Abstract
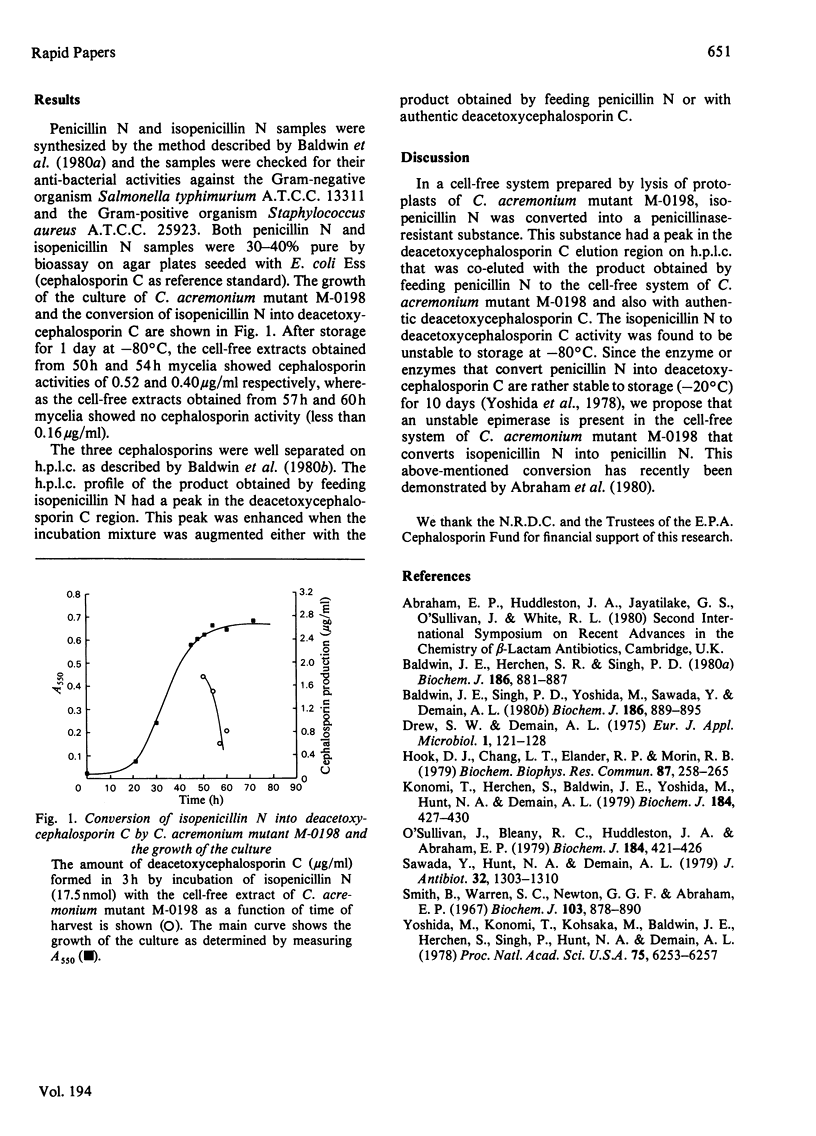
In a cell-free system prepared by lysis of protoplasts of Cephalosporium acremonium mutant M-0198, isopenicillin N was converted into a penicillinase-resistant material that behaved like deacetoxycephalosporin C on high-pressure liquid chromatography analysis. This activity was found to be unstable to storage at -80 degrees C; 70-80% of the activity was lost after 1 day.
Full text
PDF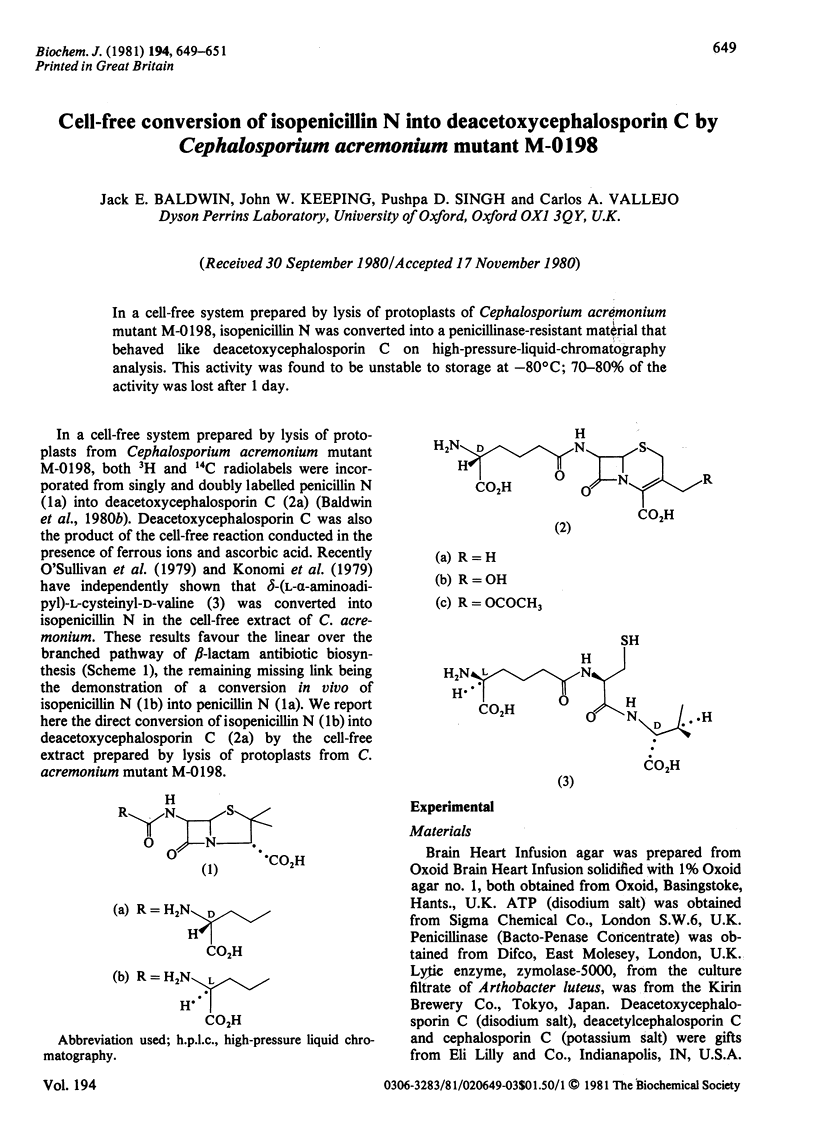

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin J. E., Herchen S. R., Singh P. D. Syntheses of penicillin N, [6 alpha-3H]penicillin N and [10-14C,6 alpha-3H]penicillin N. Biochem J. 1980 Mar 15;186(3):881–887. doi: 10.1042/bj1860881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin J. E., Singh P. D., Yoshida M., Sawada Y., Demain A. L. Incorporation of 3H and 14C from (6 alpha-3H)penicillin N and (10-14C,6 alpha-3H) penicillin N into deacetoxycephalosporin C. Biochem J. 1980 Mar 15;186(3):889–895. doi: 10.1042/bj1860889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook D. J., Chang L. T., Elander R. P., Morin R. B. Stimulation of the conversion of penicillin N to cephalosporin by ascorbic acid, alpha-ketoglutarate, and ferrous ions in cell-free extracts of strains of Cephalosporium acremonium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Mar 15;87(1):258–265. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91674-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konomi T., Herchen S., Baldwin J. E., Yoshida M., Hunt N. A., Demain A. L. Cell-free conversion of delta-(L-alpha-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine into an antibiotic with the properties of isopenicillin N in Cephalosporium acremonium. Biochem J. 1979 Nov 15;184(2):427–430. doi: 10.1042/bj1840427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan J., Bleaney R. C., Huddleston J. A., Abraham E. P. Incorporation of 3H from delta-(L-alpha-amino (4,5-3H)adipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-(4,4-3H)valine into isopenicillin N. Biochem J. 1979 Nov 15;184(2):421–426. doi: 10.1042/bj1840421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada Y., Hunt N. A., Demain A. L. Further studies on microbiological ring-expansion of penicillin N. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1979 Dec;32(12):1303–1310. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.32.1303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B., Warren S. C., Newton G. G., Abraham E. P. Biosynthesis of penicillin N and cephalosporin C. Antibiotic production and other features of the metabolism of Cephalosporium sp. Biochem J. 1967 Jun;103(3):877–890. doi: 10.1042/bj1030877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M., Konomi T., Kohsaka M., Baldwin J. E., Herchen S., Singh P., Hunt N. A., Demain A. L. Cell-free ring expansion of penicillin N to deacetoxycephalosporin C by Cephalosporium acremonium CW-19 and its mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6253–6257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


