Abstract
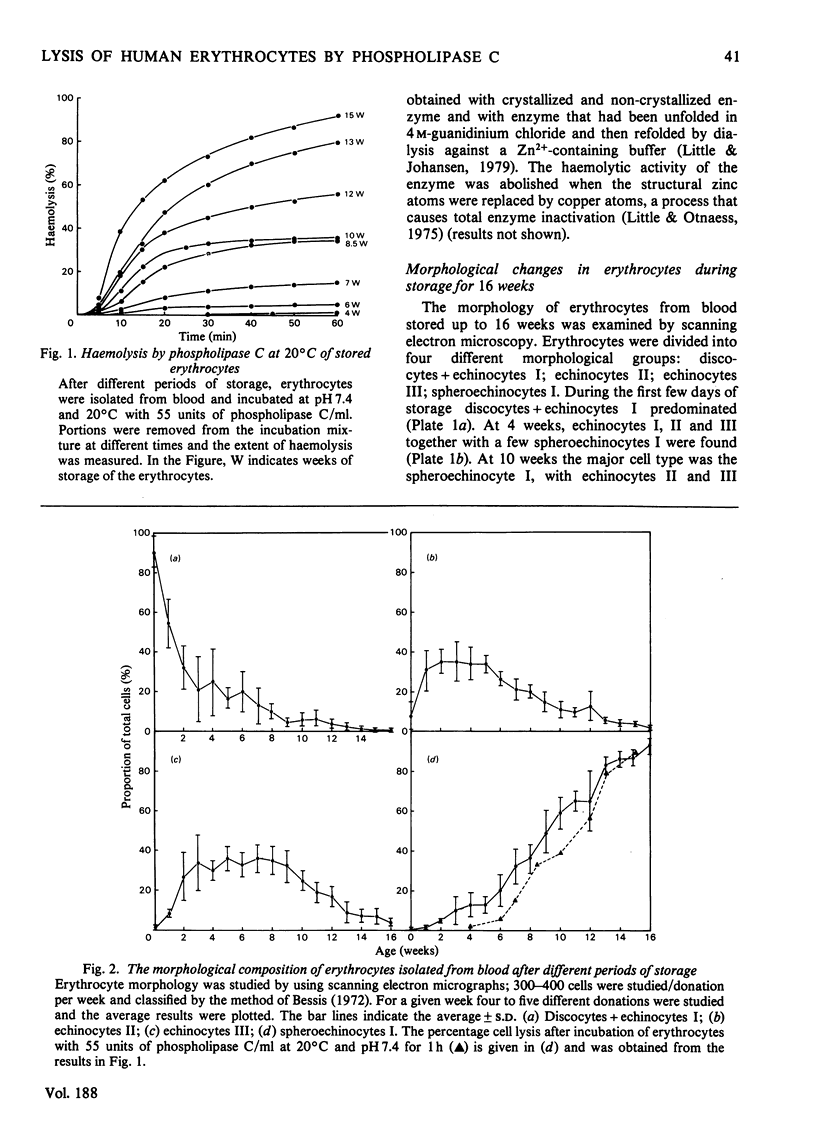
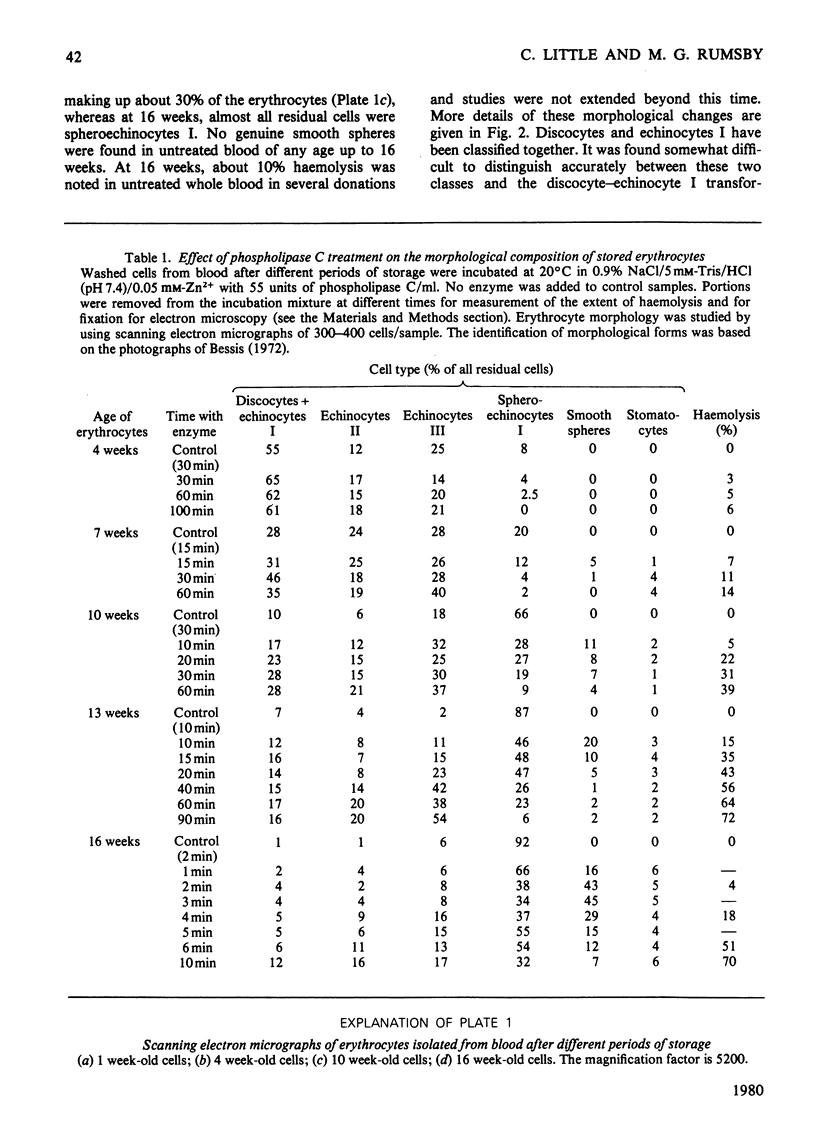
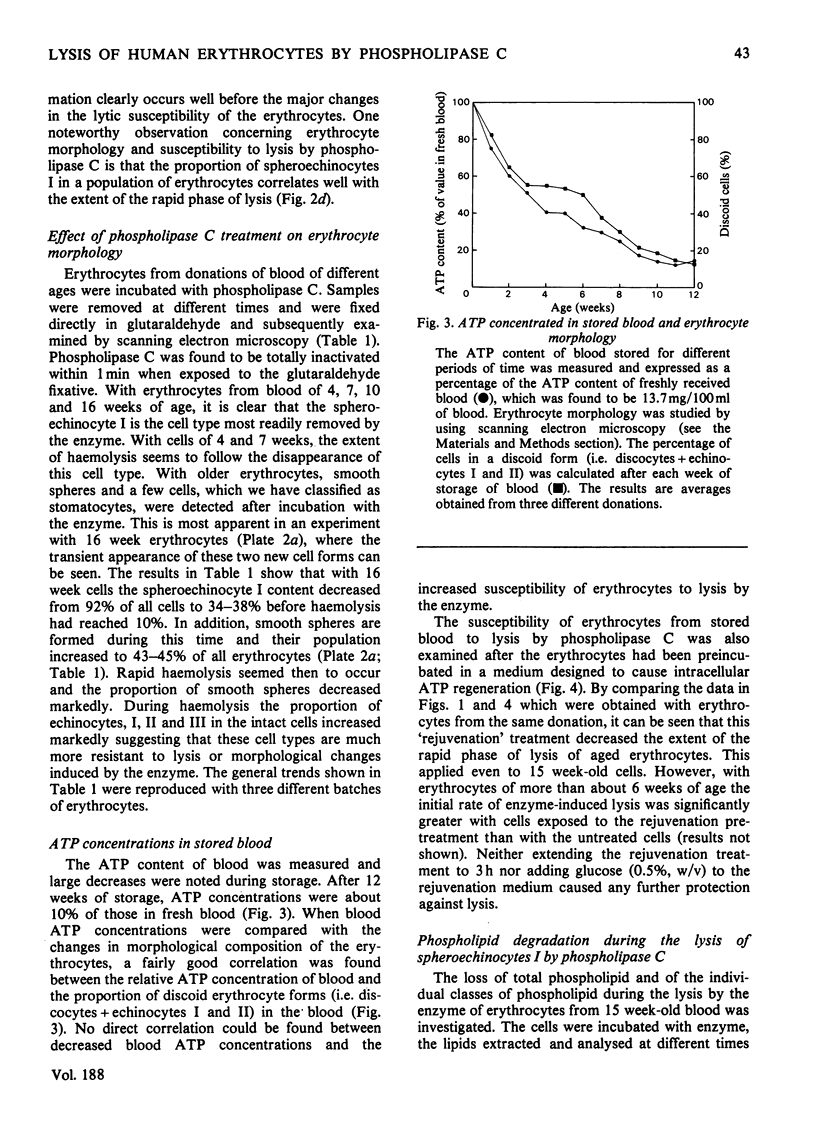
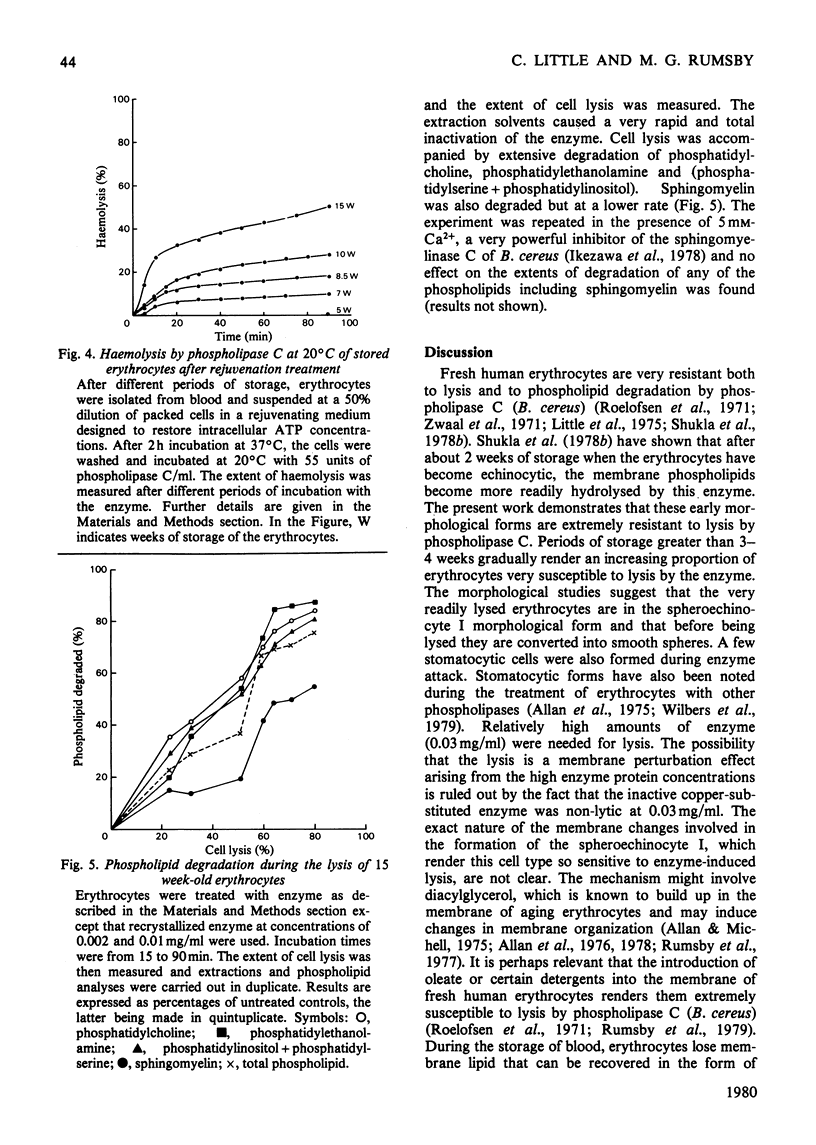
The ability of phospholipase C (Bacillus cereus) to lyse erythrocytes from human blood that had been stored under Transfusion Service conditions for up to 16 weeks has been examined. When incubated at 20 degrees C with enzyme (0.03 mg/ml, 55 units/ml) for up to 1 h fresh erythrocytes were not lysed. After about 4 weeks of storage a population of very readily lysed erythrocytes appeared. The morphological changes in erythrocytes from blood stored up to 16 weeks were examined by scanning electron microscopy. The proportion of very readily lysed erythrocytes correlated well with the proportion of spheroechinocytes I. This morphological form was shown to be preferentially removed by phospholipase C and before lysis a transient appearance of smooth spheres occurred. The decrease in blood ATP concentrations on storage was measured and found to correlate with the disappearance of discoid erythrocyte forms, but not directly with the increased susceptibility of the erythrocytes to lysis by the enzyme. However, erythrocytes of up to at least 15 weeks of age could be made less susceptible to lysis by pre-incubation in a medium designed to cause intracellular regeneration of ATP. During the lysis of spheroechinocytes I by electrophoretically pure recrystallized phospholipase C a rapid degradation of phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylserine + phosphatidylinositol) occurred together with a slower degradation of sphingomyelin.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan D., Low M. G., Finean J. B., Michell R. H. Changes in lipid metabolism and cell morphology following attack by phospholipase C (Clostridium perfringens) on red cells or lymphocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Dec 1;413(2):309–316. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90116-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan D., Michell R. H. Accumulation of 1,2-diacylglycerol in the plasma membrane may lead to echinocyte transformation of erythrocytes. Nature. 1975 Nov 27;258(5533):348–349. doi: 10.1038/258348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan D., Thomas P., Michell R. H. Rapid transbilayer diffusion of 1,2-diacylglycerol and its relevance to control of membrane curvature. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):289–290. doi: 10.1038/276289a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan D., Watts R., Michell R. H. Production of 1,2-diacylglycerol and phosphatidate in human erythrocytes treated with calcium ions and ionophore A23187. Biochem J. 1976 May 15;156(2):225–232. doi: 10.1042/bj1560225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier W., Singer S. J. On the mechanism of ATP-induced shape changes in human erythrocyte membranes. II. The role of ATP. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jun;73(3):647–659. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.3.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feo C., Mohandas N. Clarification of role of ATP in red-cell morphology and function. Nature. 1977 Jan 13;265(5590):166–168. doi: 10.1038/265166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham C., Avruch J., Fairbanks G. Phosphoprotein phosphatase of the human erythrocyte. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Sep 20;72(2):701–708. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80096-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haradin A. R., Weed R. I., Reed C. F. Changes in physical properties of stored erythrocytes relationship to survival in vivo. Transfusion. 1969 Sep-Oct;9(5):229–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.1969.tb04929.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hough E., Little C., Jynge K. Preliminary X-ray crystallographic data on phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jun 5;121(4):567–570. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90401-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikezawa H., Mori M., Ohyabu T., Taguchi R. Studies on sphingomyelinase of Bacillus cereus. I. Purification and properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 27;528(2):247–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavitt R. D. Quantitative studies on the effect of stored plasma on the discocyte-echinocyte transformation in normal red cells. Nouv Rev Fr Hematol. 1971 May-Jun;11(3):331–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little C., Aurebekk B., Otnaess A. B. Purification by affinity chromatography of phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus. FEBS Lett. 1975 Apr 1;52(2):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80800-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little C., Johansen S. Unfolding and refolding of phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus in solutions of guanidinium chloride. Biochem J. 1979 Jun 1;179(3):509–514. doi: 10.1042/bj1790509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little C., Otnåss A. B. The metal ion dependence of phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jun 24;391(2):326–333. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longster G. H., Buckley T., Sikorski J., Derrick Tovey L. A. Scanning electron microscope studies of red cell morphology. Changes occurring in red cell shape during storage and post transfusion. Vox Sang. 1972;22(2):161–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1972.tb05122.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKAO M., NAKAO T., TATIBANA M., YOSHIKAWA H., ABE T. Effect of inosine and adenine on adenosine triphosphate regeneration and shape transformation in long-stored erythrocyts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Apr;32:564–565. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90640-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otnaess A. B., Little C., Sletten K., Wallin R., Johnsen S., Flengsrud R., Prydz H. Some characteristics of phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Oct 3;79(2):459–468. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11828.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. F., Otnaess A. B., Kensil C. A., Dennis E. A. The specificity of phospholipase A2 and phospholipase C in a mixed micellar system. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1252–1257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelofsen B., Zwaal R. F., Comfurius P., Woodward C. B., van Deenen L. L. Action of pure phospholipase A 2 and phospholipase C on human erythrocytes and ghosts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 14;241(3):925–929. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumsby M. G., Sparrow S., Little C. The oleic acid-induced shape transformation of human erythrocytes [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1979 Oct;7(5):922–924. doi: 10.1042/bst0070922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumsby M. G., Trotter J., Allan D., Michell R. H. Recovery of membrane micro-vesicles from human erythrocytes stored for transfusion: a mechanism for the erythrocyte discocyte-to-spherocyte shape transformation. Biochem Soc Trans. 1977;5(1):126–128. doi: 10.1042/bst0050126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shukla S. D., Billah M. M., Coleman R., Finean J. B., Michell R. H. Modulation of the organization of erythrocyte membrane phospholipids by cytoplasmic ATP. The susceptibility of isoionic human erythrocytes ghosts to attack by detergents and phospholipase C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 4;509(1):48–57. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shukla S. D., Coleman R., Finean J. B., Michell R. H. The use of phospholipase c to detect structural changes in the membranes of human erythrocytes aged by storage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 22;512(2):341–349. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90258-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN GASTEL, VAN DEN BERG D., DE GIER J., VAN DEENEN L. SOME LIPID CHARACTERISTICS OF NORMAL RED BLOOD CELLS OF DIFFERENT AGE. Br J Haematol. 1965 Mar;11:193–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1965.tb06577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WESTERMAN M. P., PIERCE L. E., JENSEN W. N. ERYTHROCYTE LIPIDS: A COMPARISON OF NORMAL YOUNG AND NORMAL OLD POPULATIONS. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Sep;62:394–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbers K. H., Haest C. W., von Bentheim M., Deuticke B. Influence of enzymatic phospholipid cleavage on the permeability of the erythrocyte membrane. I. Transport of non-electrolytes via the lipid domain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 5;554(2):388–399. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90379-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winterbourn C. C., Batt R. D. Lipid composition of human red cells of different ages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 10;202(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90212-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaal R. F., Roelofsen B., Comfurius P., van Deenen L. L. Complete purification and some properties of phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 13;233(2):474–479. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90347-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




