Abstract
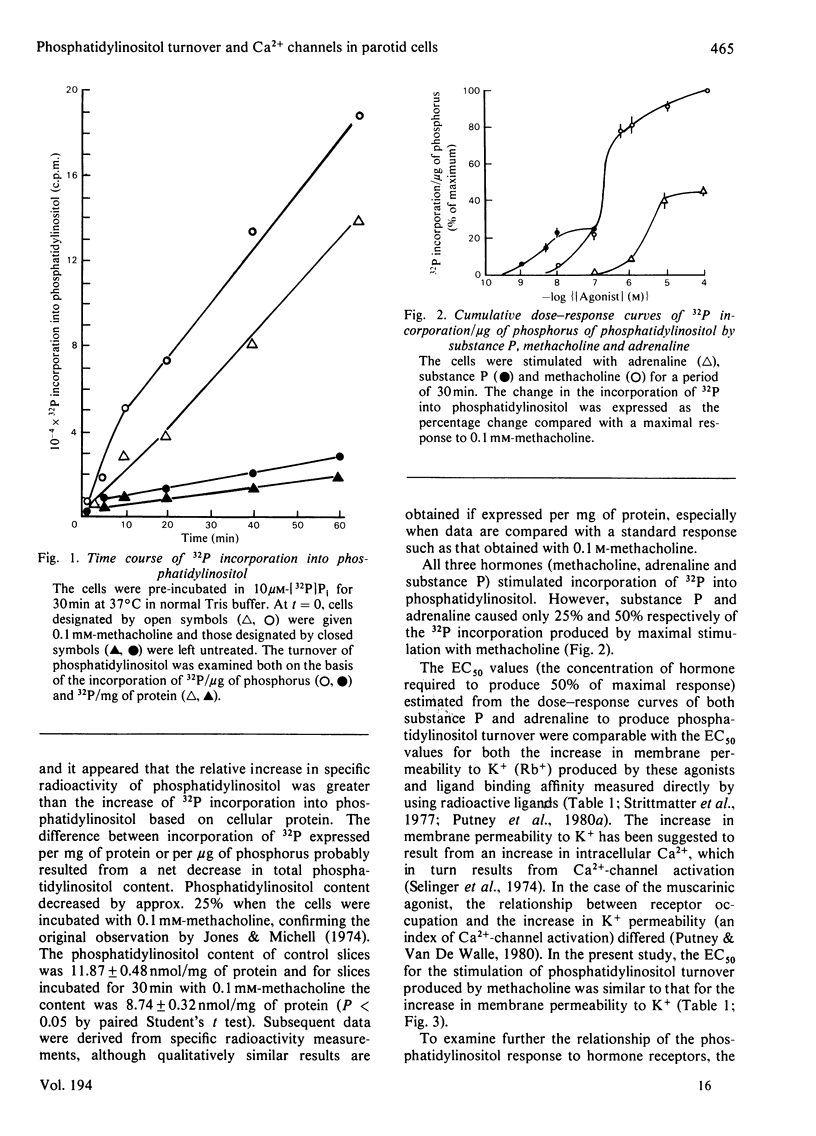
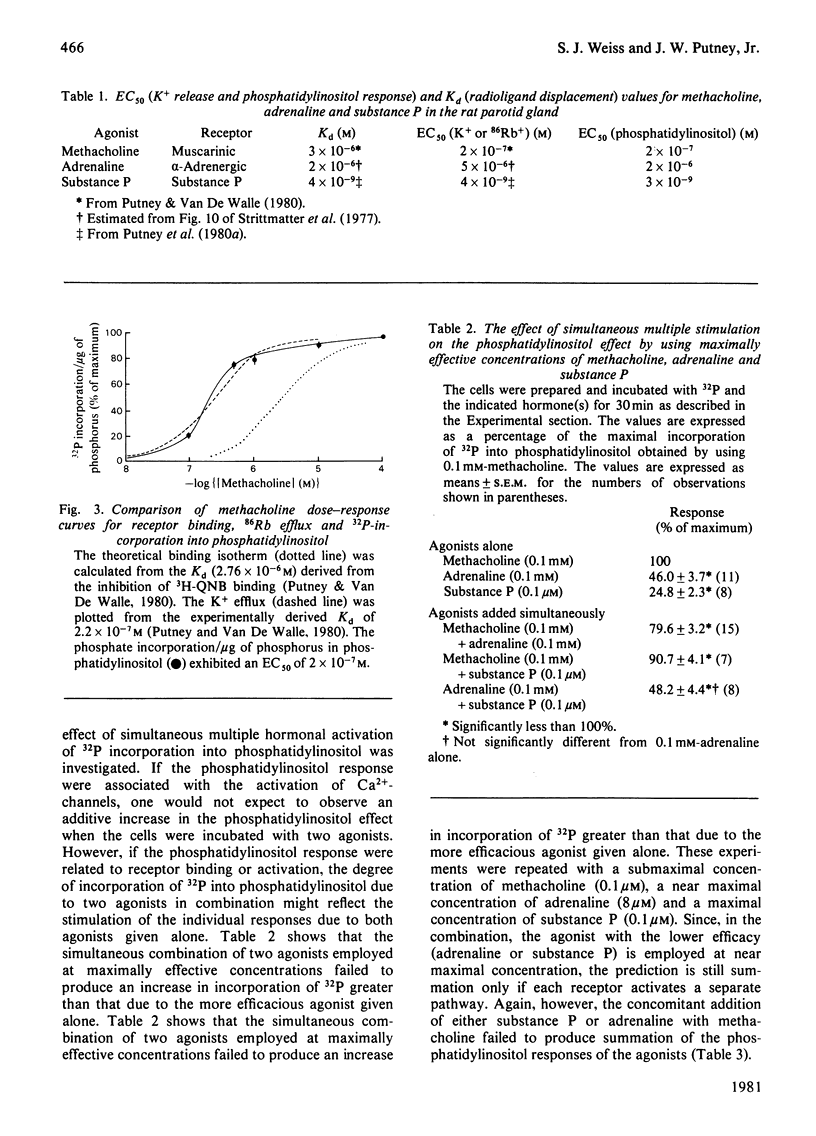
To help elucidate the possible role of phosphatidylinositol in the regulation of membrane permeability to Ca2+, the relationship in the rat parotid gland of phosphatidylinositol turnover to hormone receptor binding and to the hormone-mediated increase in K+ permeability (a Ca2+-dependent phenomenon) was investigated. The concentrations of adrenaline and substance P required to stimulate phosphatidylinositol turnover were found to be similar to those required for the Ca2+-mediated change in K+ permeability and for ligand binding. However, in the case of muscarinic (cholinergic) receptor stimulation, the phosphatidylinositol response was better correlated to the increase in membrane permeability to Ca2+, as determined by the change in K+ permeability, than to receptor occupation. Consistent with this relationship between the phosphatidylinositol response and Ca2+-channel activation were results obtained by simultaneous administration of maximal or submaximal concentrations of muscarinic and alpha-adrenergic agonists. The extent of 32P incorporation when stimulated by maximal concentrations of two agonists did not summate, but, rather, was intermediate between the response of either agonist alone. One interpretation for these observations is that the phosphatidylinositol response may not be related to receptor occupation or activation, but may be involved in the Ca2+-gating mechanism itself.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Latif A. A., Akhtar R. A., Hawthorne J. N. Acetylcholine increases the breakdown of triphosphoinositide of rabbit iris muscle prelabelled with [32P] phosphate. Biochem J. 1977 Jan 15;162(1):61–73. doi: 10.1042/bj1620061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Latif A. A., Green K., Smith J. P., McPherson J. C., Jr, Matheny J. L. Norepinephrine-stimulated breakdown of triphosphoinositide of rabbit iris smooth muscle: effects of surgical sympathetic denervation and in vivo electrical stimulation of the sympathetic nerve of the eye. J Neurochem. 1978 Mar;30(3):517–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb07804.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Fain J. N. Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol synthesis and the inactivation of calcium entry after prolonged exposure of the blowfly salivary gland to 5-hydroxytryptamine. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 15;178(1):59–69. doi: 10.1042/bj1780059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M. A hydrolytic procedure for the identification and estimation of individual phospholipids in biological samples. Biochem J. 1960 Apr;75:45–53. doi: 10.1042/bj0750045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain J. N., Berridge M. J. Relationship between hormonal activation of phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis, fluid secretion and calcium flux in the blowfly salivary gland. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 15;178(1):45–58. doi: 10.1042/bj1780045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOKIN M. R., HOKIN L. E. Effects of acetylcholine on phospholipides in the pancreas. J Biol Chem. 1954 Aug;209(2):549–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itaya K., Ui M. A new micromethod for the colorimetric determination of inorganic phosphate. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Sep;14(3):361–366. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. M., Michell R. H. Breakdown of phosphatidylinositol provoked by muscarinic cholinergic stimulation of rat parotid-gland fragments. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;142(3):583–590. doi: 10.1042/bj1420583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. M., Michell R. H. Enhanced phosphatidylinositol breakdown as a calcium-indepepdnet response of rat parotid fragments to substance P. Biochem Soc Trans. 1978;6(5):1035–1037. doi: 10.1042/bst0061035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. M., Michell R. H. The relationship of calcium to receptor-controlled stimulation of phosphatidylinositol turnover. Effects of acetylcholine, adrenaline, calcium ions, cinchocaine and a bivalent cation ionophore on rat parotid-gland fragments. Biochem J. 1975 Jun;148(3):479–485. doi: 10.1042/bj1480479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaulen H. D. Separation of phosphatidylserine and -inositol by one-dimensional thin-layer chromatography of lipid extracts. Anal Biochem. 1972 Feb;45(2):664–667. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90230-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Michell R. H. Stimulation by acetylcholine of phosphatidylinositol labelling. Subcellular distribution in rat cerebral-cortex slices. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;126(5):1141–1147. doi: 10.1042/bj1261141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd T. The effects of phosphatidylinositol on tyrosine hydroxylase. Stimulation and inactivation. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7247–7254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marier S. H., Putney J. W., Jr, Van de Walle C. M. Control of calcium channels by membrane receptors in the rat parotid gland. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:141–151. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H., Jafferji S. S., Jones L. M. Receptor occupancy dose--response curve suggests that phosphatidyl-inositol breakdown may be intrinsic to the mechanism of the muscarinic cholinergic receptor. FEBS Lett. 1976 Oct 15;69(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80640-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oron Y., Löwe M., Selinger Z. Incorporation of inorganic [32P] phosphate into rat parotid phosphatidylinositol. Induction through activation of alpha adrenergic and cholinergic receptors and relation to K+ release. Mol Pharmacol. 1975 Jan;11(1):79–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr, Van De Walle C. M. The relationship between muscarinic receptor binding and ion movements in rat parotid cells. J Physiol. 1980 Feb;299:521–531. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr, Van de Walle C. M., Wheeler C. S. Binding of 125I-physalaemin to rat parotid acinar cells. J Physiol. 1980 Apr;301:205–212. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr, VanDeWalle C. M., Leslie B. A. Receptor control of calcium influx in parotid acinar cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1978 Nov;14(6):1046–1053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr, Weiss S. J., Van De Walle C. M., Haddas R. A. Is phosphatidic acid a calcium ionophore under neurohumoral control? Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):345–347. doi: 10.1038/284345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossignol B., Herman G., Chambaut A. M., Keryer G. The calcium ionophore A 23 187 as a probe for studying the role of Ca2+ ions in the mediation of carbachol effects on rat salivary glands: protein secretion and metabolism of phospholipids and glycogen. FEBS Lett. 1974 Jul 15;43(2):241–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)81010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon D. M., Honeyman T. W. Proposed mechanism of cholinergic action in smooth muscle. Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):344–345. doi: 10.1038/284344a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinger Z., Eimerl S., Schramm M. A calcium ionophore simulating the action of epinephrine on the alpha-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):128–131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter W. J., Davis J. N., Lefkowitz R. J. alpha-Adrenergic receptors in rat parotid cells. I. Correlation of [3H]dihydroergocryptine binding and catecholamine-stimulated potassium efflux. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5472–5477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


