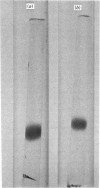
Abstract
Lung is one of the organs of the rat with a particular abundance of haemagglutinating activity that is inhibited by beta-galactosides. This lectin activity can be attributed to a single protein that has been purified from rat lung; a similar protein has been purified from human lung. The molecular weights and subunit structures were estimated from gel filtration and sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis; the human lung lectin appeared to be composed to two identical subunits, mol.wt. 14500, whereas rat lung lectin was observed as both a dimer and a tetramer of one subunit type, mol.wt. 13500. Both lectins bind to disaccharides or oligosaccharides with terminal beta-linked galactose residues. The carbohydrate moiety may be free [lactose or D-galactopyranosyl-beta-(1 leads to 4)-thiogalactopyranoside], protein-bound (asialofetuin) or lipid-bound (cerebrosides). The molecular properties of the beta-galactoside-binding proteins of rat lung and human lung are closely similar to those of embryonic chick muscle lectin [Nowak, Kobiler, Roel & Barondes (1977) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 73, 1383--1387] and calf heart lectin [De Waard, Hickman & Kornfeld (1976) J. Biol. Chem. 251, 7581--7587].
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briles E. B., Gregory W., Fletcher P., Kornfeld S. Vertebrate lectins, Comparison of properties of beta-galactoside-binding lectins from tissues of calf and chicken. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jun;81(3):528–537. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.3.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curatolo W., Yau A. O., Small D. M., Sears B. Lectin-induced agglutination of phospholipid/glycolipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1978 Dec 26;17(26):5740–5744. doi: 10.1021/bi00619a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Den H., Malinzak D. A. Isolation and properties of beta-D-galactoside-specific lectin from chick embryo thigh muscle. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5444–5448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbarth G. S., Ruffolo R. R., Jr, Walsh F. S., Nirenberg M. Lactose sensitive lectin of chick retina and spinal cord. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Aug 29;83(4):1246–1252. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91355-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson W. A., Kornfeld S. Characterization of the oligosaccharide units of the bovine erythrocyte membrane glycoprotein. Biochemistry. 1976 Apr 20;15(8):1697–1703. doi: 10.1021/bi00653a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gremo F., Kobiler D., Barondes S. H. Distribution of an endogenous lectin in the developing chick optic tectum. J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):491–499. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudgin R. L., Pricer W. E., Jr, Ashwell G., Stockert R. J., Morell A. G. The isolation and properties of a rabbit liver binding protein specific for asialoglycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 10;249(17):5536–5543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inman J. K. Covalent linkage of functional groups, ligands, and proteins to polyacrylamide beads. Methods Enzymol. 1974;34:30–58. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(74)34006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki T., Ashwell G. Chemical and physical properties of an hepatic membrane protein that specifically binds asialoglycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1296–1302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki T., Ashwell G. Isolation and characterization of an avian hepatic binding protein specific for N-acetylglucosamine-terminated glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6536–6543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobiler D., Barondes S. H. Lectin activity from embryonic chick brain, heart, and liver: changes with development. Dev Biol. 1977 Oct 1;60(1):326–330. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90130-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzillo J. J., Fanburg B. L. Membrane-bound angiotensin-converting enzyme from rat lung. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2312–2318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prieels J. P., Pizzo S. V., Glasgow L. R., Paulson J. C., Hill R. L. Hepatic receptor that specifically binds oligosaccharides containing fucosyl alpha1 leads to 3 N-acetylglucosamine linkages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2215–2219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEERS E., Jr, CRAVEN G. R., ANFINSEN C. B., BETHUNE J. L. EVIDENCE FOR NONIDENTICAL CHAINS IN THE BETA-GALACTOSIDASE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI K12. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2478–2484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid K., Kaufmann H., Isemura S., Bauer F., Emura J., Motoyama T., Ishiguro M., Nanno S. Structure of 1 -acid glycoprotein. The complete amino acid sequence, multiple amino acid substitutions, and homology with the immunoglobulins. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 3;12(14):2711–2724. doi: 10.1021/bi00738a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson D. L., Thorne D. R., Loh H. H. Developmentally regulated lectin in neonatal rat brain. Nature. 1977 Mar 24;266(5600):367–369. doi: 10.1038/266367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl P. D., Rodman J. S., Miller M. J., Schlesinger P. H. Evidence for receptor-mediated binding of glycoproteins, glycoconjugates, and lysosomal glycosidases by alveolar macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1399–1403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Pricer W. E., Jr, Ashwell G. Subcellular membrane topology and turnover of a rat hepatic binding protein specific for asialoglycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1038–1043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teichberg V. I., Silman I., Beitsch D. D., Resheff G. A beta-D-galactoside binding protein from electric organ tissue of Electrophorus electricus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1383–1387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead P. H., Sammons H. G. A simple technique for the isolation of orosomucoid from normal and pathological sera. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jul 27;124(1):209–211. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90336-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Waard A., Hickman S., Kornfeld S. Isolation and properties of beta-galactoside binding lectins of calf heart and lung. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7581–7587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]