Abstract
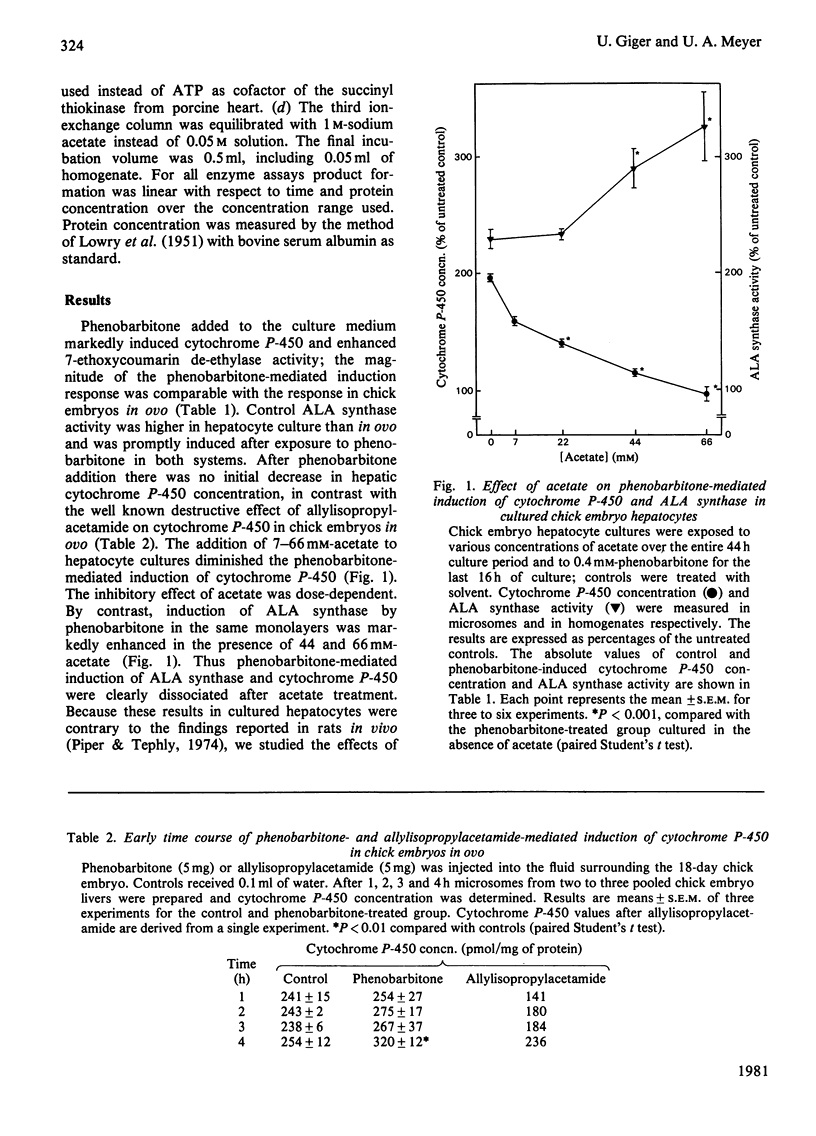
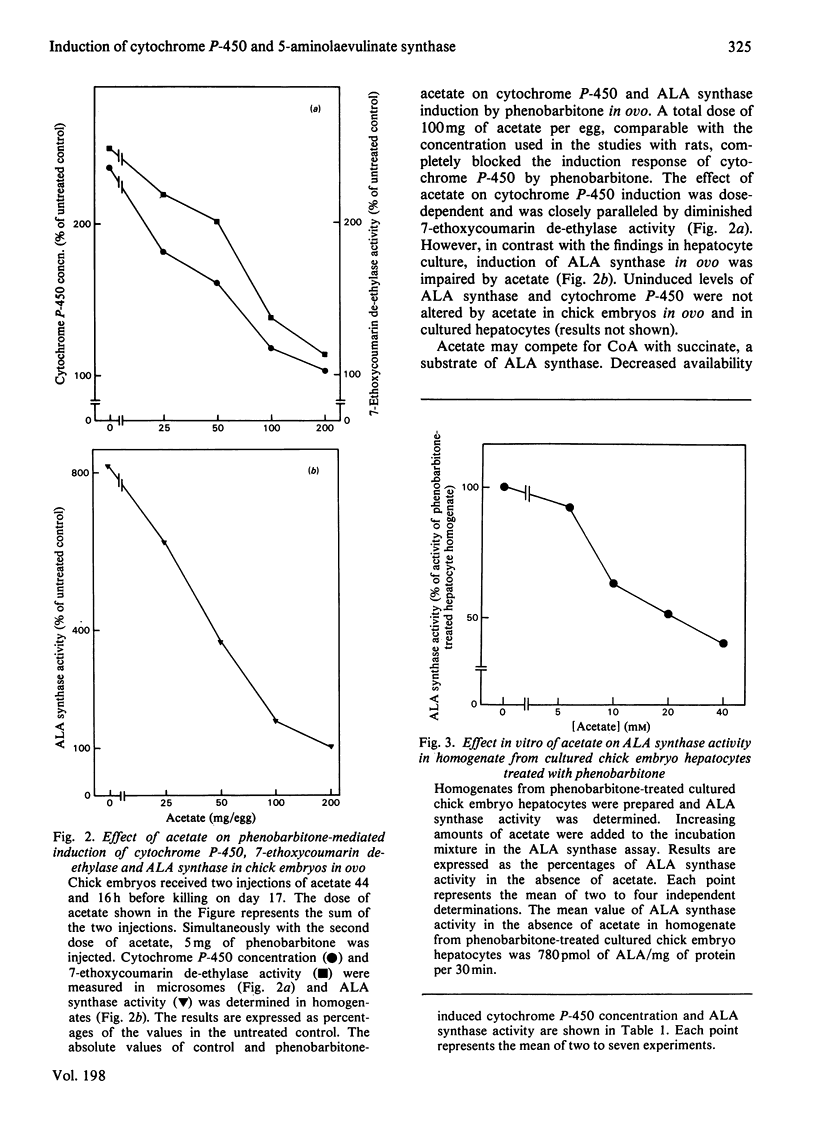
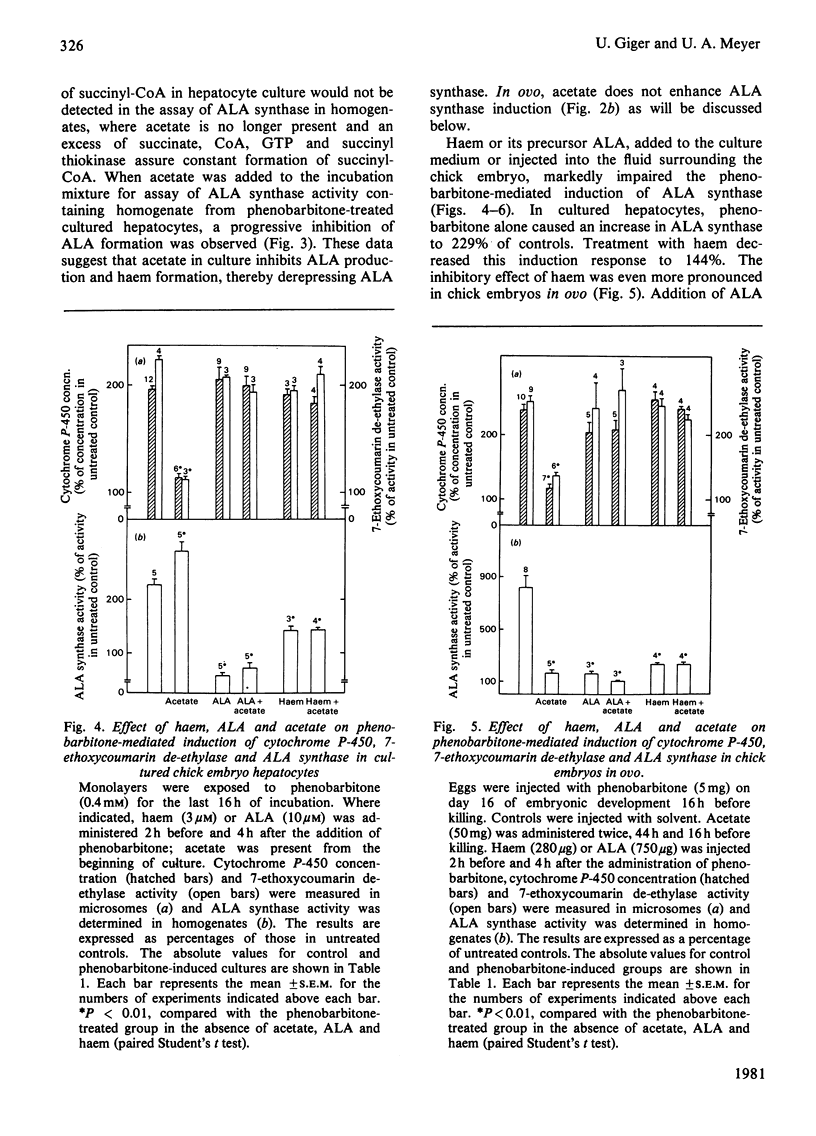
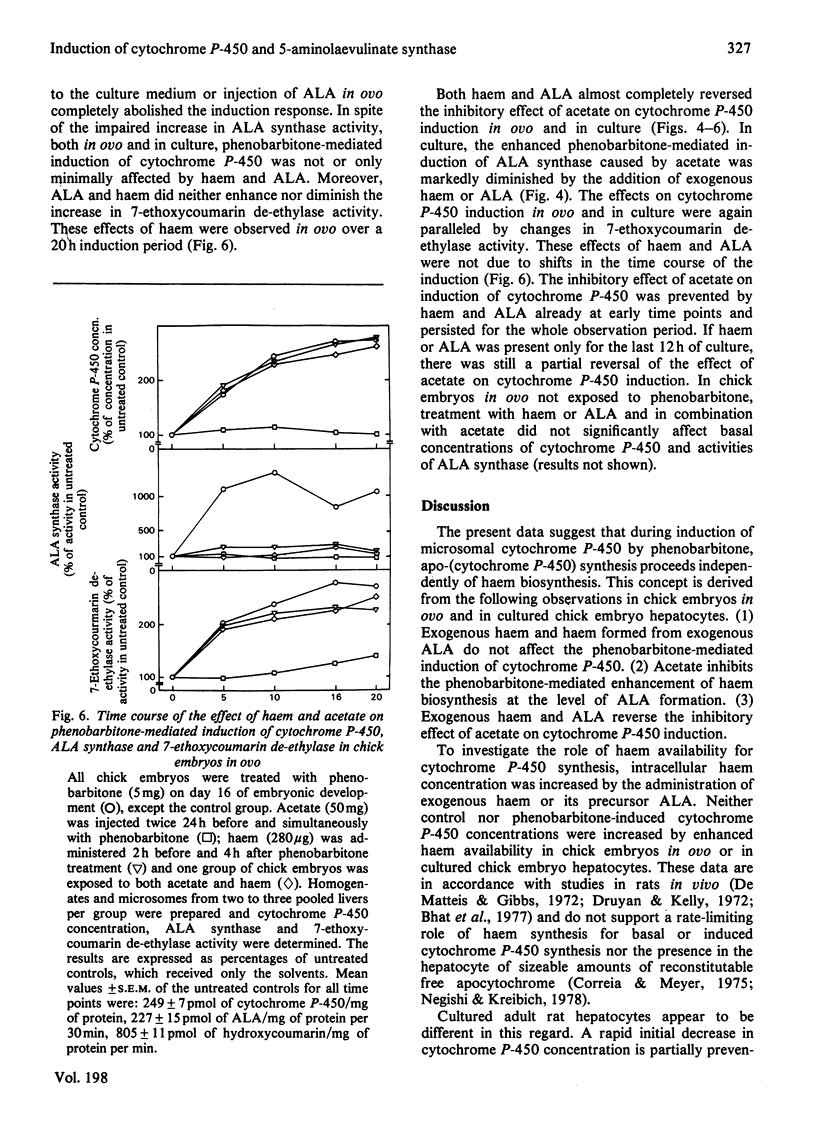
The role of haem synthesis during induction of hepatic cytochrome P-450 haemoproteins was studied in chick embryo in ovo and in chick embryos hepatocytes cultured under chemically defined conditions. 1. Phenobarbitone caused a prompt increase in the activity of 5-aminolaevulinate synthase, the rate-limiting enzyme of haem biosynthesis, and in the concentration of cytochrome P-450. This induction response occurred without measurable initial destruction of the haem moiety of cytochrome P-450. 2. When intracellular haem availability was enhanced by exogenous haem or 5-aminolaevulinate, phenobarbitone-medicated induction of cytochrome P-450 was not affected in spite of the well known repression of 5-aminolaevulinate synthase by haem. These data are consistent with the concept that haem does not regulate the synthesis of cytochrome P-450 haemoproteins. 3. Acetate inhibited haem biosynthesis at the level of 5-aminolaevulinate formation. When intracellular haem availability was diminished by treatment with acetate, phenobarbitone-medicated induction was decreased. 4. This inhibitory effect of acetate on cytochrome P-450 induction was reversed by exogenous haem or its precursor 5-aminolaevulinate. These data suggest that inhibition of haem biosynthesis does not decrease synthesis of apo-cytochrome P-450. Moreover, they indicate that exogenous haem can be incorporated into newly formed aop-cytochrome P-450.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Althaus F. R., Sinclair J. F., Sinclair P., Meyers U. A. Drug-mediated induction of cytochrome(s) P-450 and drug metabolism in cultured hepatocytes maintained in chemically defined medium. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 25;254(6):2148–2153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURNHAM B. F., PIERCE W. S., WILLIAMS K. R., BOYER M. H., KIRBY C. K. delta-aminolaevulate dehydratase from Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Biochem J. 1963 Jun;87:462–472. doi: 10.1042/bj0870462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Nun S., Kreibich G., Adesnik M., Alterman L., Negishi M., Sabatini D. D. Synthesis and insertion of cytochrome P-450 into endoplasmic reticulum membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):965–969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat K. S., Sardana M. K., Padmanaban G. Role of haem in the synthesis and assembly of cytochrome P-450. Biochem J. 1977 May 15;164(2):295–303. doi: 10.1042/bj1640295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock K. W., Krauss E., Fröhling W. Regulation of -aminolevulinic acid synthetase by drugs and steroids in vivo and in isolated perfused rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Nov 11;23(2):366–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correia M. A., Farrell G. C., Schmid R., Ortiz de Montellano P. R., Yost G. S., Mico B. A. Incorporation of exogenous heme into hepatic cytochrome P-450 in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 10;254(1):15–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correia M. A., Meyer U. A. Apocytochrome P-450: reconstitution of functional cytochrome with hemin in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):400–404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Matteis F. Drug-induced destruction of cytochrome P-450. Drug Metab Dispos. 1973 Jan-Feb;1(1):267–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Matteis F., Gibbs A. Stimulation of liver 5-aminolaevulinate synthetase by drugs and its relevance to drug-induced accumulation of cytochrome P-450. Studies with phenylbutazone and 3,5-diethoxycarbonyl-1,4-dihydrocollidine. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;126(5):1149–1160. doi: 10.1042/bj1261149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Matteis F. Loss of haem in rat liver caused by the porphyrogenic agent 2-allyl-2-isopropylacetamide. Biochem J. 1971 Oct;124(4):767–777. doi: 10.1042/bj1240767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehlinger P. J., Schimke R. T. Effects of phenobarbital, 3-methylcholanthrene, and hematin on the synthesis of protein components of rat liver microsomal membranes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1257–1264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Druyan R., Kelly A. The effect of exogenous -aminolaevulinate on rat liver haem and cytochromes. Biochem J. 1972 Oct;129(5):1095–1099. doi: 10.1042/bj1291095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell G. C., Correia M. A. Structural and functional reconstitution of hepatic cytochrome P-450 in vivo. Reversal of allylisopropylacetamide-mediated destruction of the hemoprotein by exogenous heme. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10128–10133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granick S., Sinclair P., Sassa S., Grieninger G. Effects by heme, insulin, and serum albumin on heme and protein synthesis in chick embryo liver cells cultured in a chemically defined medium, and a spectrofluorometric assay for porphyrin composition. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 25;250(24):9215–9225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granick S. The induction in vitro of the synthesis of delta-aminolevulinic acid synthetase in chemical porphyria: a response to certain drugs, sex hormones, and foreign chemicals. J Biol Chem. 1966 Mar 25;241(6):1359–1375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayzel A. I., Hörchner P., London I. M. The stimulation of globin synthesis by heme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Mar;55(3):650–655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.3.650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenlee W. F., Poland A. An improved assay of 7-ethoxycoumarin O-deethylase activity: induction of hepatic enzyme activity in C57BL/6J and DBA/2J mice by phenobarbital, 3-methylcholanthrene and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1978 Jun;205(3):596–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzelian P. S., Bissell D. M. Effect of cobalt on synthesis of heme and cytochrome P-450 in the liver. Studies of adult rat hepatocytes in primary monolayer culture and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4421–4427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. S., Jones O. T. The structural organization of haem synthesis in rat liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1969 Jul;113(3):507–514. doi: 10.1042/bj1130507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupa V., Creighton J. C., Freeman M., Marks G. S. Drug-induced porphyrin biosynthesis--XII. Levels of cytochrome P-450 in chick embryo liver following administration of allylisopropylacetamide and propylisopropylacetamide. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1974 Aug;52(4):891–895. doi: 10.1139/y74-114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin W., Jacobson M., Sernatinger E., Kuntzman R. Breakdown of cytochrome P-450 heme by secobarbital and other allyl-containing barbiturates. Drug Metab Dispos. 1973 Jan-Feb;1(1):275–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin W., Kuntzman R. Biphasic decrease of radioactive hemoprotein from liver microsomal CO-binding particles. Effect of 3-methylcholanthrene. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 10;244(13):3671–3676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim L. K., Srivastava G., Brooker J. D., May B. K., Elliott W. H. Evidence that in chick embryos destruction of hepatic microsomal cytochrome P-450 haem is a general mechanism of induction of delta-aminolaevulinate synthase by porphyria-causing drugs. Biochem J. 1980 Sep 15;190(3):519–526. doi: 10.1042/bj1900519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maines M. D., Kappas A. The degradative effects of porphyrins and heme compounds on components of the microsomal mixed function oxidase system. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 25;250(6):2363–2369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marver H. S., Schmid R., Schützel H. Heme and methemoglobin: naturally occurring repressors of microsomal cytochrome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Dec 30;33(6):969–974. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90408-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier P. J., Spycher M. A., Meyer U. A. Isolation of a subfraction of rough endoplasmic reticulum closely associated with mitochondria. Evidence for its role in cytochrome P450 synthesis. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Feb;111(2):479–483. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90197-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer U. A., Marver H. S. Chemically induced porphyria: increased microsomal heme turnover after treatment with allylisopropylacetamide. Science. 1971 Jan 8;171(3966):64–66. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3966.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negishi M., Kreibich G. Coordinated polypeptide synthesis and insertion of protoheme in cytochrome P-450 during development of endoplasmic reticulum membranes. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 10;253(13):4791–4797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz de Montellano P. R., Yost G. S., Mico B. A., Dinizo S. E., Correia M. A., Kumbara H. Destruction of cytochrome P-450 by 2-isopropyl-4-pentenamide and methyl 2-isopropyl-4-pentenoate: mass spectrometric characterization of prosthetic heme adducts and nonparticipation of epoxide metabolites. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Oct 15;197(2):524–533. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90276-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper W. N., Tephly T. R. The reversal of experimental porphyria and the prevention of induction of hepatic mixed-function oxidase by acetate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Sep;164(1):351–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajamanickam C., Amrutavalli J., Rao M. R., Padmanaban G. Effect of hexachlorobenzene on haem synthesis. Biochem J. 1972 Sep;129(2):381–387. doi: 10.1042/bj1290381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajamanickam C., Rao M. R., Padmanaban G. On the sequence of reactions leading to cytochrome P-450 synthesis-effect of drugs. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 25;250(6):2305–2310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao M. R., Padmanaban G. Biochemical effects of the porphyrinogenic drug allylisopropylacetamide. A comparative study with phenobarbital. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;134(4):859–868. doi: 10.1042/bj1340859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassa S., Kappas A. Induction of aminolevulinate synthase and porphyrins in cultured liver cells maintained in chemically defined medium. Permissive effects of hormones on induction process. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 10;252(7):2428–2436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava G., Brooker J. D., May B. K., Elliott W. H. Haem control in experimental porphyria. The effect of haemin on the induction of delta-aminolaevulinate synthase in isolated chick-embryo liver cells. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 15;188(3):781–788. doi: 10.1042/bj1880781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strand L. J., Manning J., Marver H. S. The induction of -aminolevulinic acid synthetase in cultured liver cells. The effects of end product and inhibitors of heme synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2820–2827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strand L. J., Swanson A. L., Manning J., Branch S., Marver H. S. Radiochemical microassay of delta-aminolevulinic acid synthetase in hepatic and erythroid tissues. Anal Biochem. 1972 Jun;47(2):457–470. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90139-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonita Y., Oashi A., Kikuchi G. Induction of delta-aminolevulinate synthetase in organ culture of chick embryo liver by allylisopropylacetamide and 3,5-dicarbethoxy-1,4-dihydrocollidine. J Biochem. 1974 May;75(5):1007–1007. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell D. L., Marks G. S. Drug-induced porphyrin biosynthesis. V. Effect of protohemin on the transcriptional and post-transcriptional phases of -aminolevulinic acid synthetase induction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1972 Aug 1;21(15):2077–2093. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(72)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoda B., Schacter B. A., Israels L. G. Delta-aminolevulinic acid synthetase assay in chicken liver homogenates and particulate fractions. Anal Biochem. 1975 May 26;66(1):221–233. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90740-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


