Abstract
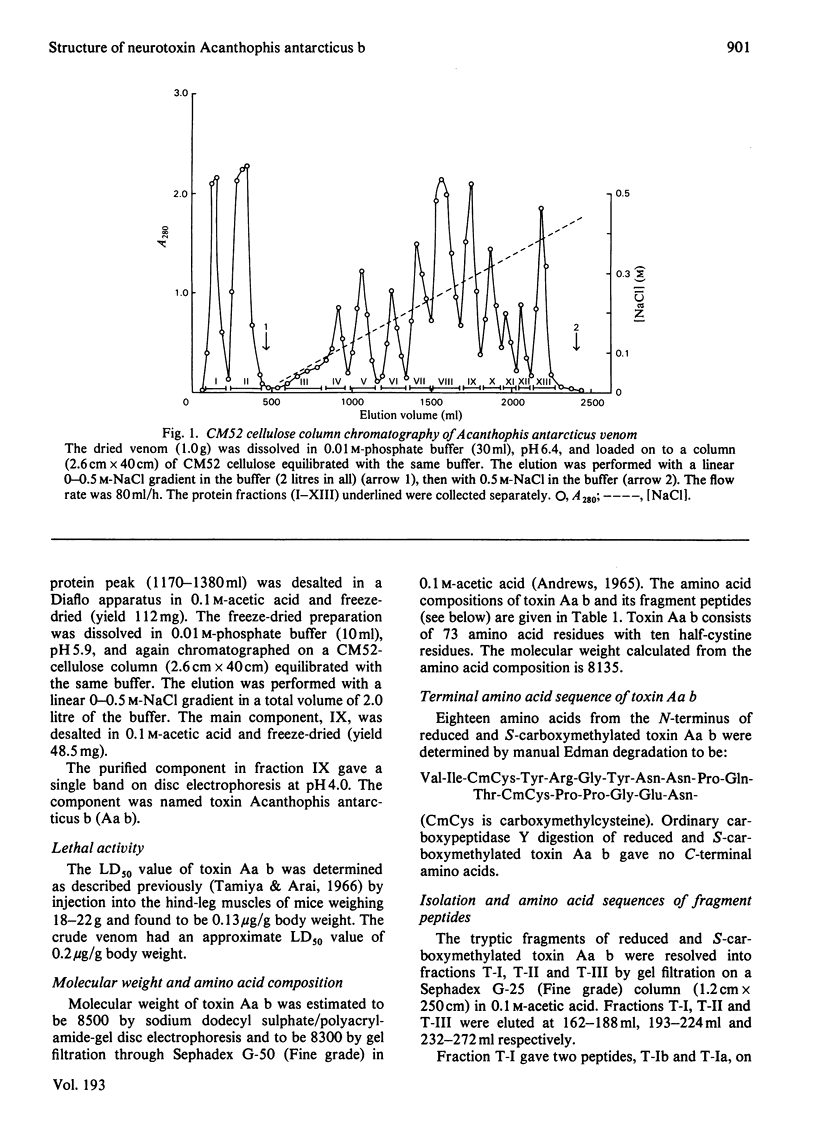
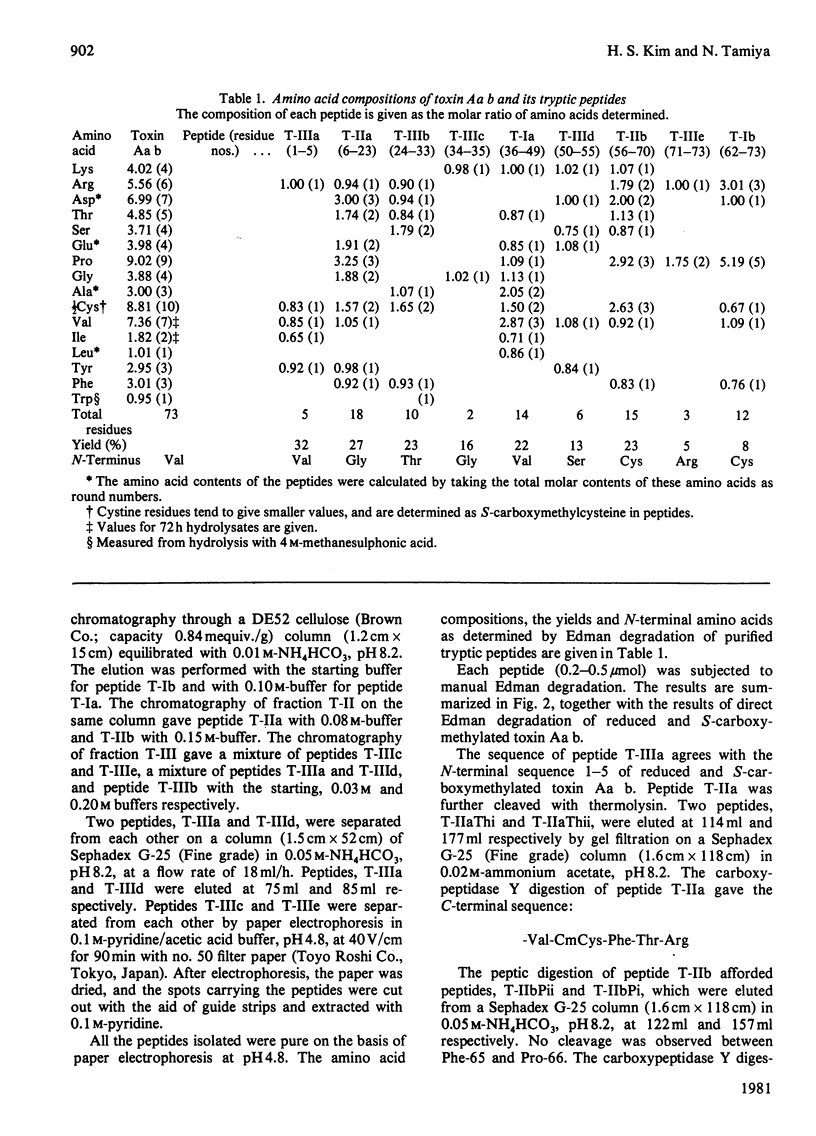
The venom of an Australian elapid snake, the common death adder (Acanthophis antarcticus), was chromatographed on a CM-cellulose CM52 column. One of the neurotoxic components, Acanthophis antarcticus b (toxin Aa b) was isolated in about 9.4% (A280) yield. The complete amino acid sequence of toxin Aa b was elucidated. Toxin Aa b is composed of 73 amino acid residues, with ten half-cystine residues, and has a formula weight of 8135. Toxin Aa b has no histidine or methionine residue in its sequence. The amino acid sequence of toxin Aa b is homologous with those of other neurotoxins with known sequences, although it is novel in having a valine residue at its N-terminus and an arginine residue at position-23, where a lysine residue is found in almost all the so-far-known neurotoxins. Irrespective of the latter replacement, the toxin Aa b is fully active, with an LD50 value (in mice) of 0.13 microgram/g body weight on intramuscular injection.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botes D. P. Snake venom toxins. The amino acid sequences of toxins b and d from Naja melanoleuca venom. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2866–2871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRESTFIELD A. M., MOORE S., STEIN W. H. The preparation and enzymatic hydrolysis of reduced and S-carboxymethylated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1963 Feb;238:622–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H. Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1948–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlanger B. F., Cooper A. G., Cohen W. The inactivation of chymotrypsin by diphenylcarbamyl chloride and its reactivation by nucleophilic agents. Biochemistry. 1966 Jan;5(1):190–196. doi: 10.1021/bi00865a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpert J., Fohlman J., Eaker D. Amino acid sequence of a postsynaptic neurotoxin from the venom of the Australian tiger snake Notechis scutatus scutatus. Biochimie. 1979;61(5-6):719–723. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(79)80172-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki F., Miyazawa T., Hori H., Tamiya N. Conformation of erabutoxins a and b in aqueous solution as studied by nuclear magnetic resonance and circular dichroism. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Sep 1;89(2):433–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12546.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagami T. Simultaneous identification of PTH derivatives of histidine and arginine by thin-layer chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1973 Mar;52(1):318–321. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90356-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwanaga S., Wallén P., Gröndahl N. J., Henschen A., Blombäck B. On the primary structure of human fibrinogen. Isolation and characterization of N-terminal fragments from plasmic digests. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Mar;8(2):189–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joubert F. J. Snake venom toxins the amino acid sequences of two toxins from Ophiophagus hannah (King cobra) venom. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 12;317(1):85–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low B. W., Preston H. S., Sato A., Rosen L. S., Searl J. E., Rudko A. D., Richardson J. S. Three dimensional structure of erabutoxin b neurotoxic protein: inhibitor of acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):2991–2994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.2991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Tamiya N. Three neurotoxins from the venom of a sea snake Astrotia stokesii, including two long-chain neurotoxic proteins with amidated C-termini. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 1;175(2):507–517. doi: 10.1042/bj1750507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendez E., Lai C. Y. Regeneration of amino acids from thiazolinones formed in the Edman degradation. Anal Biochem. 1975 Sep;68(1):47–53. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90677-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISFELD R. A., LEWIS U. J., WILLIAMS D. E. Disk electrophoresis of basic proteins and peptides on polyacrylamide gels. Nature. 1962 Jul 21;195:281–283. doi: 10.1038/195281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheumack D. D., Howden M. E., Spence I. Isolation and partial characterisation of a lethal neurotoxin from the venom of the Australian death adder (Acanthophis antarcticus). Toxicon. 1979;17(6):609–616. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(79)90235-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strydom D. J. Snake venom toxins. The amino acid sequences of two toxins from Dendroaspis polylepis polylepis (black mamba) venom. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):4029–4042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamiya N., Arai H. Studies on sea-snake venoms. Crystallization of erabutoxins a and b from Laticauda semifasciata venom. Biochem J. 1966 Jun;99(3):624–630. doi: 10.1042/bj0990624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsernoglou D., Petsko G. A. The crystal structure of a post-synaptic neurotoxin from sea snake at A resolution. FEBS Lett. 1976 Sep 15;68(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80390-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsernoglou D., Petsko G. A. Three-dimensional structure of neurotoxin a from venom of the Philippines sea snake. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):971–974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walkinshaw M. D., Saenger W., Maelicke A. Three-dimensional structure of the "long" neurotoxin from cobra venom. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2400–2404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


