Abstract
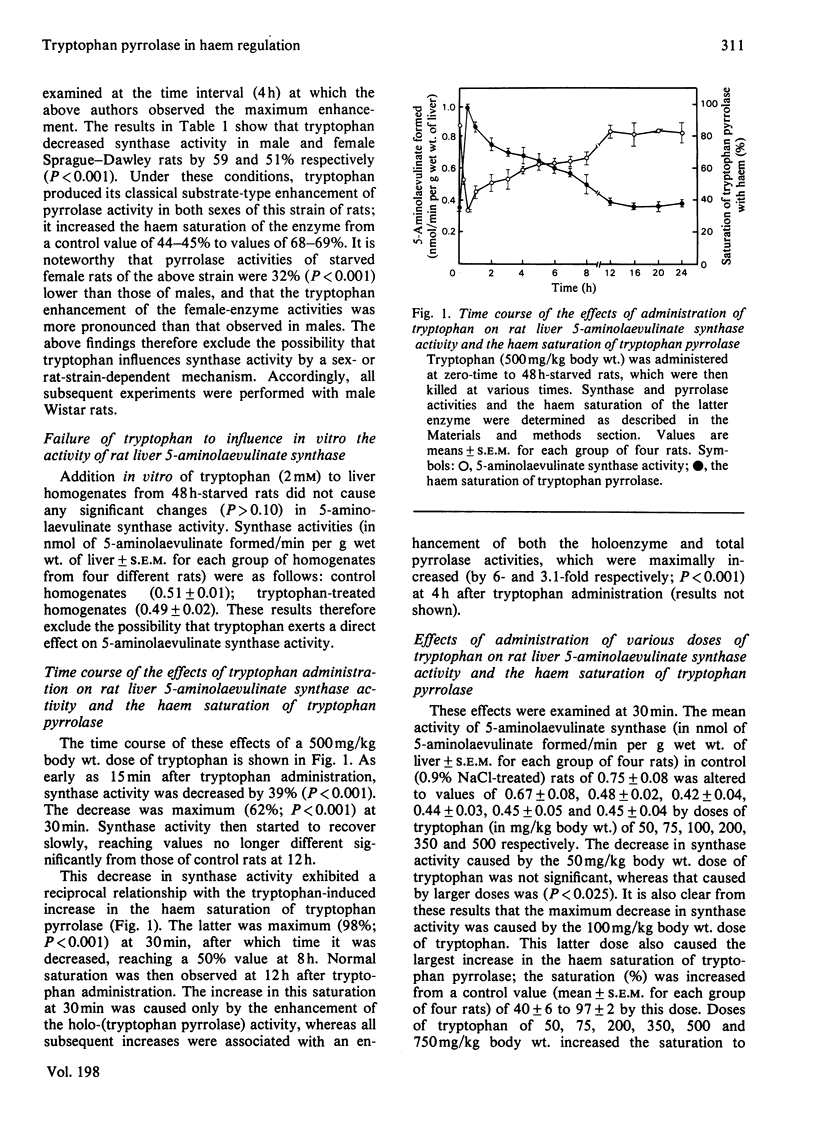
1. Administration of tryptophan to starved rats causes a rapid decrease in liver 5-aminolaevulinate synthase activity associated with an increase in the haem saturation of tryptophan pyrrolase. Both effects are maximally produced at 30 min by a 100 mg/kg body wt. dose of tryptophan. 2. Pb2+ prevents both effects. 3. Prevention by allopurinol or benserazide of the tryptophan-induced increase in the haem saturation of tryptophan pyrrolase renders this haem available for further repression of synthase synthesis. 4. The opposite effects on synthase activity and pyrrolase saturation with haem caused by administration of 5-aminolaevulinate, but not those by that of haematin, are potentiated by tryptophan. 5. It is suggested that tryptophan decreases 5-aminolaevulinate synthase activity and causes the initial increase in the haem saturation of tryptophan pyrrolase by enhancing the conversion of 5-aminolaevulinate into haem by a process requiring protein synthesis.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badawy A. A. Central role of tryptophan pyrrolase in haem metabolism. Biochem Soc Trans. 1979 Jun;7(3):575–583. doi: 10.1042/bst0070575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badawy A. A., Evans M. Regulation of rat liver tryptophan pyrrolase by its cofactor haem: Experiments with haematin and 5-aminolaevulinate and comparison with the substrate and hormonal mechanisms. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;150(3):511–520. doi: 10.1042/bj1500511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badawy A. A., Evans M. The mechanism of inhibition of rat liver tryptophan pyrrolase activity by 4-hydroxypyrazolo(3,4-d)pyrimidine (Allopurinol). Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):585–591. doi: 10.1042/bj1330585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badawy A. A., Morgan C. J. Tryptophan pyrrolase in haem regulation. The relationship between the depletion of rat liver tryptophan pyrrolase haem and the enhancement of 5-aminolaevulinate synthase activity by 2-allyl-2-isopropylacetamide. Biochem J. 1980 Mar 15;186(3):763–772. doi: 10.1042/bj1860763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badawy A. A. The effects of acetate, metal cations, phenobarbitone, porphyrogens and substrates of glycine acyltransferase on the utilization of haem by rat liver apo-(tryptophan pyrrolase). Biochem J. 1977 May 15;164(2):431–438. doi: 10.1042/bj1640431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissell D. M., Hammaker L. E. Effect of endotoxin on tryptophan pyrrolase and delta-aminolaevulinate synthase: evidence for an endogenous regulatory haem fraction in rat liver. Biochem J. 1977 Aug 15;166(2):301–304. doi: 10.1042/bj1660301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Matteis F. Loss of haem in rat liver caused by the porphyrogenic agent 2-allyl-2-isopropylacetamide. Biochem J. 1971 Oct;124(4):767–777. doi: 10.1042/bj1240767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Druyan R., Kelly A. The effect of exogenous -aminolaevulinate on rat liver haem and cytochromes. Biochem J. 1972 Oct;129(5):1095–1099. doi: 10.1042/bj1291095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENGARD O., FEIGELSON P. The activation and induction of rat liver tryptophan pyrrolase in vivo by its substrate. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jan;236:158–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. Lead poisoning and haem biosynthesis. Br J Haematol. 1972 Nov;23(5):521–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb07087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox W. E. The regulation of tryptophan pyrrolase activity by tryptophan. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1966;4:287–297. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(66)90023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marver H. S., Tschudy D. P., Perlroth M. G., Collins A. Coordinate synthesis of heme and apoenzyme in the formation of tryptophan pyrrolase. Science. 1966 Oct 28;154(3748):501–503. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3748.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell J. D., Meyer U. A. Effect of lead on hepatic delta-aminolaevulinic acid synthetase activity in the rat: a model for drug sensitivity in intermittent acute porphyria. Eur J Clin Invest. 1976 Sep 10;6(5):373–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1976.tb00531.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan C. J., Badawy A. A. Tryptophan pyrrolase in haem regulation. The mechanism of the permissive effect of cortisol on the enhancement of 5-aminolaevulinate synthase activity by 2-allyl-2-isopropylacetamide in the adrenalectomized-rat liver. Biochem J. 1980 Mar 15;186(3):993–996. doi: 10.1042/bj1860993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHIMKE R. T., SWEENEY E. W., BERLIN C. M. THE ROLES OF SYNTHESIS AND DEGRADATION IN THE CONTROL OF RAT LIVER TRYPTOPHAN PYRROLASE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:322–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch A. N., Badawy A. A. Tryptophan pyrrolase in haem regulation. Experiments with administered haematin and the relationship between the haem saturation of tryptophan pyrrolase and the activity of 5-aminolaevulinate synthase in rat liver. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 15;192(2):403–410. doi: 10.1042/bj1920403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. N., St-Arnaud-McKenzie D., Sourkes T. L. Importance of tryptophan pyrrolase and aromatic amino acid decarboxylase in the catabolism of tryptophan. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978 Mar 1;27(5):763–767. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90517-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


