Abstract
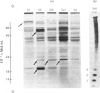
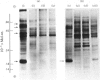
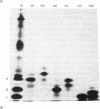
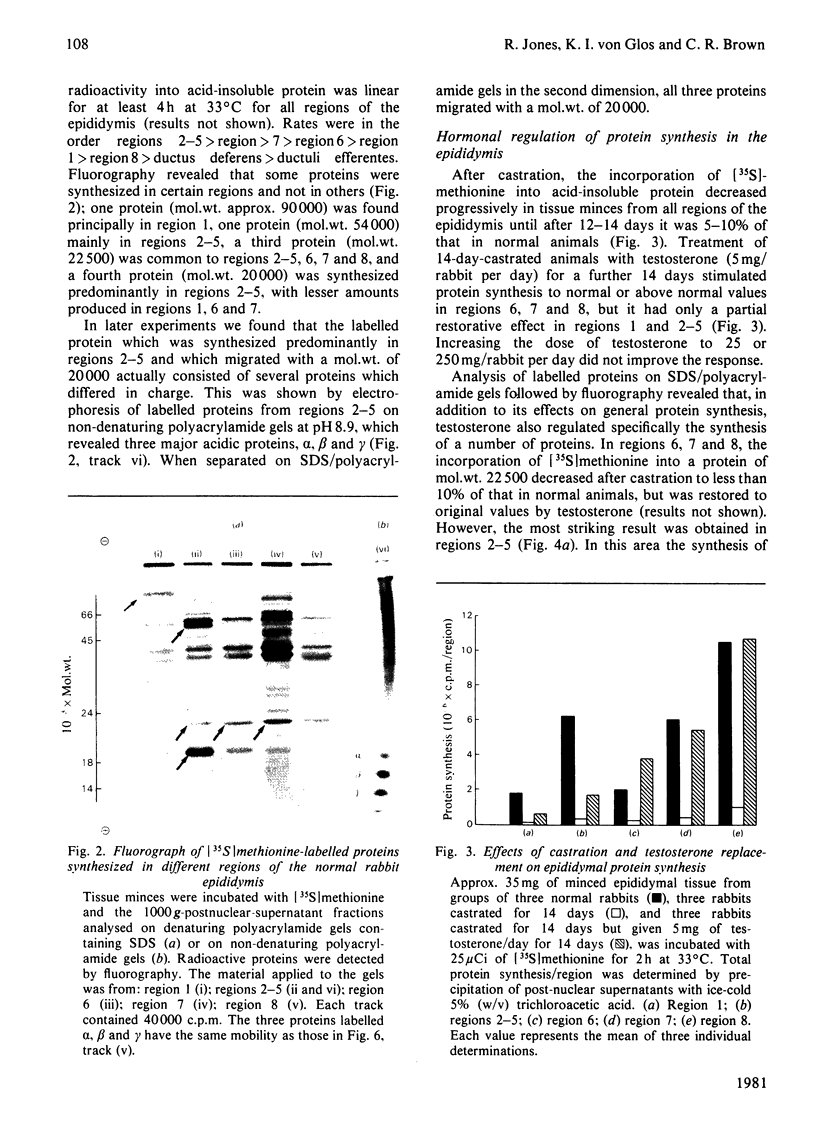
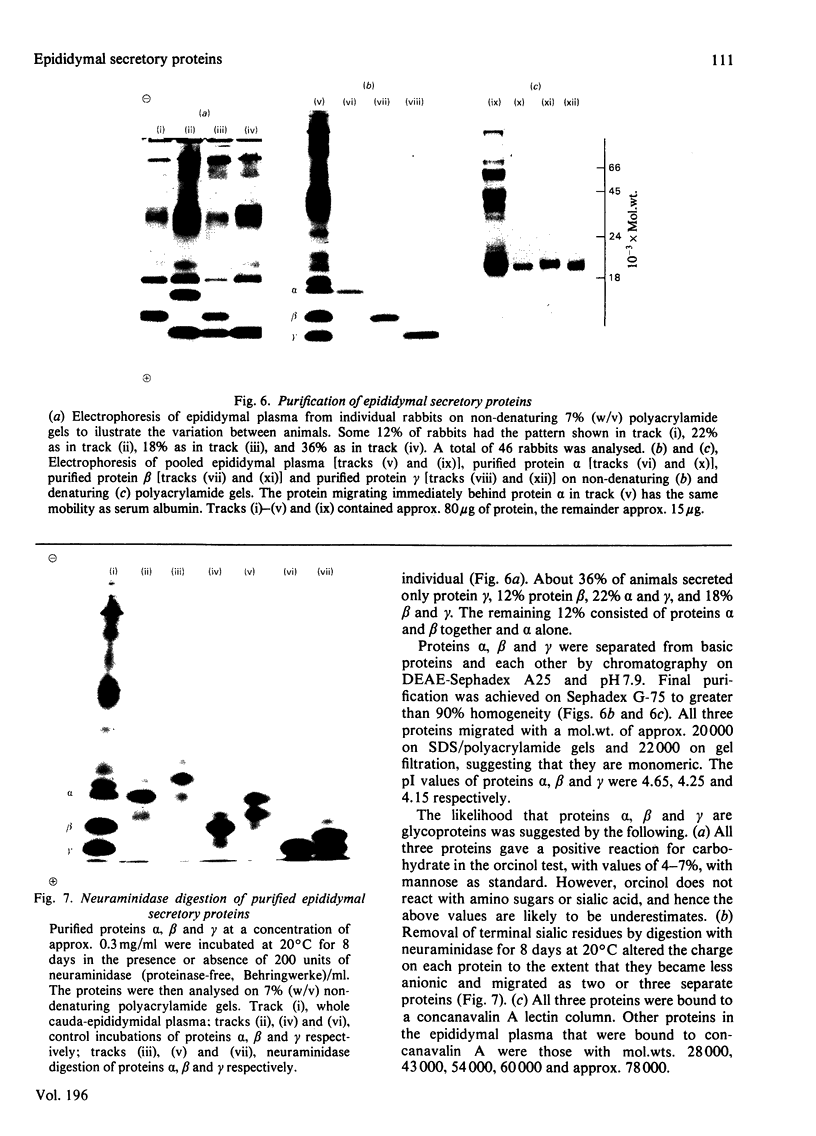
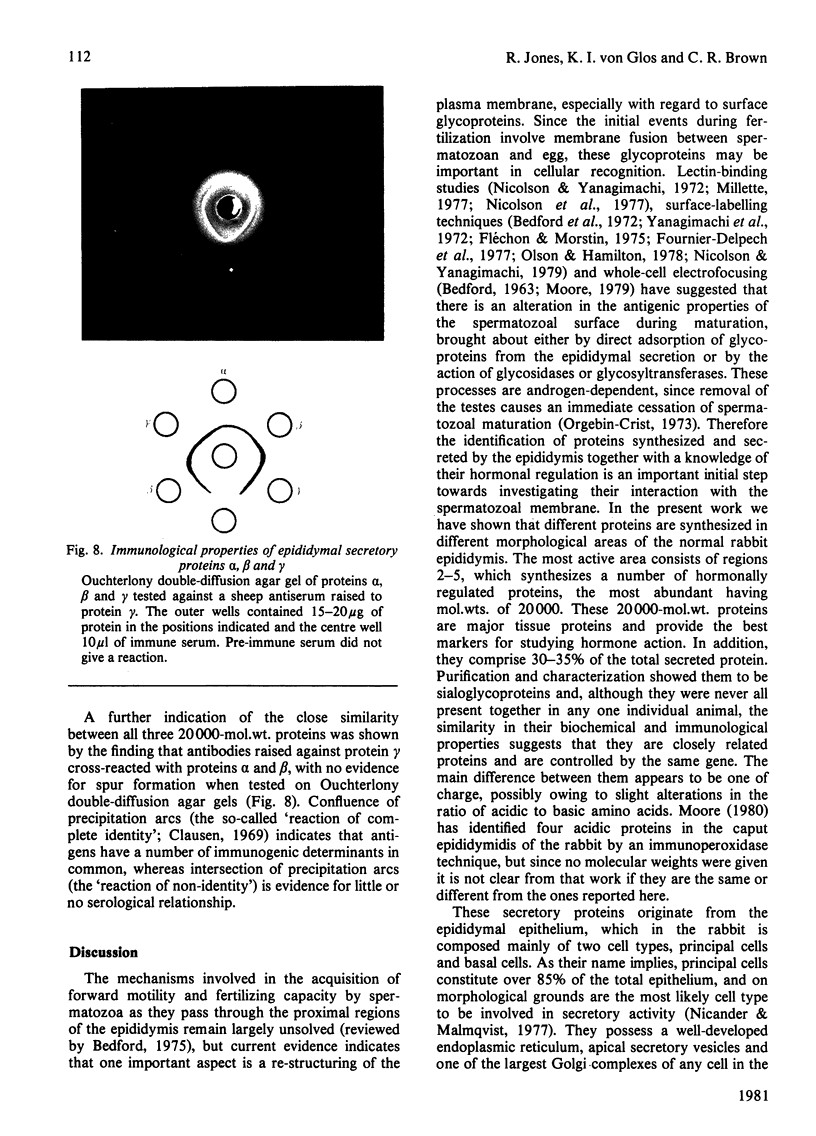
1. The incorporation of [35S]methionine into protein was investigated in tissue minces from different regions of the rabbit epididymis incubated in vitro. Rates of synthesis were in the order: epididymal regions 2-5 greater than region 7 greater than region 6 greater than region 1 greater than region 8 greater than ductus deferens greater than ductuli efferentes. 2. Separation of labelled proteins on polyacrylamide gels containing sodium dodecyl sulphate followed by fluorography revealed that one protein (mol.wt. approx. 90 000) was characteristic of region 1, four proteins (one of mol.wt. 54 000 and three of mol.wt. 20 000) were synthesized principally in regions 2-5, and one protein (mol.wt. 22 500) was produced mainly in regions 6, 7 and 8. 3. Castration for 14 days decreased incorporation of [35S]methionine into total protein to less than 10% of that in controls in all regions of the epididymis. However, testosterone treatment for a further period of 14 days restored protein synthesis to normal values in regions 6, 7 and 8, but not in region 1 or regions 2-5. In regions 2-5 the synthesis of three proteins of mol.wt. 20 000 declined after castration, but was not stimulated by exogenous testosterone. Since the 20 000-mol.wt. proteins were major tissue proteins, accounting for 16-25% of the total synthesized, they were used as markers for investigating hormone action in the epididymis. 4. Castration followed immediately by testosterone treatment or ligation of the ductuli efferentes resulted in a decrease in their synthesis, suggesting that they are partially dependent on factors in testicular fluid. Purification and characterization showed them to be acidic glycoproteins with a number of biochemical and immunological properties in common. 5. It is suggested that there is a synergistic action between blood androgens and factors in testicular fluid in regulating protein synthesis in the proximal regions of the rabbit epididymis.
Full text
PDF

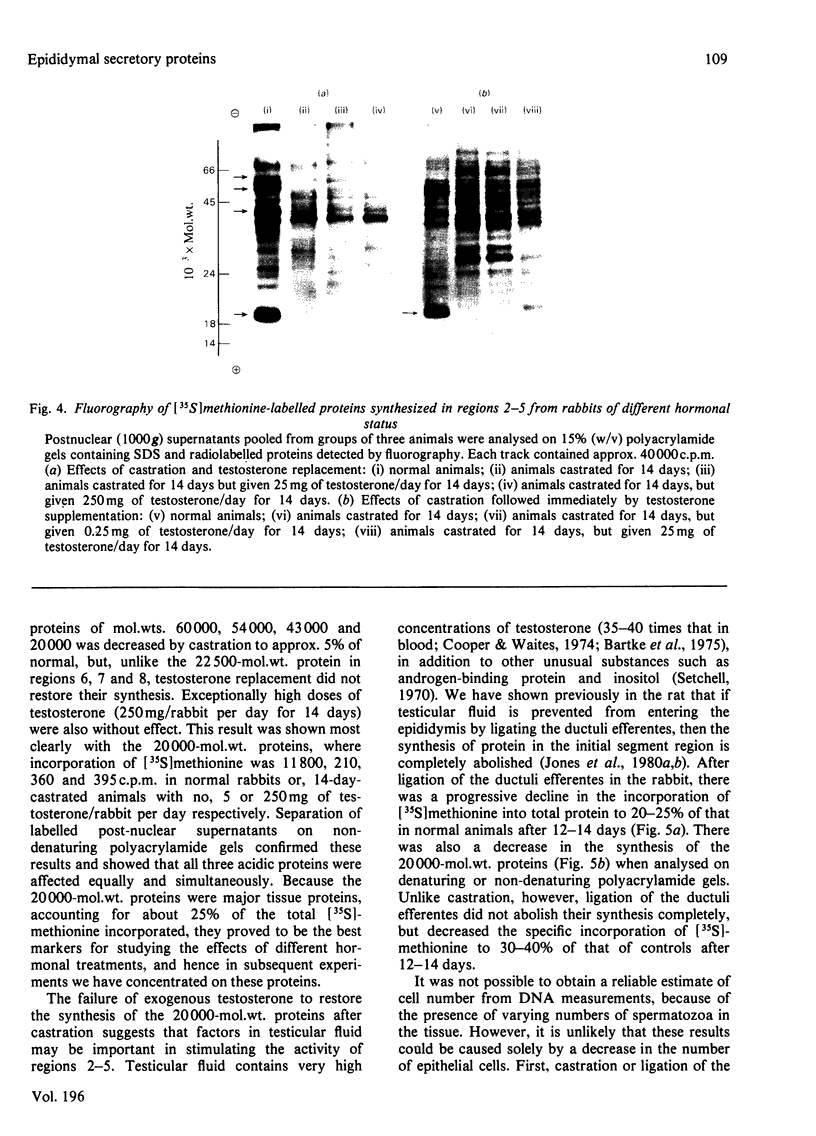
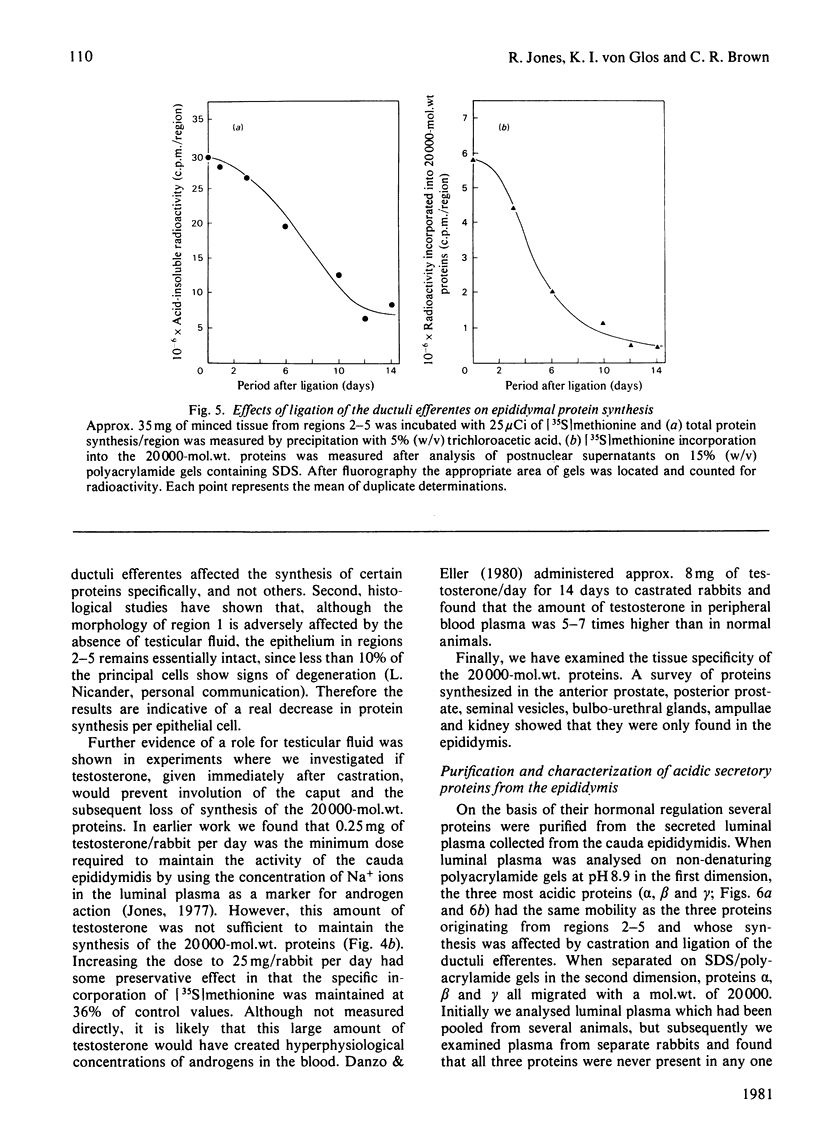


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEDFORD J. M. CHANGES IN THE ELECTROPHORETIC PROPERTIES OF RABBIT SPERMATOZOA DURING PASSAGE THROUGH THE EPIDIDYMIS. Nature. 1963 Dec 21;200:1178–1180. doi: 10.1038/2001178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth W. D., Jones R. The extragonadal origin of 5 alpha-reduced androgens in the peripheral circulation of the adult male rabbit. Int J Androl. 1980 Dec;3(6):692–702. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.1980.tb00156.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boursnell J. C., Hartree E. F., Briggs P. A. Studies of the bulbo-urethral (Cowper's)-gland mucin and seminal gel of the boar. Biochem J. 1970 May;117(5):981–988. doi: 10.1042/bj1170981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calandra R. S., Blaquier J. A., del Castillo E. J., Rivarola M. A. Androgen dependency of the androgen receptor in rat epididymis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 3;67(1):97–102. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90288-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calandra R. S., Purvis K., Attramadal A., Hansson V. Androgen receptors in the rat epididymis do not disappear after castration. J Steroid Biochem. 1977 Nov;8(11):1205–1206. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(77)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper T. G., Waites G. M. Testosterone in rete testis fluid and blood of rams and rats. J Endocrinol. 1974 Sep;62(3):619–629. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0620619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Agostino A., Jones R., White R., Parker M. G. Androgenic regulation of messenger RNA in rat epididymis. Biochem J. 1980 Sep 15;190(3):505–512. doi: 10.1042/bj1900505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danzo B. J., Cooper T. G., Orgebin-Crist M. C. Androgen binding protein (ABP) in fluids collected from the rete testis and cauda epididymidis of sexually mature and immature rabbits and observations on morphological changes in the epididymis following ligation of the ductuli efferentes. Biol Reprod. 1977 Aug;17(1):64–77. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod17.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danzo B. J., Eller B. C. Androgen metabolism by and binding to mature rabbit epididymal tissue: studies on cytosol. J Steroid Biochem. 1978 Mar;9(3):209–217. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(78)90151-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danzo B. J., Eller B. C. Androgen metabolism by mature rabbit epididymal tissue: the effects of castration and androgen replacement. J Steroid Biochem. 1980 Jun;13(6):661–667. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(80)90033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danzo B. J., Eller B. C. Nuclear binding of [3H]-androgens by the epididymis of sexually mature castrated rabbits. J Steroid Biochem. 1976 Oct;7(10):733–739. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(76)90172-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett D. W., Hoffer A. P. Failure of exogenous androgen to prevent regression of the initial segments of the rat epididymis after efferent duct ligation or orchidectomy. Biol Reprod. 1979 Mar;20(2):162–181. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod20.2.162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feig L. A., Bellvé A. R., Erickson N. H., Klagsbrun M. Sertoli cells contain a mitogenic polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4774–4778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fléchon J. E., Morstin J. Localisation des glycoprotéines et des charges négatives et positives dans le revêtement de surface des spermatozoïdes éjaculés de lapin et de taureau. Ann Histochim. 1975 Oct-Dec;20(4):291–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartree E. F. Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins S. J., Burchell J. M., Mainwaring W. I. Androgen-dependent synthesis of basic secretory proteins by the rat seminal vesicle. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 15;158(2):271–282. doi: 10.1042/bj1580271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins S. J., Burchell J. M., Parker M. G., Herries D. G. Effects of testosterone on sequence complexity of polyadenylated RNA from rat seminal vesicle. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Nov 15;91(2):327–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins S. J., Gehring U. Molecular mechanisms of steroid hormone action. Adv Cancer Res. 1978;28:313–397. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60650-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R., Brown C. R., Von Glós K. I., Parker M. G. Hormonal regulation of protein synthesis in the rat epididymis. Characterization of androgen-dependent and testicular fluid-dependent proteins. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 15;188(3):667–676. doi: 10.1042/bj1880667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. Effects of testosterone, testosterone metabolites and anti-androgens on the function of the male accessory glands in the rabbit and rat. J Endocrinol. 1977 Jul;74(1):75–88. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0740075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R., Hamilton D. W., Fawcett D. W. Morphology of the epithelium of the extratesticular rete testis, ductuli efferentes and ductus epididymidis of the adult male rabbit. Am J Anat. 1979 Nov;156(3):373–400. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001560307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R., Hamilton D. W., Fawcett D. W. Some effects of testosterone, 5alpha-dihydrotestosterone, and 5alpha-androstane-3alpha, 17beta-diol on the morphology of the rabbit epididymis and prostate. J Ultrastruct Res. 1979 May;67(2):194–208. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(79)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskimies A. I., Kormano M. Proteins in fluids from different segments of the rat epididymis. J Reprod Fertil. 1975 May;43(2):345–348. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0430345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mainwaring W. I., Mangan F. R. A study of the androgen receptors in a variety of androgen-sensitive tissues. J Endocrinol. 1973 Oct;59(1):121–139. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0590121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moniem K. A., Glover T. D., Lubicz-Nawrocki C. W. Effects of duct ligation and orchidectomy on histochemical reactions in the hamster epididymis. J Reprod Fertil. 1978 Sep;54(1):173–176. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0540173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore H. D. Localization of specific glycoproteins secreted by the rabbit and hamster epididymis. Biol Reprod. 1980 Apr;22(3):705–718. doi: 10.1093/biolreprod/22.3.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
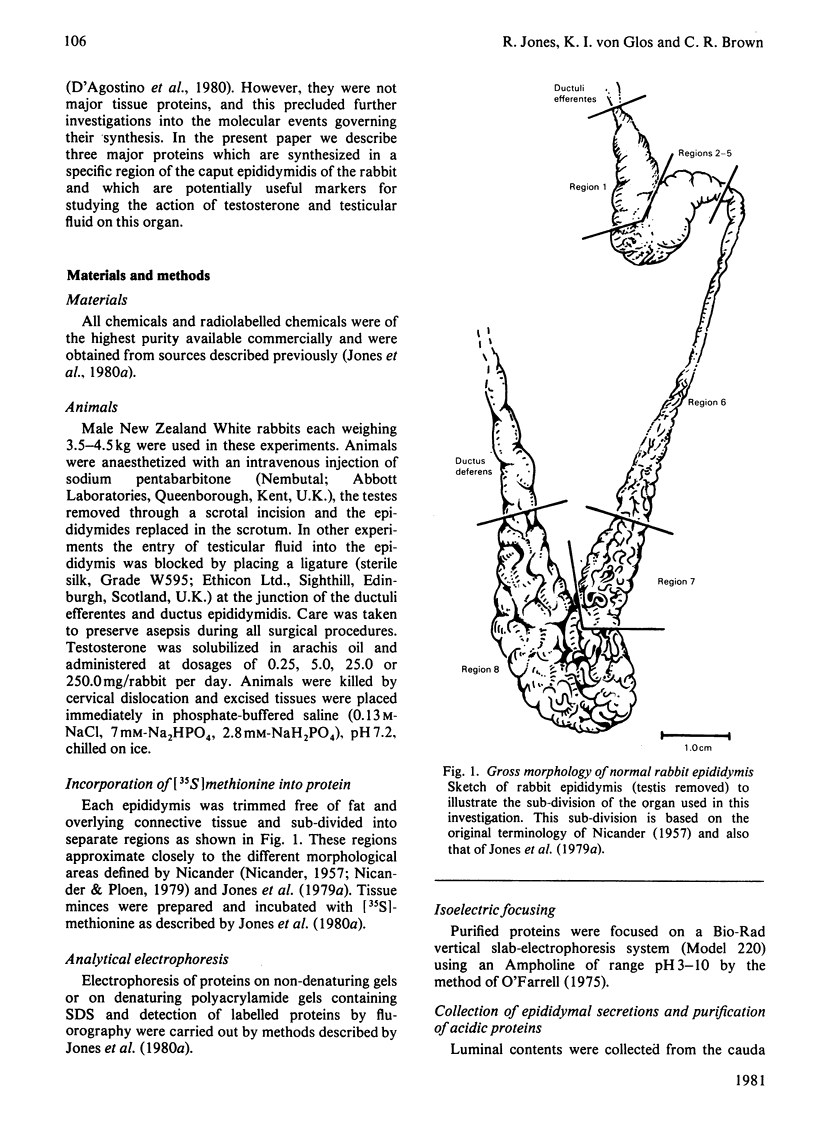
- NICANDER L. On the regional histology and cytochemistry of the ductus epididymidis in rabbits. Acta Morphol Neerl Scand. 1957;1(2):99–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicander L., Malmqvist M. Ultrastructural observations suggesting merocrine secretion in the initial segment of the mammalian epididymis. Cell Tissue Res. 1977 Nov 23;184(4):487–490. doi: 10.1007/BF00220971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L., Usui N., Yanagimachi R., Yanagimachi H., Smith J. R. Lectin-binding sites on the plasma membranes of rabbit spermatozoa. Changes in surface receptors during epididymal Maturation and after ejaculation. J Cell Biol. 1977 Sep;74(3):950–962. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.3.950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L., Yanagimachi R. Terminal saccharides on sperm plasma membranes: identification by specific agglutinins. Science. 1972 Jul 21;177(4045):276–279. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4045.276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson G. E., Hamilton D. W. Characterization of the surface glycoproteins of rat spermatozoa. Biol Reprod. 1978 Aug;19(1):26–35. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod19.1.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orgebin-Crist M. C. Maturation of spermatozoa in the rabbit epididymis: effect of castration and testosterone replacement. J Exp Zool. 1973 Sep;185(3):301–310. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401850304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. G., Mainwaring W. I. Effects of androgens on the complexity of poly(A) RNA from rat prostate. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):401–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90116-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. G., Scrace G. T., Mainwaring W. I. Testosterone regulates the synthesis of major proteins in rat ventral prostate. Biochem J. 1978 Jan 15;170(1):115–121. doi: 10.1042/bj1700115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritzén E. M., French F. S. Demonstration of an androgen binding protein (ABP) in rabbit testis: secretion in efferent duct fluid and passage into epididymis. J Steroid Biochem. 1974 Apr;5(2):151–154. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(74)90121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robaire B., Ewing L. L., Zirkin B. R., Irby D. C. Steroid delta4-5alpha-reductase and 3alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in the rat epididymis. Endocrinology. 1977 Nov;101(5):1379–1390. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-5-1379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schanbacher B. D., Ewing L. L. Simultaneous determination of testosterone, 5alpha-androstan-17beta-ol-3-one, 5alpha-androstane-3alpha,17beta-diol and 5alpha-androstane-3beta,17beta-diol in plasma of adult male rabbits by radioimmunoassay(1). Endocrinology. 1975 Oct;97(4):787–792. doi: 10.1210/endo-97-4-787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan J. N., Strott C. A. Evidence for an androgen-independent mechanism regulating the levels of receptor in target tissue. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 10;248(9):3202–3208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. D. Sexual differentiation. Annu Rev Physiol. 1978;40:279–306. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.40.030178.001431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagimachi R., Noda Y. D., Fujimoto M., Nicolson G. L. The distribution of negative surface charges on mammalian spermatozoa. Am J Anat. 1972 Dec;135(4):497–519. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001350405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]