Abstract
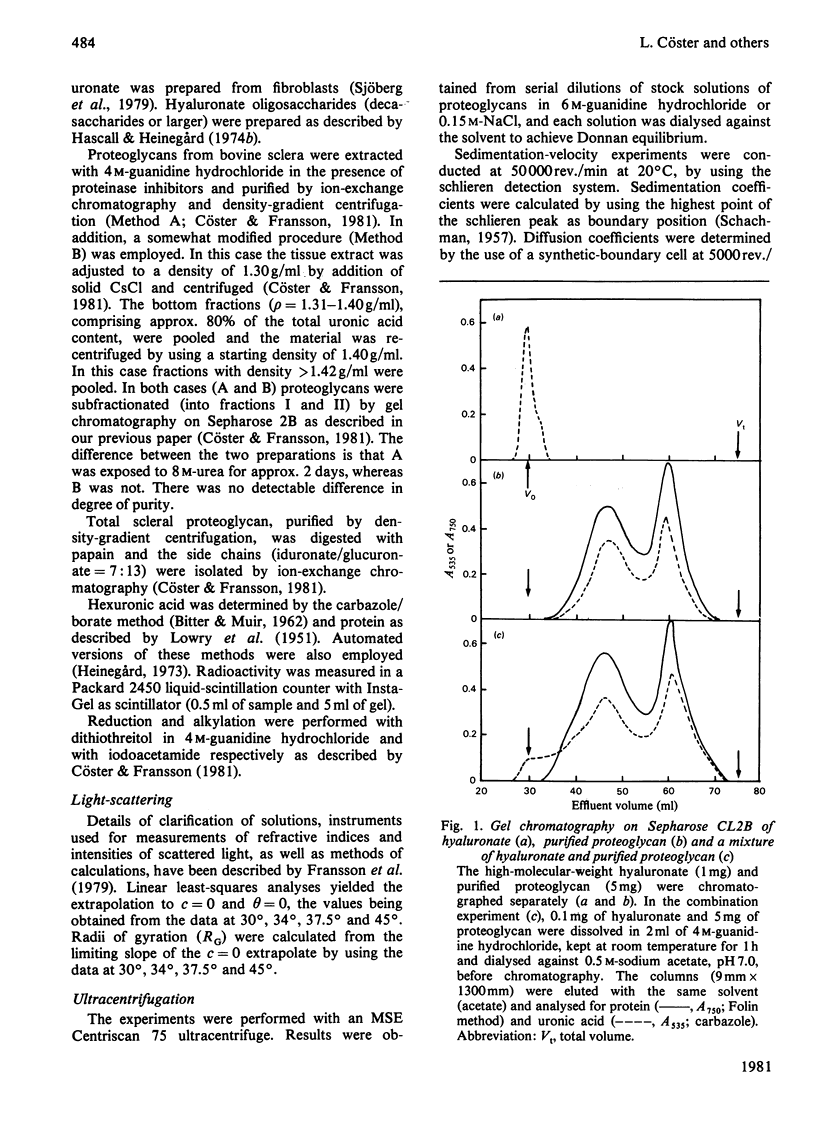
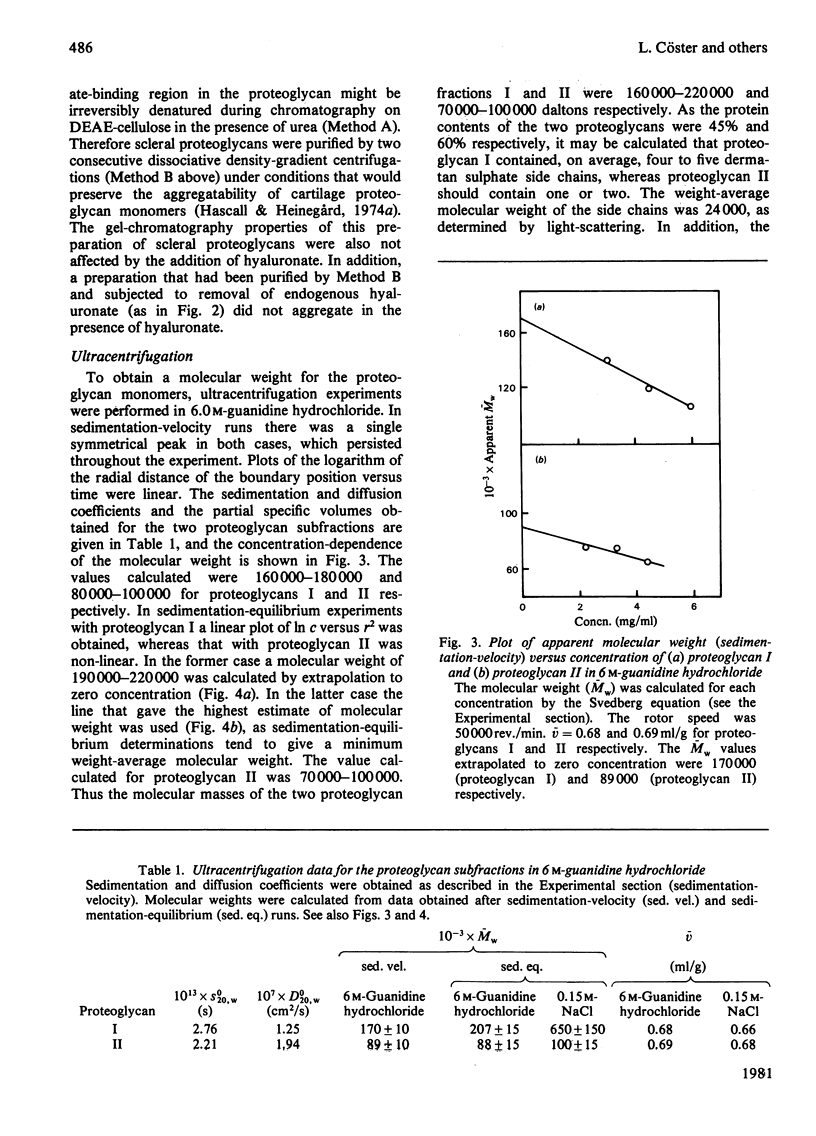
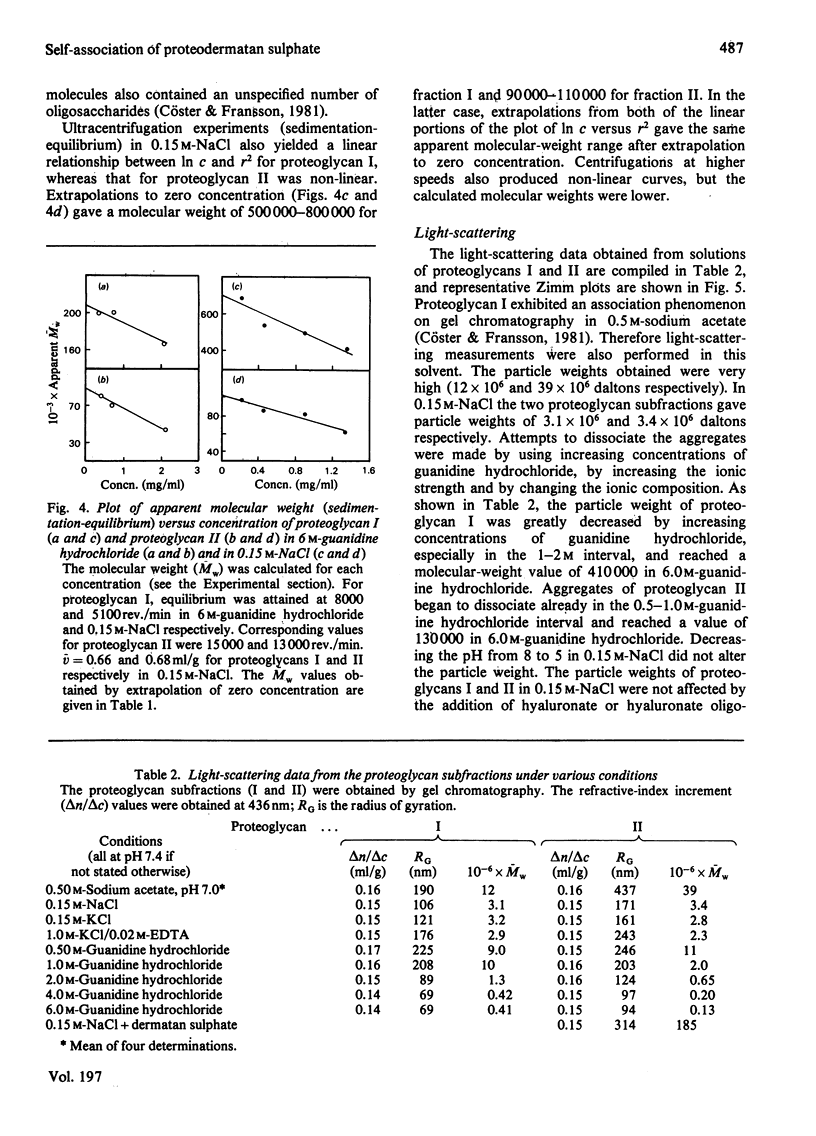
1. Two proteodermatan sulphate fractions (I and II) from bovine sclera were studied by gel chromatography, light-scattering and ultracentrifugation under various conditions. 2. Gel chromatography of proteoglycans in the absence or presence of hyaluronate was performed under associative conditions. No effect on the elution profile was noted. 3. Ultracentrifugation experiments (sedimentation-velocity and sedimentation-equilibrium) with proteoglycan I and II in 6 M-guanidine hydrochloride gave molecular weights (Mw) of 160000-220000 and 70000-100000 respectively. As the protein contents were 45% and 60% respectively, it may be calculated that proteoglycan I contained four to five side chains, whereas proteoglycan II contained one or two. Sedimentation-equilibrium runs performed in 0.15 M-NaCl gave an apparent molecular weight (Mw) of 500000-800000 for proteoglycan I and 90000-110000 for proteoglycan II. 4. In light-scattering experiments both proteoglycans I and II yielded high particle weights in 0.15 M-NaCl (3.1 X 10(6) and 3.4 X 10(6) daltons respectively). In the presence of 6 M-guanidine hydrochloride the molecular weights decreased to 410000 and 130000 respectively. The particle weights in 0.15 M-NaCl were not altered by the addition of hyaluronate or hyaluronate oligosaccharides. 5. The dermatan sulphate side chains of scleral proteoglycans (L-iduronate/D-glucuronate ratio 7:13) gave a particle weight of 100000 daltons in 0.15 M-NaCl. In 1.00 M-KCl/0.02M-EDTA the molecular weight was 24000. Addition of free scleral dermatan sulphate chains to a solution of proteoglycan II promoted further multimerization of the macromolecule.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. C. Isolation of a glycoprotein and proteodermatan sulphate from bovine achilles tendon by affinity chromatography on concanavalin A-Sepharose. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 27;379(2):444–455. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90151-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelsson I., Heinegård D. Characterization of the keratan sulphate proteoglycans from bovine corneal stroma. Biochem J. 1978 Mar 1;169(3):517–530. doi: 10.1042/bj1690517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BITTER T., MUIR H. M. A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Anal Biochem. 1962 Oct;4:330–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cöster L., Fransson L. A. Isolation and characterization of dermatan sulphate proteoglycans from bovine sclera. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 1;193(1):143–153. doi: 10.1042/bj1930143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damle S. P., Kieras F. J., Tzeng W. K., Gregory J. D. Isolation and characterization of proteochondroitin sulfate from pig skin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1614–1620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich K. C., Radhakrishnamurthy B., Berenson G. S. Isolation of a chondroitin sulfate--dermatan sulfate proteoglycan from bovine aorta. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Nov;171(1):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein R., Larsson S. E., Kuettner K. E., Sorgente N., Hascal V. C. The ground substance of the arterial wall. Part 1. Extractability of glycosaminoglycans and the isolation of a proteoglycan from bovine aorta. Atherosclerosis. 1975 Jul-Aug;22(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(75)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransson L. A., Cöster L. Interaction between dermatan sulphate chains. II. Structural studies on aggregating glycan chains and oligosaccharides with affinity for dermatan sulphate-substituted agarose. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 4;582(1):132–144. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90296-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransson L. A. Interaction between dermatan sulphate chains. I. Affinity chromatography of copolymeric galactosaminioglycans on dermatan sulphate-substituted agarose. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 23;437(1):106–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90351-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Muir H. Binding of oligosaccharides of hyaluronic acid to proteoglycans. Biochem J. 1973 Dec;135(4):905–908. doi: 10.1042/bj1350905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Muir H. Hyaluronic acid in cartilage and proteoglycan aggregation. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):565–581. doi: 10.1042/bj1390565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Muir H. The specific interaction of hyaluronic acid with cartillage proteoglycans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 15;279(2):401–405. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90160-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Heinegård D. Aggregation of cartilage proteoglycans. I. The role of hyaluronic acid. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4232–4241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Heinegård D. Aggregation of cartilage proteoglycans. II. Oligosaccharide competitors of the proteoglycan-hyaluronic acid interaction. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4242–4249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radhakrishnamurthy B., Ruiz H. A., Jr, Berenson G. S. Isolation and characterization of proteoglycans from bovine aorta. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4831–4841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöberg I., Carlstedt I., Cöster L., Malmström A., Fransson L. A. Structure and metabolism of sulphated glycosaminoglycans in cultures of human fibroblasts. Structural characteristics of co-polymeric galactosaminoglycans in sequential extracts of fibroblasts during pulse-chase experiments. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 15;178(2):257–270. doi: 10.1042/bj1780257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toole B. P., Lowther D. A. Dermatan sulfate-protein: isolation from and interaction with collagen. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Dec;128(3):567–578. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toole B. P., Lowther D. A. The isolation of a dermatan sulphate-protein complex from bovine heart valves. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Nov 1;101(3):364–366. doi: 10.1016/0926-6534(65)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANTIS D. A. EQUILIBRIUM ULTRACENTRIFUGATION OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:297–317. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


