Abstract
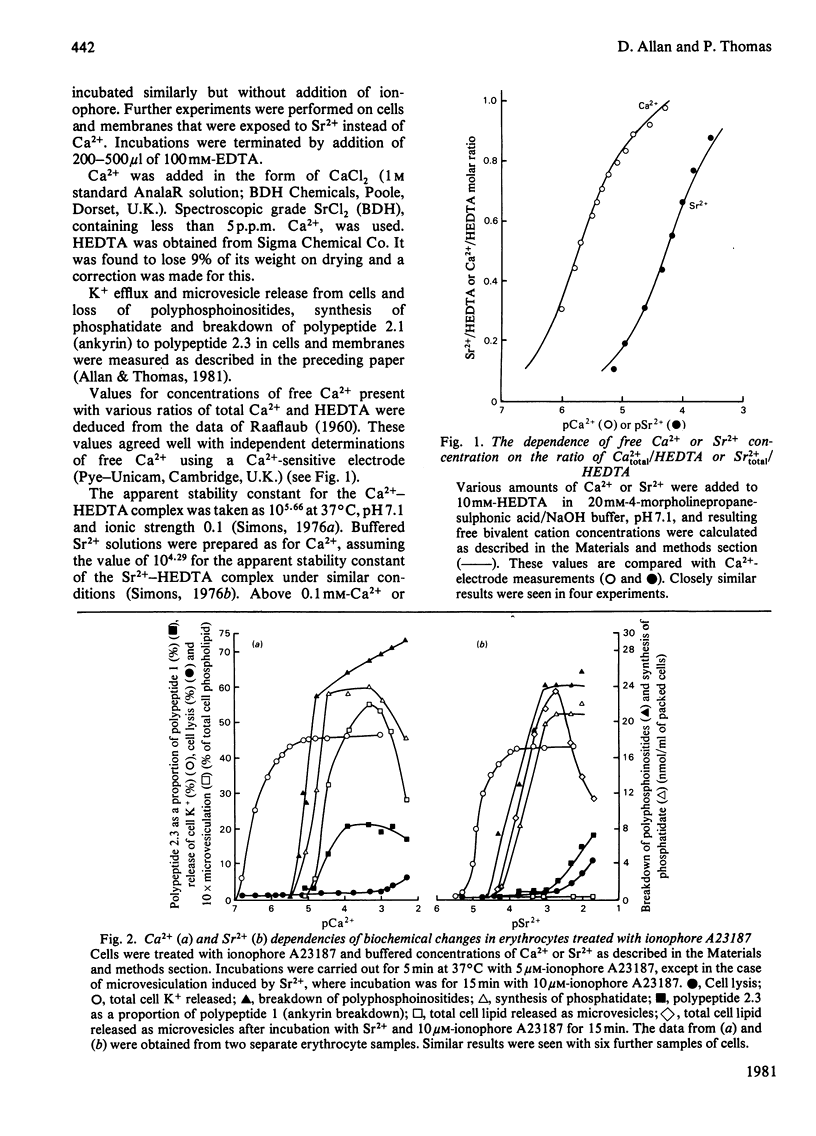
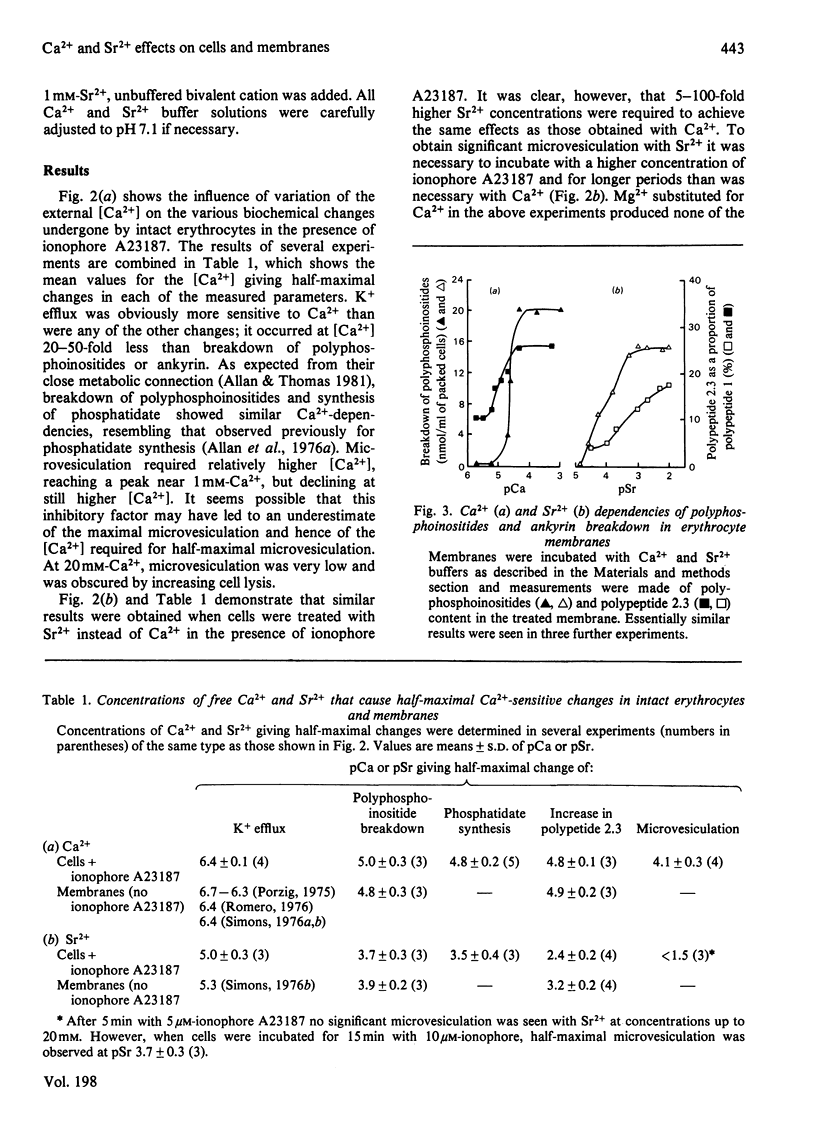
1. The Ca2+-dependency of K+ efflux, microvesiculation and breakdown of polyphosphoinositides and of ankyrin have been measured in intact human erythrocytes exposed to ionophore A23187 and HEDTA [N'-(2-hydroxyethyl)ethylenediamine NNN'-triacetate]-Ca2+ buffers. Half-maximal responses were observed at pCa values of 6.4, 4.1, 5.0 and 4.8 respectively. 2. The Ca2+ dependencies of K+ efflux and breakdown of polyphosphoinositides and ankyrin measured in erythrocyte ghosts without addition of ionophore showed almost identical values with those seen in whole cells treated with ionophore. 3. We conclude that ionophore A23187 is able to cause rapid equilibration of extracellular and intracellular [Ca2+] in intact cells and that in the presence of a suitable Ca2+ buffer, ionophore A23187 can be used to precisely fix the intracellular concentration of Ca2+ in erythrocytes. 4. The relatively high concentration of Ca2+ required to produce microvesiculation in intact cells may indicate that microvesiculation could be at least partly dependent on a direct interaction of Ca2+ with phospholipid. 5. Results obtained with Sr2+ paralleled those with Ca2+, although higher Sr2+ concentrations were required to achieve the same effects as Ca2+. Mg2+ produced none of the changes seen with Ca2+ or Sr2+.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson M. B., Colacicco G., Curci R., Rapport M. M. Ionic properties of acidic lipids. Phosphatidylinositol. Biochemistry. 1968 May;7(5):1692–1698. doi: 10.1021/bi00845a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan D., Billah M. M., Finean J. B., Michell R. H. Release of diacylglycerol-enriched vesicles from erythrocytes with increased intracellular (Ca2+). Nature. 1976 May 6;261(5555):58–60. doi: 10.1038/261058a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan D., Michell R. H. Production of 1,2-diacylglycerol in human erythrocyte membranes exposed to low concentrations of calcium ions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 14;455(3):824–830. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan D., Thomas P. Ca2+-induced biochemical changes in human erythrocytes and their relation to microvesiculation. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 15;198(3):433–440. doi: 10.1042/bj1980433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan D., Thomas P., Limbrick A. R. The isolation and characterization of 60 nm vesicles ('nanovesicles') produced during ionophore A23187-induced budding of human erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 15;188(3):881–887. doi: 10.1042/bj1880881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan D., Watts R., Michell R. H. Production of 1,2-diacylglycerol and phosphatidate in human erythrocytes treated with calcium ions and ionophore A23187. Biochem J. 1976 May 15;156(2):225–232. doi: 10.1042/bj1560225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton P. G. The influence of surface charge density of phosphatides on the binding of some cations. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 25;243(14):3884–3890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullis P. R., Hope M. J. Effects of fusogenic agent on membrane structure of erythrocyte ghosts and the mechanism of membrane fusion. Nature. 1978 Feb 16;271(5646):672–674. doi: 10.1038/271672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira H. G., Lew V. L. Use of ionophore A23187 to measure cytoplasmic Ca buffering and activation of the Ca pump by internal Ca. Nature. 1976 Jan 1;259(5538):47–49. doi: 10.1038/259047a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson H. S., Fullington J. G. Stabilities of metal complexes of phospholipids: Ca(II), Mg(II), and Ni(II) complexes of phosphatidylserine and triphosphoinositide. Biochemistry. 1965 Aug;4(8):1599–1605. doi: 10.1021/bi00884a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mombers C., de Gier J., Demel R. A., van Deenen L. L. Spectrin-phospholipid interaction. A monolayer study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec 2;603(1):52–62. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90390-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D., Poste G., Schaeffer B. E., Vail W. J. Membrane fusion and molecular segregation in phospholipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 30;352(1):10–28. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D., Vail W. J., Pangborn W. A., Poste G. Studies on membrane fusion. II. Induction of fusion in pure phospholipid membranes by calcium ions and other divalent metals. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 5;448(2):265–283. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90241-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porzig H. Comparative study of the effects of propranolol and tetracaine on cation movements in resealed human red cell ghosts. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(1):27–49. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAAFLAUB J. Applications of metal buffers and metal indicators in biochemistry. Methods Biochem Anal. 1956;3:301–325. doi: 10.1002/9780470110195.ch10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichstein E., Rothstein A. Effects of quinine on Ca++-induced K+ efflux from human red blood cells. J Membr Biol. 1981 Mar 15;59(1):57–63. doi: 10.1007/BF01870821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero P. J. Role of membrane-bound Ca in ghost permeability to Na and K. J Membr Biol. 1976 Nov 29;29(4):329–343. doi: 10.1007/BF01868969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons T. J. Calcium-dependent potassium exchange in human red cell ghosts. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;256(1):227–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons T. J. The preparation of human red cell ghosts containing calcium buffers. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;256(1):209–225. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


