Abstract
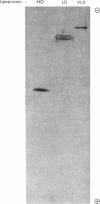
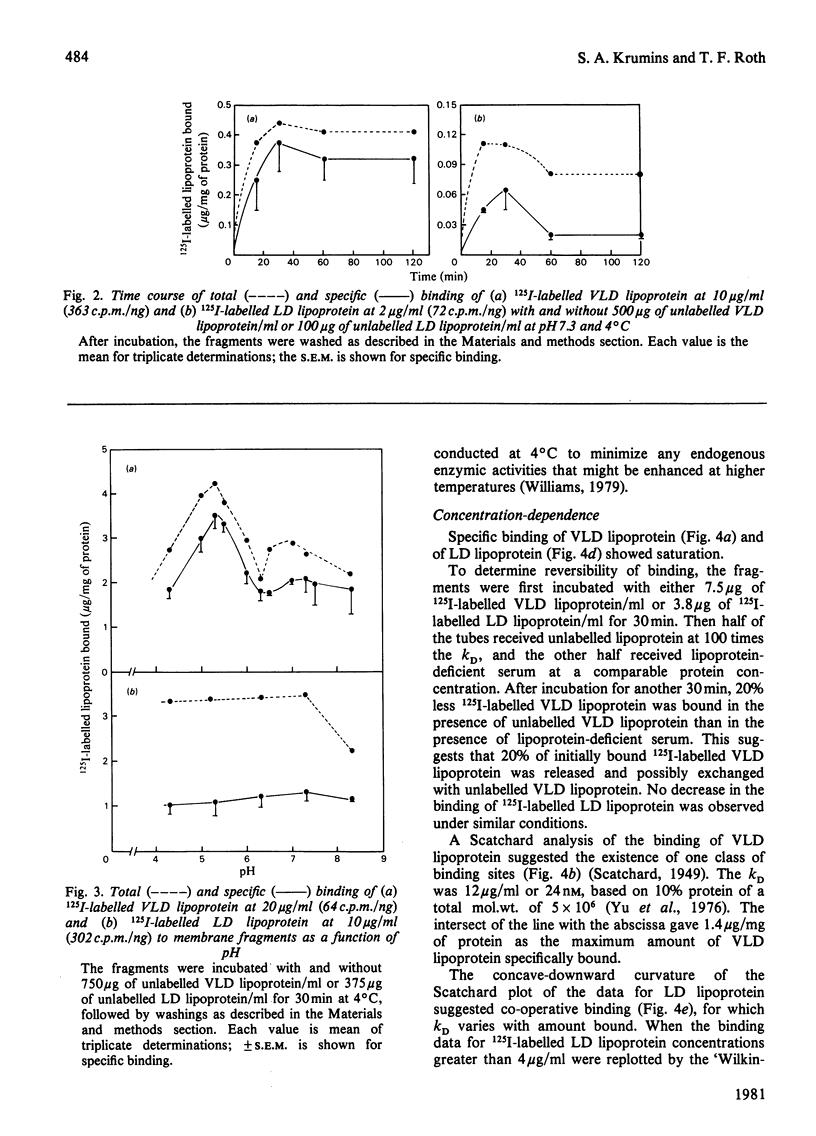
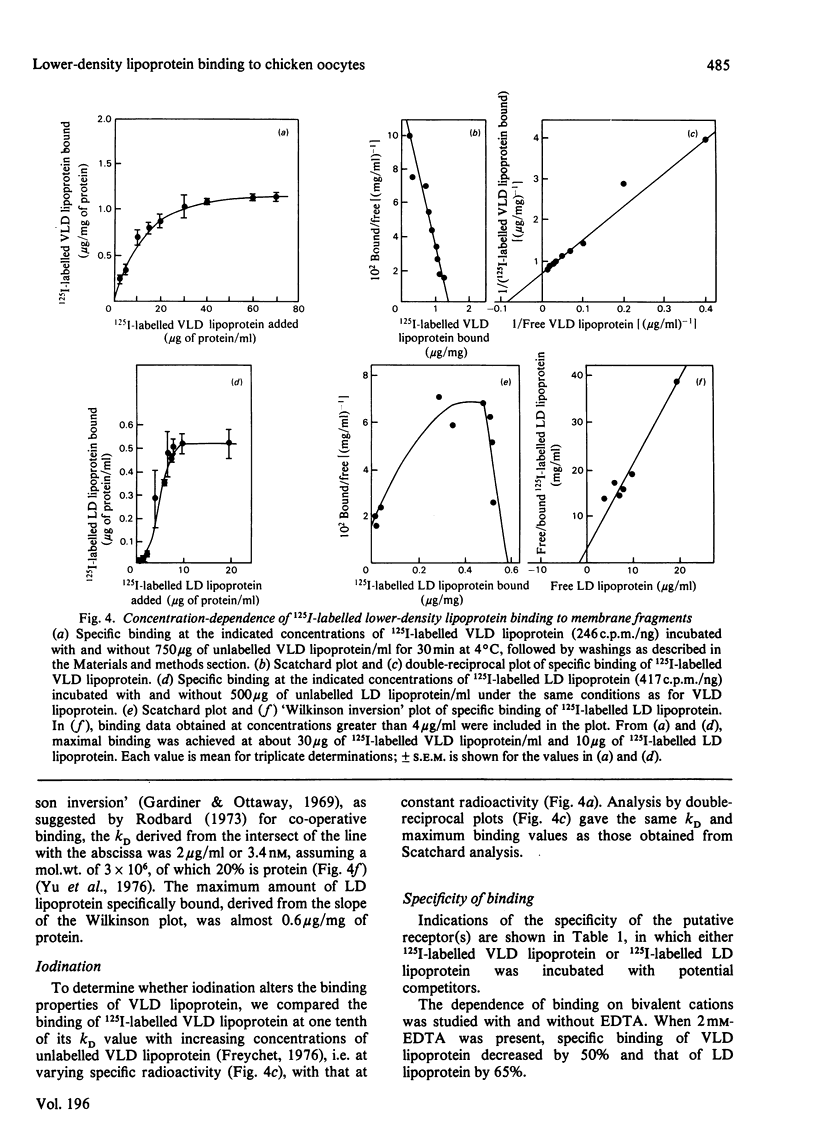
Oocyte membrane fragments bind specifically radioiodinated VLD lipoprotein (very-low density lipoprotein) and LD lipoprotein (low-density lipoprotein). Competitive binding assays showed 2-3 times more VLD lipoprotein than LD lipoprotein bound at 4 degrees C. Equilibrium-binding data revealed the presence of one class of non-interacting sites for VLD lipoprotein (kD 12 microgram/ml) and co-operative binding for LD lipoprotein. The binding of VLD lipoprotein showed a distinct pH maximum at 5.3, whereas an indistinct maximum at about pH 7.3 was observed for LD lipoprotein. Unlabelled VLD lipoprotein did compete with 125I-labelled LD lipoprotein binding, but unlabelled LD lipoprotein did not compete with 125I-labelled VLD lipoprotein binding. VLD lipoprotein binding was inhibited by HD lipoprotein (high-density lipoprotein), but not by lysozyme, collagen, poly-L-lysine or poly-L-arginine; LD lipoprotein binding was inhibited by lysozyme and collagen, but not by HD lipoprotein. On the basis of these studies, we suggest that: (1) VLD lipoprotein and LD lipoprotein enter the oocytes by a receptor-mediated transport mechanism; (2) the receptors for VLD lipoprotein and LD lipoprotein are distinct; and (3) the binding of LD lipoprotein to chicken oocyte membranes differs from that to other cell types.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. G., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Role of the coated endocytic vesicle in the uptake of receptor-bound low density lipoprotein in human fibroblasts. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):351–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacon W. L., Brown K. I., Musser M. A. Low density lipoproteins of chicken, turkey and quail egg yolk. Poult Sci. 1973 Sep;52(5):1741–1744. doi: 10.3382/ps.0521741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu S. K., Brown M. S., Ho Y. K., Goldstein J. L. Degradation of low density lipoprotein . dextran sulfate complexes associated with deposition of cholesteryl esters in mouse macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7141–7146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu S. K., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Characterization of the low density lipoprotein receptor in membranes prepared from human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3852–3856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Anderson R. G., Goldstein J. L. Mutations affecting the binding, internalization, and lysosomal hydrolysis of low density lipoprotein in cultured human fibroblasts, lymphocytes, and aortic smooth muscle cells. J Supramol Struct. 1977;6(1):85–94. doi: 10.1002/jss.400060107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Deuel T. F., Basu S. K., Goldstein J. L. Inhibition of the binding of low-density lipoprotein to its cell surface receptor in human fibroblasts by positively charged proteins. J Supramol Struct. 1978;8(3):223–234. doi: 10.1002/jss.400080302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Familial hypercholesterolemia: defective binding of lipoproteins to cultured fibroblasts associated with impaired regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):788–792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Receptor-mediated endocytosis: insights from the lipoprotein receptor system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3330–3337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman M. J., Goldstein S., Laudat M. H. Characterization and comparative aspects of the serum very low and low density lipoproteins and their apoproteins in the chicken (Gallus domesticus). Biochemistry. 1977 Jun 28;16(13):3006–3015. doi: 10.1021/bi00632a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Basu S. K., Brunschede G. Y., Brown M. S. Release of low density lipoprotein from its cell surface receptor by sulfated glycosaminoglycans. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90258-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. The low-density lipoprotein pathway and its relation to atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Ho Y. K., Basu S. K., Brown M. S. Binding site on macrophages that mediates uptake and degradation of acetylated low density lipoprotein, producing massive cholesterol deposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):333–337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gornall D. A., Kuksis A. Alterations in lipid composition of plasma lipoproteins during deposition of egg yolk. J Lipid Res. 1973 Mar;14(2):197–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillyard L. A., White H. M., Pangburn S. A. Characterization of apolipoproteins in chicken serum and egg yolk. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 15;11(4):511–518. doi: 10.1021/bi00754a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdsworth G., Michell R. H., Finean J. B. Transfer of very low density lipoprotein from hen plasma into egg yolk. FEBS Lett. 1974 Mar 1;39(3):275–277. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson B. S., Branton D. Plasma membrane: rapid isolation and exposure of the cytoplasmic surface by use of positively charged beads. Science. 1977 Jan 21;195(4275):302–304. doi: 10.1126/science.831278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordanov J., Boyadjieva-Michailova A. Ultrastructural aspects of lipoprotein passage through oocyte envelopes and storage in ooplasm during avian vitellopoiesis. Acta Anat (Basel) 1974;89(4):616–632. doi: 10.1159/000144320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Quantitative aspects of the insulin-receptor interaction in liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2249–2257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCFARLANE A. S. Labelling of plasma proteins with radioactive iodine. Biochem J. 1956 Jan;62(1):135–143. doi: 10.1042/bj0620135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L., Pitas R. E., Weisgraber K. H., Brown J. H., Gross E. Inhibition of lipoprotein binding to cell surface receptors of fibroblasts following selective modification of arginyl residues in arginine-rich and B apoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7279–7287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masket B. H., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. The use of polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in differentiating type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 May;81(5):794–802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble R. P. Electrophoretic separation of plasma lipoproteins in agarose gel. J Lipid Res. 1968 Nov;9(6):693–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M. M., Gilbert A. B. Yolk transport in the ovarian follicle of the hen (Gallus domesticus): lipoprotein-like particles at the periphery of the oocyte in the rapid growth phase. J Cell Sci. 1979 Oct;39:257–272. doi: 10.1242/jcs.39.1.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RADDING C. M., STEINBERG D. Studies on the synthesis and secretion of serum lipoproteins by rat liver slices. J Clin Invest. 1960 Oct;39:1560–1569. doi: 10.1172/JCI104177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTH T. F., PORTER K. R. YOLK PROTEIN UPTAKE IN THE OOCYTE OF THE MOSQUITO AEDES AEGYPTI. L. J Cell Biol. 1964 Feb;20:313–332. doi: 10.1083/jcb.20.2.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raju K. S., Mahadevan S. Protein components in the very low density lipoproteins of hen's egg yolks. Identification of highly aggregating (gelling) and less aggregating (non-gelling) proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 28;446(2):387–398. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbard D. Mathematics of hormone-receptor interaction. I. Basic principles. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1973;36(0):289–326. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3237-4_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth T. F., Cutting J. A., Atlas S. B. Protein transport: a selective membrane mechanism. J Supramol Struct. 1976;4(4):527–548. doi: 10.1002/jss.400040413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHJEIDE O. A. Studies of the New Hampshire chicken embryo. III. Nitrogen and lipide analyses of ultracentrifugal fractions of plasma. J Biol Chem. 1954 Nov;211(1):355–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Role of lysine residues of plasma lipoproteins in high affinity binding to cell surface receptors on human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):9053–9062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. L. Apoproteins of avian very low density lipoprotein: demonstration of a single high molecular weight apoprotein. Biochemistry. 1979 Mar 20;18(6):1056–1063. doi: 10.1021/bi00573a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu JY-L, Campbell L. D., Marquardt R. R. Immunological and compositional patterns of lipoproteins in chicken (Gallus domesticus) plasma. Poult Sci. 1976 Sep;55(5):1626–1631. doi: 10.3382/ps.0551626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yusko S. C., Roth T. F. Binding to specific receptors on oocyte plasma membranes by serum phosvitin-lipovitellin. J Supramol Struct. 1976;4(1):89–97. doi: 10.1002/jss.400040109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]