Abstract
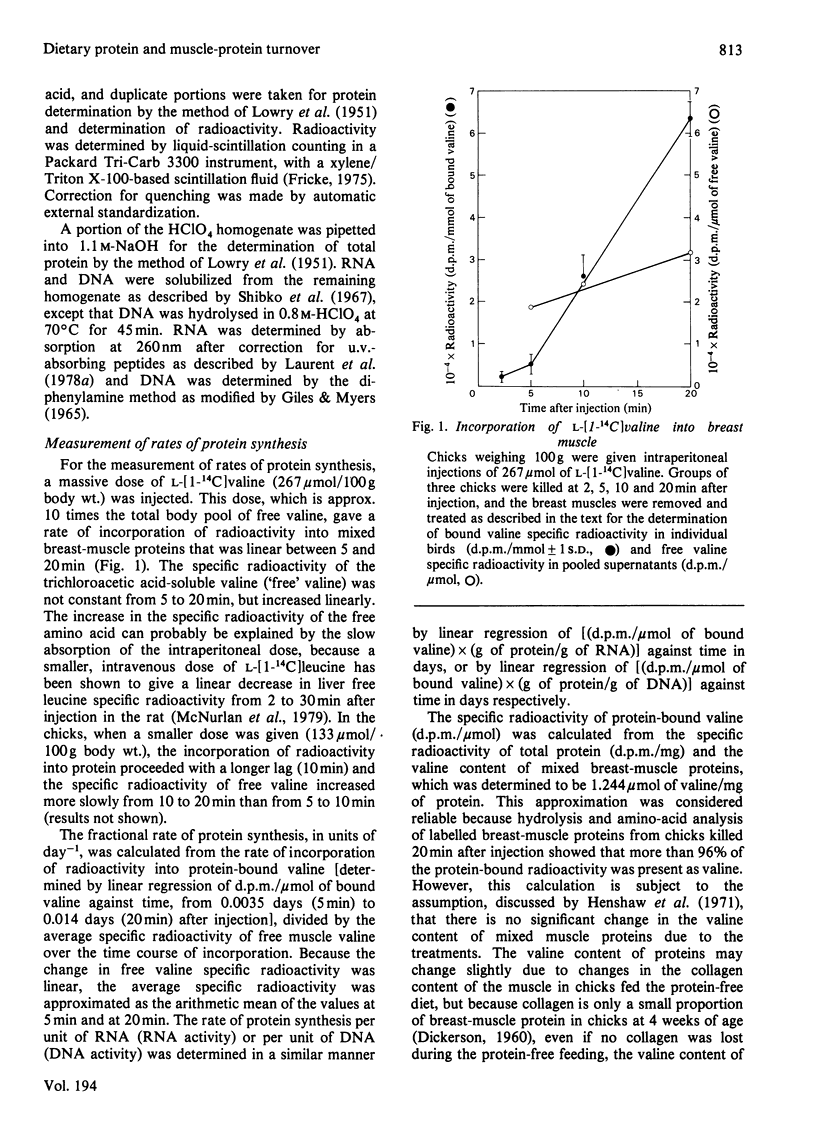
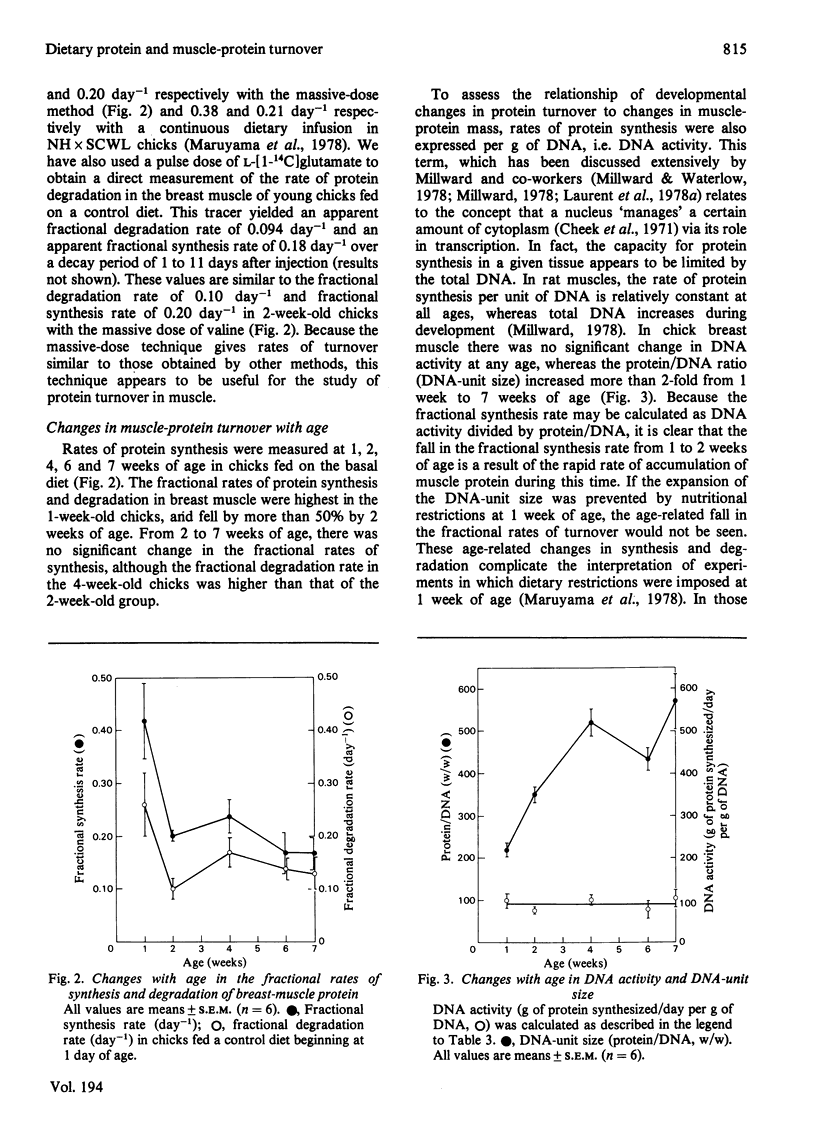
Rates of growth and protein turnover in the breast muscle of young chicks were measured in order to assess the roles of protein synthesis and degradation in the regulation of muscle mass. Rates of protein synthesis were measured in vivo by injecting a massive dose of L-[1-14C]valine, and rates of protein degradation were estimated as the difference between the synthesis rate and the growth rate of muscle protein. In chicks fed on a control diet for up to 7 weeks of age, the fractional rate of synthesis decreased from 1 to 2 weeks of age and then changed insignificantly from 2 to 7 weeks of age, whereas DNA activity was constant for 1 to 7 weeks. When 4-week-old chicks were fed on a protein-free diet for 17 days, the total amount of breast-muscle protein synthesized and degraded per day and the amount of protein synthesized per unit of DNA decreased. Protein was lost owing to a greater decrease in the rate of protein synthesis, as a result of the loss of RNA and a lowered RNA activity. When depleted chicks were re-fed the control diet, rapid growth was achieved by a doubling of the fractional synthesis rate by 2 days. Initially, this was a result of increased RNA activity; by 5 days, the RNA/DNA ratio also increased. There was no evidence of a decrease in the fractional degradation rate during re-feeding. These results indicate that dietary-protein depletion and repletion cause changes in breast-muscle protein mass primarily through changes in the rate of protein synthesis.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buse M. G., Reid S. S. Leucine. A possible regulator of protein turnover in muscle. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1250–1261. doi: 10.1172/JCI108201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICKERSON J. W. The effect of growth on the composition of avian muscle. Biochem J. 1960 Apr;75:33–37. doi: 10.1042/bj0750033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX M. R., BRIGGS G. M. Salt mixtures for purified-type diets. III. An improved salt mixtures for chicks. J Nutr. 1960 Oct;72:243–250. doi: 10.1093/jn/72.2.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricke U. Tritosol: a new scintillation cocktail based on Triton X-100. Anal Biochem. 1975 Feb;63(2):555–558. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90379-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funabiki R., Watanabe Y., Nishizawa N., Hareyama S. Quantitative aspect of the myofibrillar protein turnover in transient state on dietary protein depletion and repletion revealed by urinary excretion of N7-methylhistid;ne. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 18;451(1):143–150. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90266-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlick P. J., Burk T. L., Swick R. W. Protein synthesis and RNA in tissues of the pig. Am J Physiol. 1976 Apr;230(4):1108–1112. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.4.1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlick P. J., Millward D. J., James W. P., Waterlow J. C. The effect of protein deprivation and starvation on the rate of protein synthesis in tissues of the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Nov 18;414(1):71–84. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90126-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harney M. E., Swick R. W., Benevenga N. J. Estimation of tissue protein synthesis in rats fed diets labeled with (U-14C)tyrosine. Am J Physiol. 1976 Oct;231(4):1018–1023. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.4.1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper A. E., Benevenga N. J., Wohlhueter R. M. Effects of ingestion of disproportionate amounts of amino acids. Physiol Rev. 1970 Jul;50(3):428–558. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1970.50.3.428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverberg L. N., Deckelbaum L., Bilmazes C., Munro H. N., Young V. R. Myofibrillar protein turnover and urinary N-tau-methylhistidine output. Response to dietary supply of protein and energy. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;152(3):503–510. doi: 10.1042/bj1520503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henshaw E. C., Hirsch C. A., Morton B. E., Hiatt H. H. Control of protein synthesis in mammalian tissues through changes in ribosome activity. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jan 25;246(2):436–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent G. J., Sparrow M. P., Bates P. C., Millward D. J. Turnover of muscle protein in the fowl (Gallus domesticus). Rates of protein synthesis in fast and slow skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscle of the adult fowl. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 15;176(2):393–401. doi: 10.1042/bj1760393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent G. J., Sparrow M. P., Millward D. J. Turnover of muscle protein in the fowl. Changes in rates of protein synthesis and breakdown during hypertrophy of the anterior and posterior latissimus dorsi muscles. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 15;176(2):407–417. doi: 10.1042/bj1760407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASTER R. W. POSSIBLE SYNTHESIS OF POLYRIBONUCLEOTIDES OF KNOWN BASE-TRIPLET SEQUENCES. Nature. 1965 Apr 3;206:93–93. doi: 10.1038/206093b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. L., Augustine S. L., Burk T. L., Swick R. W. A comparison of methods for the measurement of protein turnover in vivo. Biochem J. 1979 Nov 15;184(2):473–476. doi: 10.1042/bj1840473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin A. F., Rabinowitz M., Blough R., Prior G., Zak R. Measurements of half-life of rat cardiac myosin heavy chain with leucyl-tRNA used as precursor pool. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3422–3429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Sunde M. L., Swick R. W. Growth and muscle protein turnover in the chick. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 15;176(2):573–582. doi: 10.1042/bj1760573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee E. E., Cheung J. Y., Rannels D. E., Morgan H. E. Measurement of the rate of protein synthesis and compartmentation of heart phenylalanine. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1030–1040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNurlan M. A., Tomkins A. M., Garlick P. J. The effect of starvation on the rate of protein synthesis in rat liver and small intestine. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 15;178(2):373–379. doi: 10.1042/bj1780373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millward D. J., Garlick P. J., James W. P., Nnanyelugo D. O., Ryatt J. S. Relationship between protein synthesis and RNA content in skeletal muscle. Nature. 1973 Jan 19;241(5386):204–205. doi: 10.1038/241204a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millward D. J., Garlick P. J., Nnanyelugo D. O., Waterlow J. C. The relative importance of muscle protein synthesis and breakdown in the regulation of muscle mass. Biochem J. 1976 Apr 15;156(1):185–188. doi: 10.1042/bj1560185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millward D. J., Garlick P. J., Stewart R. J., Nnanyelugo D. O., Waterlow J. C. Skeletal-muscle growth and protein turnover. Biochem J. 1975 Aug;150(2):235–243. doi: 10.1042/bj1500235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millward D. J. The regulation of muscle-protein turnover in growth and development. Biochem Soc Trans. 1978;6(3):494–499. doi: 10.1042/bst0060494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millward D. J., Waterlow J. C. Effect of nutrition on protein turnover in skeletal muscle. Fed Proc. 1978 Jul;37(9):2283–2290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibko S., Koivistoinen P., Tratnyek C. A., Newhall A. R., Friedman L. A method for sequential quantitative separation and determination of protein, RNA, DNA, lipid, and glycogen from a single rat liver homogenate or from a subcellular fraction. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jun;19(3):514–528. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90242-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidrich A., Airhart J., Bruno M. K., Khairallah E. A. Compartmentation of free amino acids for protein biosynthesis. Influence of diurnal changes in hepatic amino acid concentrations of the composition of the precursor pool charging aminoacyl-transfer ribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1977 Feb 15;162(2):257–266. doi: 10.1042/bj1620257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young V. R., Stothers S. C., Vilaire G. Synthesis and degradation of mixed proteins, and composition changes in skeletal muscle of malnourished and refed rats. J Nutr. 1971 Oct;101(10):1379–1390. doi: 10.1093/jn/101.10.1379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


