Abstract
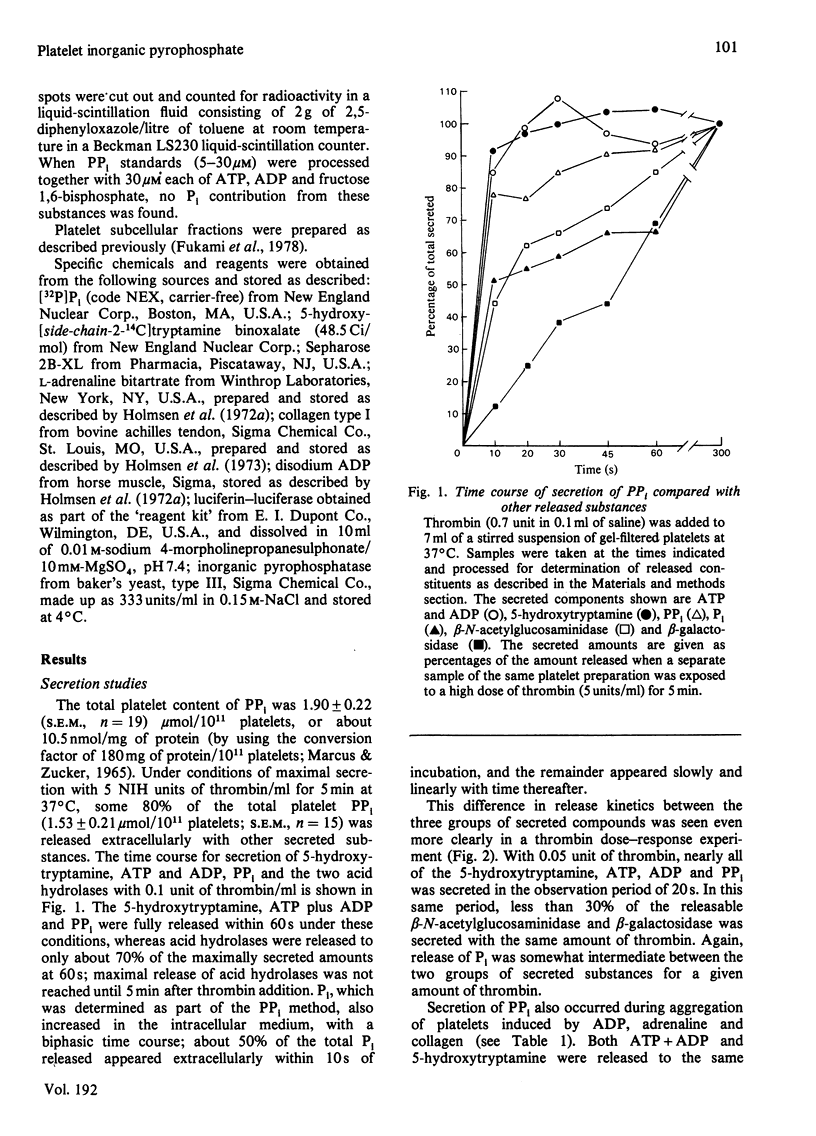
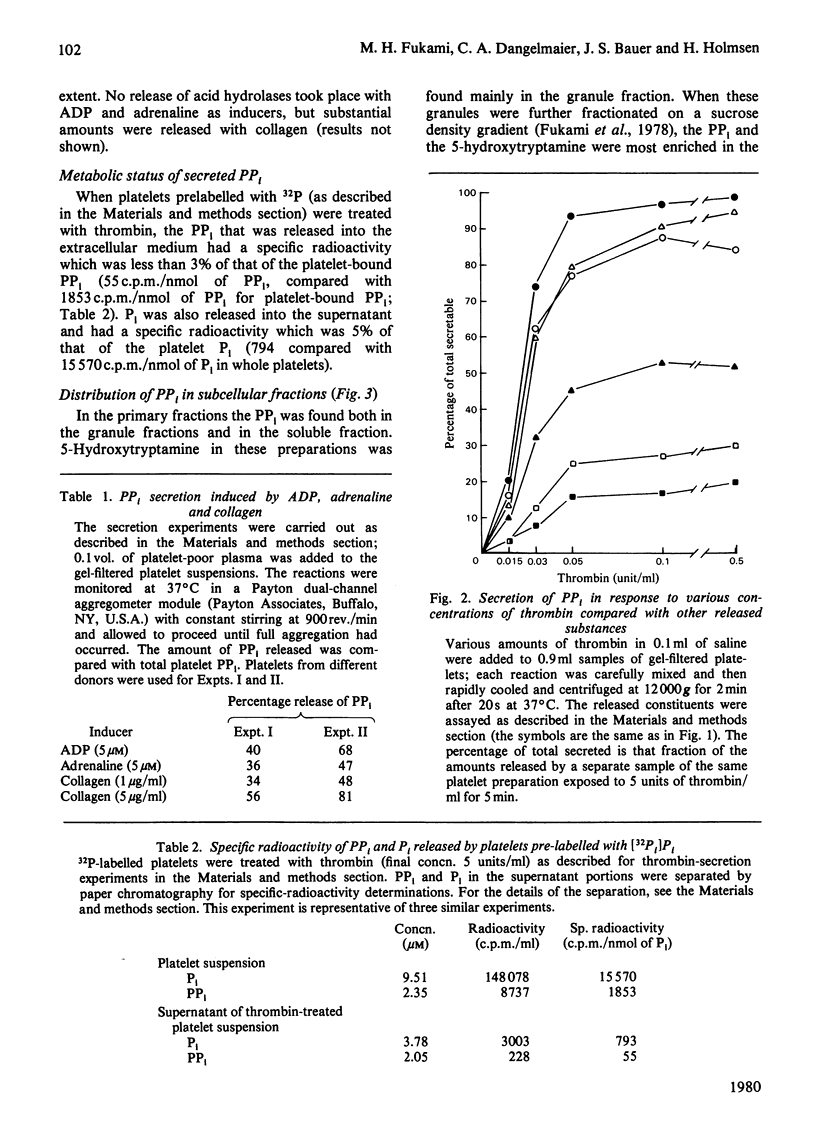
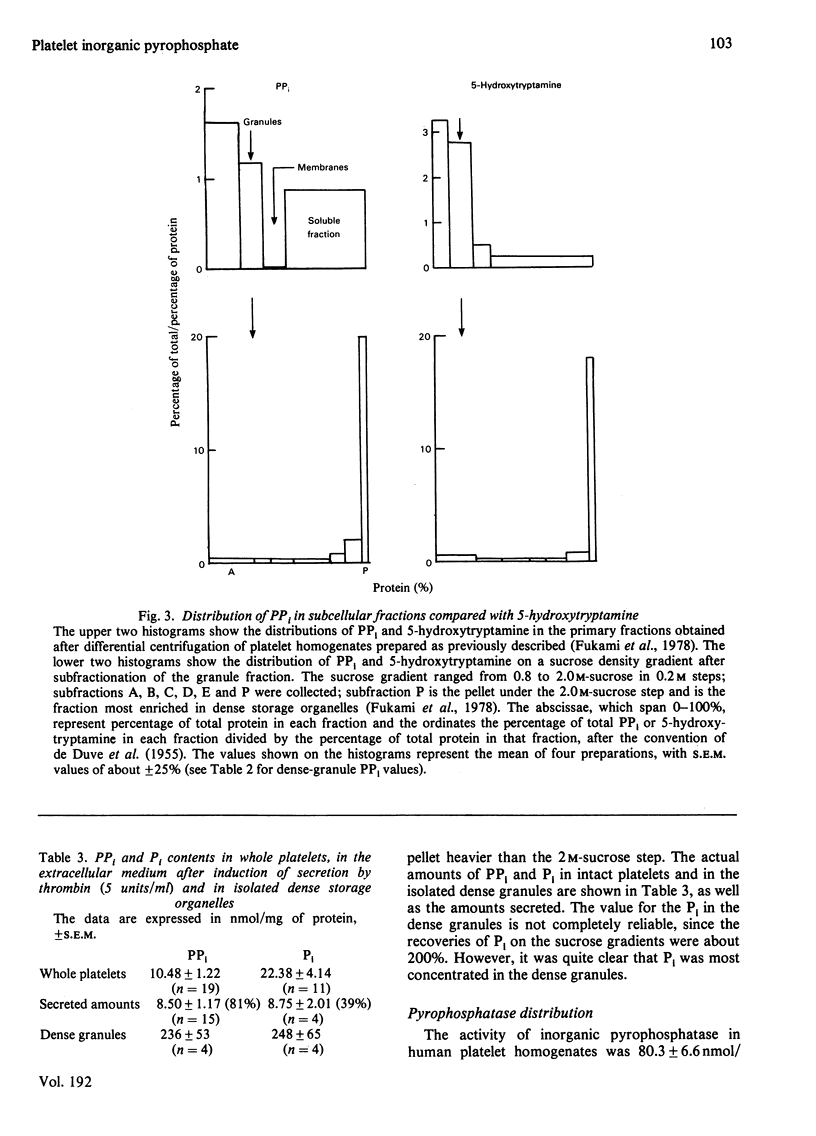
The platelet content of PPi is 1.90 +/- mumol/10(11) platelets (S.E.M., n = 19) or about 10.5 nmol/mg of protein, several hundred times that found for rat liver. Some 80% of this PPi is secreted by platelets treated with thrombin with a time course and dose-response relationship similar to secretion of ATP, ADP and 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) from the platelet dense granules. During platelet aggregation induced by ADP and adrenaline, substantial amounts of PPi were secreted, but no release of acid hydrolases was observed. Subcellular-fractionation studies showed that the PPi is highly enriched in the same fraction that contains the storage organelles which store ATP, ADP, Ca2+ and 5-hydroxytryptamine. Inorganic pyrophosphatase was present mainly in the soluble fraction and in the mitochondria. Secretion studies done with platelets prelabelled with [32P]Pi showed that the sequestered PPi was relatively metabolically inactive, as is the ATP and ADP in the storage organelles. The possible participation of PPi in the formation of a bivalent-cation-nucleotide complex associated with amine storage is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berneis K. H., Da Prada M., Pletscher A. Metal-dependent aggregation of nucleotides with formation of biphasic liquid systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 22;215(3):547–549. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90106-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE DUVE C., PRESSMAN B. C., GIANETTO R., WATTIAUX R., APPELMANS F. Tissue fractionation studies. 6. Intracellular distribution patterns of enzymes in rat-liver tissue. Biochem J. 1955 Aug;60(4):604–617. doi: 10.1042/bj0600604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake H. L., Goss N. H., Wood H. G. A new, convenient method for the rapid analysis of inorganic pyrophosphate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Apr 1;94(1):117–120. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90800-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukami M. H., Bauer J. S., Stewart G. J., Salganicoff L. An improved method for the isolation of dense storage granules from human platelets. J Cell Biol. 1978 May;77(2):389–399. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.2.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guynn R. W., Veloso D., Lawson J. W., Veech R. L. The concentration and control of cytoplasmic free inorganic pyrophosphate in rat liver in vivo. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;140(3):369–375. doi: 10.1042/bj1400369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANES C. S., ISHERWOOD F. A. Separation of the phosphoric esters on the filter paper chromatogram. Nature. 1949 Dec 31;164(4183):1107-12, illust. doi: 10.1038/1641107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMSEN H. COLLAGEN-INDUCED RELEASE OF ADENOSINE DIPHOSPHATE FROM BLOOD PLATELETS INCUBATED WITH RADIOACTIVE PHOSPHATE IN VITRO. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1965;17:239–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess H. H., Derr J. E. Assay of inorganic and organic phosphorus in the 0.1-5 nanomole range. Anal Biochem. 1975 Feb;63(2):607–613. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90388-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H. Changes in the radioactivity of P-32-labelled acid-soluble organophosphates in blood platelets during collagen-and adenosine diphosphate-induced platelet aggregation. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1965;17(6):537–548. doi: 10.1080/00365516509083362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Day H. J., Setkowsky C. A. Secretory mechanisms. Behaviour of adenine nucleotides during the platelet release reaction induced by adenosine diphosphate and adrenaline. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;129(1):67–82. doi: 10.1042/bj1290067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Setkowsky C. A., Lages B., Day H. J., Weiss H. J., Scrutton M. C. Content and thrombin-induced release of acid hydrolases in gel-filtered platelets from patients with storage pool disease. Blood. 1975 Jul;46(1):131–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Storm E., Day H. J. Determination of ATP and ADP in blood platelets: a modification of the firefly luciferase assay for plasma. Anal Biochem. 1972 Apr;46(2):489–501. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90323-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Weiss H. J. Secretable storage pools in platelets. Annu Rev Med. 1979;30:119–134. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.30.020179.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ireland D. M. Effect of thrombin on the radioactive nucleotides of human washed platelets. Biochem J. 1967 Nov;105(2):857–867. doi: 10.1042/bj1050857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS H. A., HEMS R. Some reactions of adenosine and inosine phosphates in animal tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1953 Sep-Oct;12(1-2):172–180. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(53)90136-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lages B., Scrutton M. C., Holmsen H. Secretion by gel-filtered human platelets: response of platelet Ca2+, Mg2+, and K+ to secretory agents. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Nov;90(5):873–882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lages B., Scrutton M. C., Holmsen H. Studies on gel-filtered human platelets: isolation and characterization in a medium containing no added Ca2+, Mg2+, or K+. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 May;85(5):811–825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansurova S. E., Shakhov Y. A., Kulaev I. S. Mitochondrial pyrophosphatase is a coupling factor of respiration and pyrophosphate synthesis. FEBS Lett. 1977 Feb 15;74(1):31–34. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80745-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STETTEN D., Jr Biosynthesis and pyrophosphate. Am J Med. 1960 Jun;28:867–870. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(60)90195-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silcox D. C., Jacobelli S., McCarty D. J. Identification of inorganic pyrophosphate in human platelets and its release on stimulation with thrombin. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jul;52(7):1595–1600. doi: 10.1172/JCI107336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugurbil K., Holmsen H., Shulman R. G. Adenine nucleotide storage and secretion in platelets as studied by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2227–2231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood H. G. Some reactions in which inorganic pyrophosphate replaces ATP and serves as a source of energy. Fed Proc. 1977 Aug;36(9):2197–2206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood T. The detection and identification of intermediates of the pentose phosphate cycle and related compounds. J Chromatogr. 1968 Jun 18;35(3):352–361. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)82396-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


