Abstract
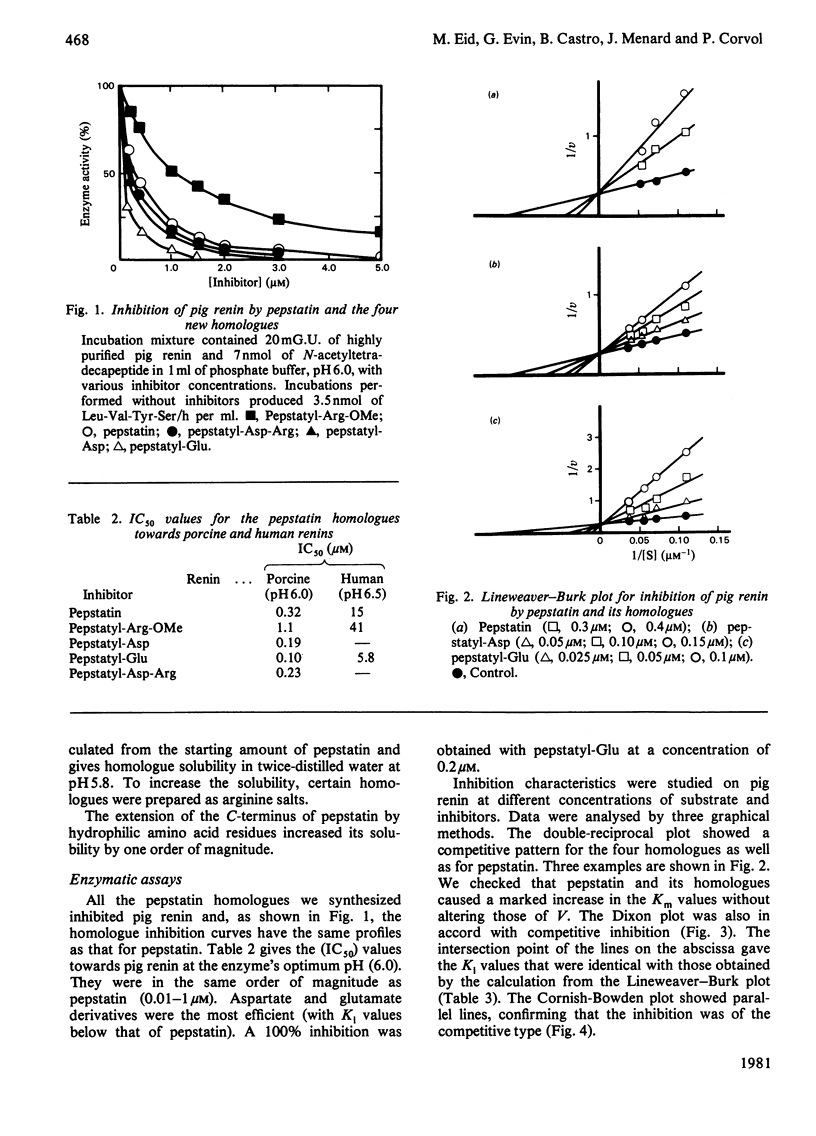
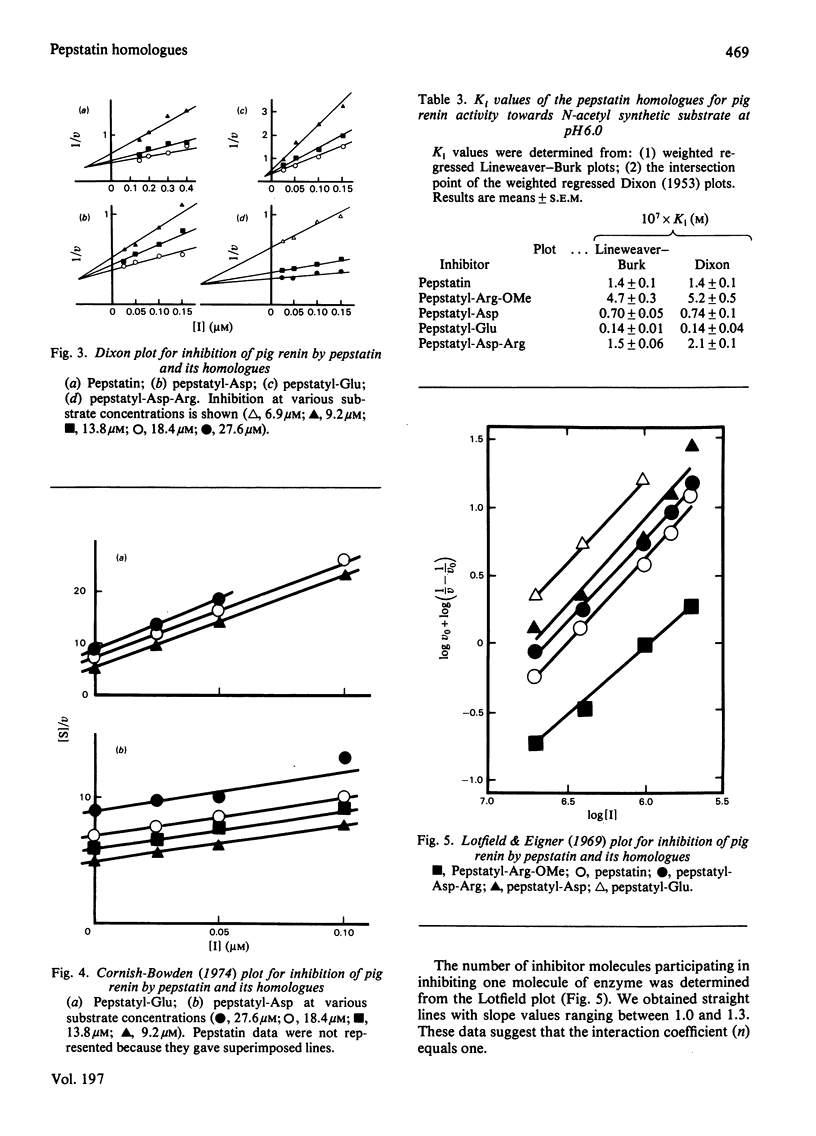
Four homologues of pepstatin, the potent but poorly soluble inhibitor of aspartic proteinases, were synthesized by coupling to the C-terminus of the natural pentapeptide the following amino acid residues: L-arginine methyl ester, L-aspartic acid, L-glutamic acid and the dipeptide L-aspartyl-L-arginine. The peptide-coupling reagent we used, benzotriazolyloxytris(dimethylamino)phosphonium hexafluorophosphate, allowed us to obtain readily pure pepstatin homologues with high yields (60-83%). Pepstatylarginine methyl ester and pepstatylglutamic acid were about one order of magnitude more water-soluble than pepstatin. The four homologues and pepstatin were tested in vitro as inhibitors for highly purified pig and human renins acting on the N-acetyltetradecapeptide substrate. The 50% inhibitory concentrations (IC50) of the homologues were ranged from 0.01 to 1 microM against porcine renin at pH 6.0 (pepstatin IC50 approximately 0.32 microM) and from 5.8 to 41 microM against human renin at pH 6.5 (pepstatin IC 50 approximately 17 microM). By three different graphical methods we showed that pepstatin and the four homologues behaved as competitive inhibitors for porcine renin. The most potent inhibitors were pepstatylaspartic acid and pepstatylglutamic acid, with inhibitory constants respectively 2- and 10-fold smaller than that of pepstatin. By coupling glutamic acid to pepstatin, the ratio solubility/Ki was increased by two orders of magnitude.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoyagi T., Kunimoto S., Morishima H., Takeuchi T., Umezawa H. Effect of pepstatin on acid proteases. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Oct;24(10):687–694. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. Protein degradation in health and disease. Introduction: the classification of proteinases. Ciba Found Symp. 1979;(75):1–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornish-Bowden A. A simple graphical method for determining the inhibition constants of mixed, uncompetitive and non-competitive inhibitors. Biochem J. 1974 Jan;137(1):143–144. doi: 10.1042/bj1370143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corvol P., Devaux C., Ito T., Sicard P., Ducloux J., Menard J. Large scale purification of hog renin. Physicochemical characterization. Circ Res. 1977 Nov;41(5):616–622. doi: 10.1161/01.res.41.5.616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corvol P., Devaux C., Menard J. Pepstatin, an inhibitor for renin purification by affinity chromatography. FEBS Lett. 1973 Aug 15;34(2):189–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80790-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON M. The determination of enzyme inhibitor constants. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):170–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0550170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIRI K. V., RAO N. A. N. A technique for the identification of amino-acids separated by circular paper chromatography. Nature. 1952 May 31;169(4309):923–924. doi: 10.1038/169923a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galen F. X., Devaux C., Grogg P., Menard J., Corvol P. Fluorimetric assay of renin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 12;523(2):485–493. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galen F. X., Devaux C., Guyenne T., Menard J., Corvol P. Multiple forms of human renin. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4848–4855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardes J., Evin G., Castro B., Corvol P., Menard J. Synthesis and renin inhibitory properties of a new soluble pepstatin derivative. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1980 Sep-Oct;2(5):687–698. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198009000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber E. George C. Griffith lecture. The role of renin in normal and pathological cardiovascular homeostasis. Circulation. 1976 Dec;54(6):849–861. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.54.6.849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackenthal E., Hackenthal R., Hilgenfeldt U. Isorenin, pseudorenin, cathepsin D and renin. A comparative enzymatic study of angiotensin-forming enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 10;522(2):574–588. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90089-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. L., Poisner A. M. Inhibition of pseudorenin by pepstatin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Apr 1;26(7):639–641. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight C. G., Barrett A. J. Interaction of human cathepsin D with the inhibitor pepstatin. Biochem J. 1976 Apr 1;155(1):117–125. doi: 10.1042/bj1550117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loftfield R. B., Eigner E. A. Molecular order of participation of inhibitors (or activators) in biological systems. Science. 1969 Apr 18;164(3877):305–308. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3877.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciniszyn J., Jr, Hartsuck J. A., Tang J. Mode of inhibition of acid proteases by pepstatin. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 25;251(22):7088–7094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKown M. M., Workman R. J., Gregerman R. I. Pepstatin inhibition of human renin. Kinetic studies and estimation of enzyme purity. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):7770–7774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich D. H., Sun E. T., Ulm E. Synthesis of analogues of the carboxyl protease inhibitor pepstatin. Effects of structure on inhibition of pepsin and renin. J Med Chem. 1980 Jan;23(1):27–33. doi: 10.1021/jm00175a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Aoyagi T., Morishima H., Matsuzaki M., Hamada M. Pepstatin, a new pepsin inhibitor produced by Actinomycetes. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 May;23(5):259–262. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.23.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON G. N. Statistical estimations in enzyme kinetics. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:324–332. doi: 10.1042/bj0800324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman R. J., Burkitt D. W. Pepsin inhibition by a high specific activity radioiodinated derivative of pepstatin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Apr 15;194(1):157–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90605-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


