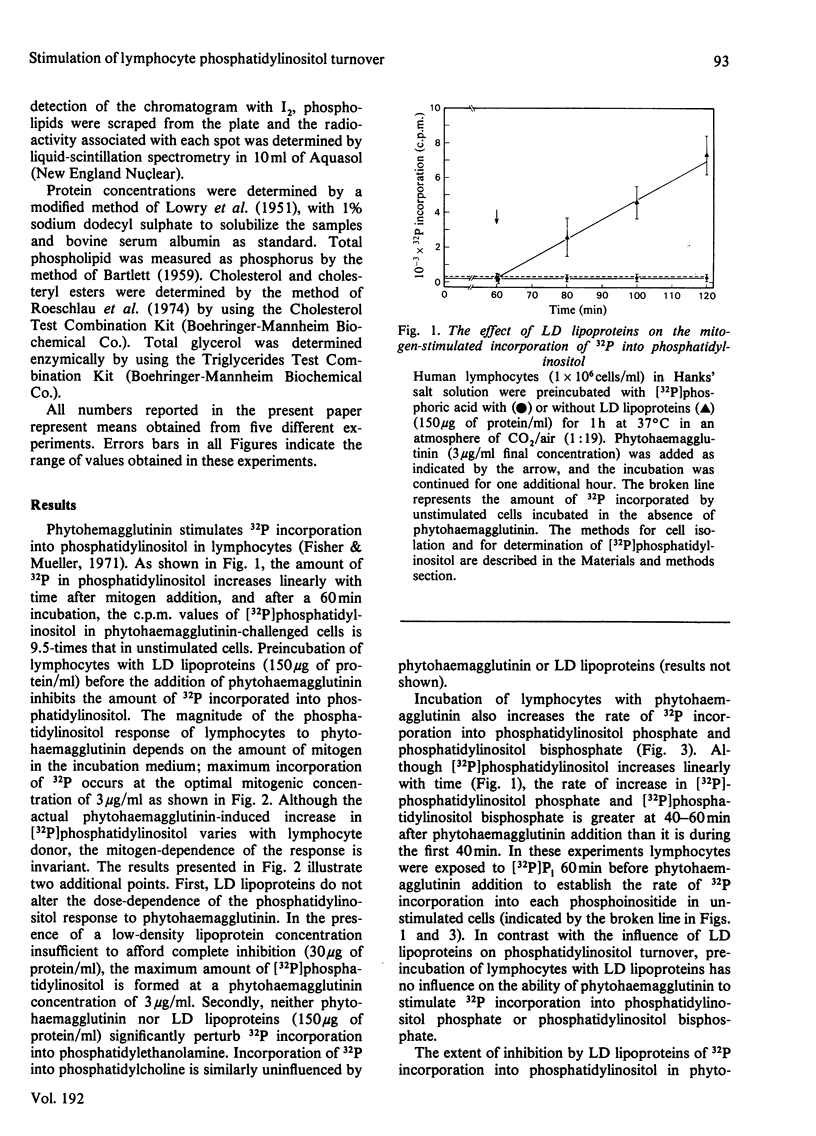
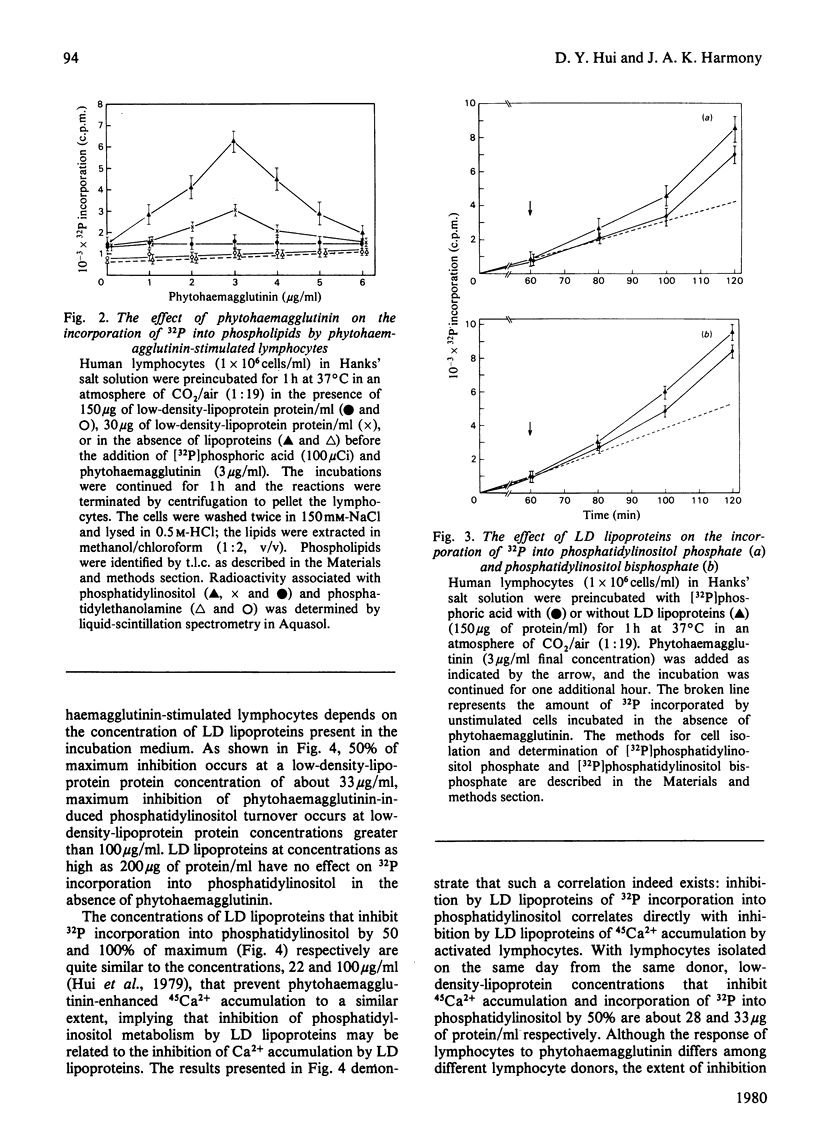
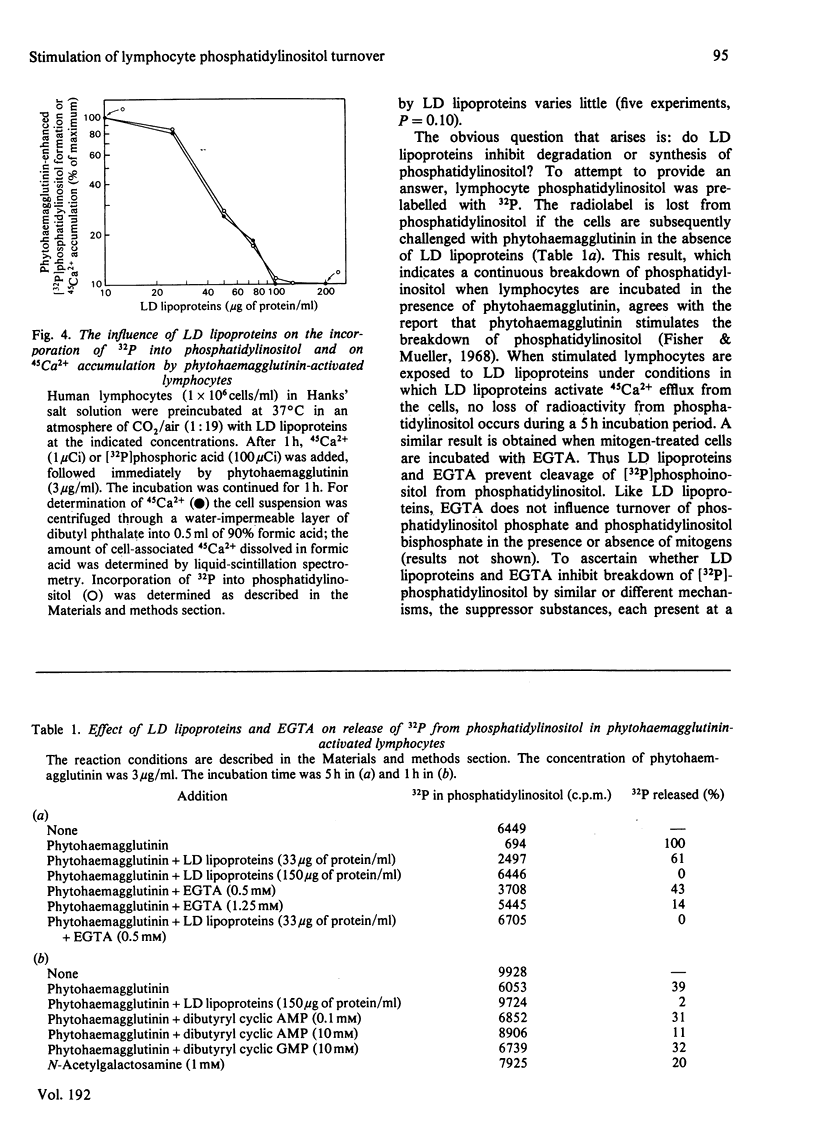
Low-density (LD) lipoproteins inhibit phytohaemagglutinin-enhanced turnover of phosphatidylinositol in human peripheral lymphocytes. Turnover was assessed by 32P incorporation into phospholipids and by loss of 32P from [32P]phosphatidylinositol. Inhibition of lipid turnover by LD lipoproteins is not the result of a change in the amount of phytohaemagglutinin required for maximum cellular response. Neither phytohaemagglutinin nor LD lipoproteins influence 32P incorporation into phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine during the first 60min after mitogenic challenge. The extent of inhibition of phosphatidylinositol turnover by LD lipoproteins depends on the concentration of LD lipoproteins present in the incubation medium: 50% of maximum inhibition occurs at a low-density-lipoprotein protein concentration of 33μg/ml and maximum inhibition occurs at low-density-lipoprotein protein concentrations above 100μg/ml. Phytohaemagglutinin stimulates 32P incorporation into phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidylinositol phosphate and phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate. However, LD lipoproteins abolish 32P incorporation into phosphatidylinositol without affecting incorporation into phosphatidylinositol phosphate and phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate. The ability of LD lipoproteins to inhibit phytohaemagglutinin-induced phosphatidylinositol turnover is mimicked by EGTA. Furthermore, inhibition of LD lipoproteins by phytohaemagglutinin-induced 32P incorporation into phosphatidylinositol correlates directly with inhibition by LD lipoproteins of Ca2+ accumulation. These results suggest that Ca2+ accumulation and turnover of phosphatidylinositol are coupled responses in lymphocytes challenged by mitogens. The step in phosphatidylinositol metabolism that is sensitive to LD lipoproteins and, by inference, that is coupled to Ca2+ accumulation is release of [32P]phosphoinositol from phosphatidylinositol.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan D., Michell R. H. A comparison of the effects of phytohaemagglutinin and of calcium ionophore A23187 on the metabolism of glycerolipids in small lymphocytes. Biochem J. 1977 May 15;164(2):389–397. doi: 10.1042/bj1640389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan D., Michell R. H. Phosphatidylinositol cleavage in lymphocytes. Requirement for calcium ions at a low concentration and effects of other cations. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;142(3):599–604. doi: 10.1042/bj1420599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benditt E. P., Benditt J. M. Evidence for a monoclonal origin of human atherosclerotic plaques. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1753–1756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewster M. E., Ihm J., Brainard J. R., Harmony J. A. Transfer of phosphatidylcholine facilitated by a component of human plasma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 28;529(1):147–159. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90113-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch G. E. Editorial: Viruses and arteriosclerosis. Am Heart J. 1974 Apr;87(4):407–412. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(74)90163-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V. Immunoregulatory properties of human plasma in very low density lipoproteins. J Immunol. 1977 Dec;119(6):2129–2136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss L. K., Edgington T. S. Effect of LDL-In, a normal immunoregulatory human serum low density lipoprotein, on the interaction of macrophages with lymphocytes proliferating in response to mitogen and allogeneic stimulation. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):1966–1970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss L. K., Edgington T. S. Identification of a lymphocyte surface receptor for low density lipoprotein inhibitor, an immunoregulatory species of normal human serum low density lipoprotein. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1298–1308. doi: 10.1172/JCI109047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss L. K., Edgington T. S. Regulatory serum lipoproteins: regulation of lymphocyte stimulation by a species of low density lipoprotein. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1452–1458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamantstein T., Ulmer A. The antagonistic action of cyclic GMP and cyclic AMP on proliferation of B and T lymphocytes. Immunology. 1975 Jan;28(1):113–119. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. B., Mueller G. C. An early alteration in the phospholipid metabolism of lymphocytes by phytohemagglutinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1396–1402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Sastre F., Folch-Pi J. Thin-layer chromatography of the phosphoinositides. J Lipid Res. 1968 Jul;9(4):532–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene W. C., Parker C. M., Parker C. W. Calcium and lymphocyte activation. Cell Immunol. 1976 Jul;25(1):74–89. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90098-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho Y. K., Brown S., Bilheimer D. W., Goldstein J. L. Regulation of low density lipoprotein receptor activity in freshly isolated human lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Dec;58(6):1465–1474. doi: 10.1172/JCI108603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui D. Y., Berebitsky G. L., Harmony J. A. Mitogen-stimulated calcium ion accumulation by lymphocytes. Influence of plasma lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4666–4673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui D. Y., Harmony J. A. Interaction of plasma lipoproteins with erythrocytes. I. Alteration of erythrocyte morphology. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 2;550(3):407–424. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90145-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui D. Y., Harmony J. A. Interaction of plasma lipoproteins with erythrocytes. II. Modulation of membrane-associated enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 2;550(3):425–434. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90146-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl-Kiessling K. Mechanism of phytohemagglutinin (PHA) action. V. PHA compared with concanavalin A (Con A). Exp Cell Res. 1972 Jan;70(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90176-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maino V. C., Hayman M. J., Crumpton M. J. Relationship between enhanced turnover of phosphatidylinositol and lymphocyte activation by mitogens. Biochem J. 1975 Jan;146(1):247–252. doi: 10.1042/bj1460247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse J. H., Witte L. D., Goodman D. S. Inhibition of lymphocyte proliferation stimulated by lectins and allogeneic cells by normal plasma lipoproteins. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1791–1803. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pairault J., Levilliers J., Chapman M. J. Human serum lipoproteins activate adipocyte plasma membrane adenylate cyclase. Nature. 1977 Oct 13;269(5629):607–609. doi: 10.1038/269607a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röschlau P., Bernt E., Gruber W. Enzymatische Bestimmung des Gesamt-Cholesterins im Serum. Z Klin Chem Klin Biochem. 1974 Sep;12(9):403–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore V., Shore B. Stimulation of human erythrocyte Mg++ -ATPASE by plasma lipoproteins1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Aug 18;65(4):1250–1256. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80364-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg D., Nestel P. J., Weinstein D. B., Remaut-Desmeth M., Chang C. M. Interactions of native and modified human low density lipoproteins with human skin fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 27;528(2):199–212. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90194-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. G., Lewis J. C., Rudel L. L., Biddulph D. M. Low density lipoprotein modulation of CAMP in avian thrombocytes. Thromb Res. 1979;14(4-5):799–803. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90135-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


