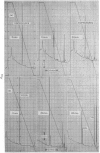
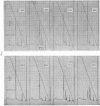
Abstract
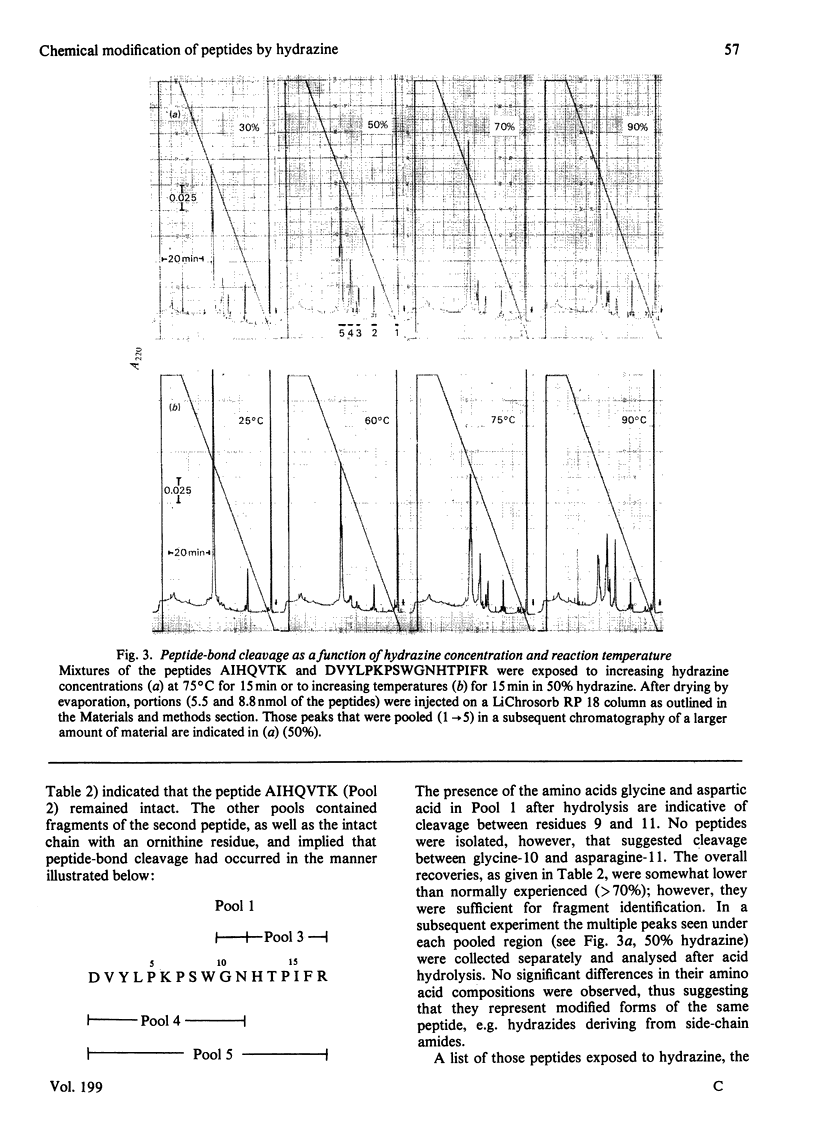
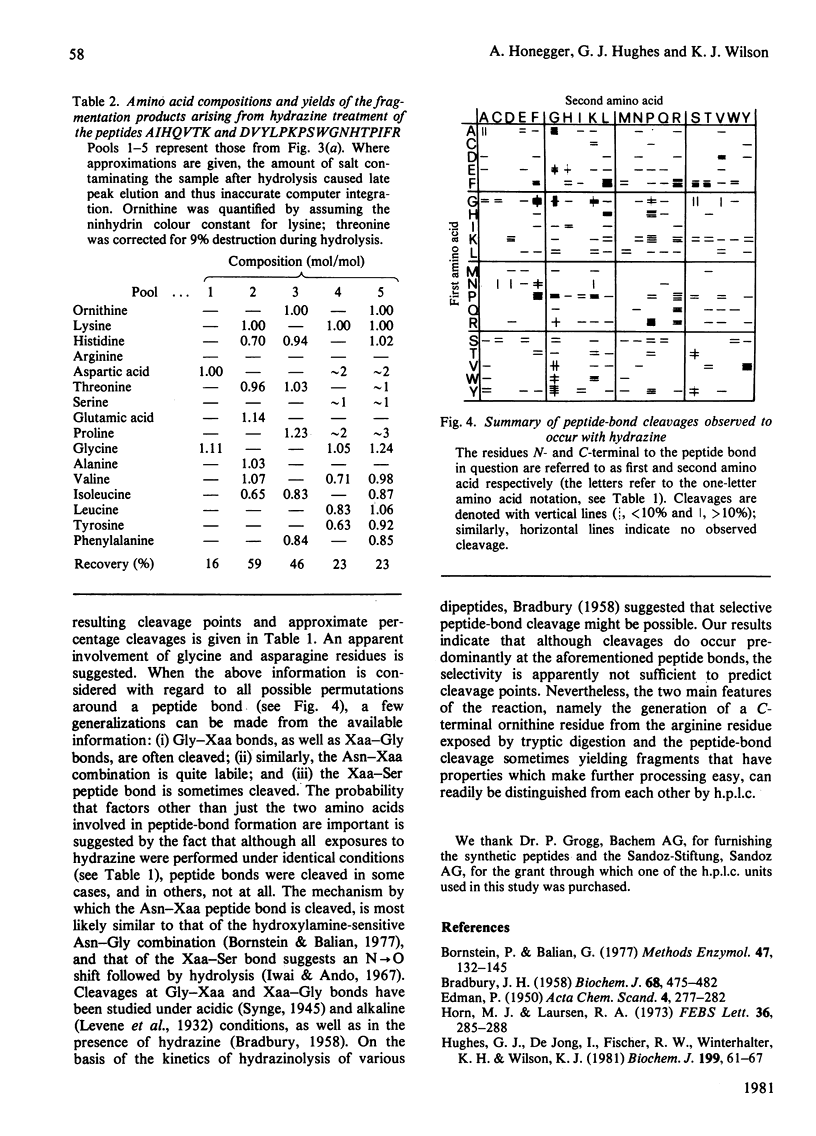
High pressure ('performance') liquid chromatography on reverse-phase supports has been used to characterize the products arising from the hydrazine treatment of peptides. In addition to converting arginine residues into ornithine, the reaction was found to cleave predominately Gly-Xaa, Xaa-Gly, Asn-Xaa and Xaa-Ser peptide bonds. Peptide-bond cleavage and deguanidation was studied as a function of time of exposure to hydrazine, hydrazine concentration and temperature. The convenience of this method of chromatography for the rapid low-cost separation and isolation of peptides, as well as their reaction products, is illustrated at the level of material required for solid-phase microsequencing.
Full text
PDF

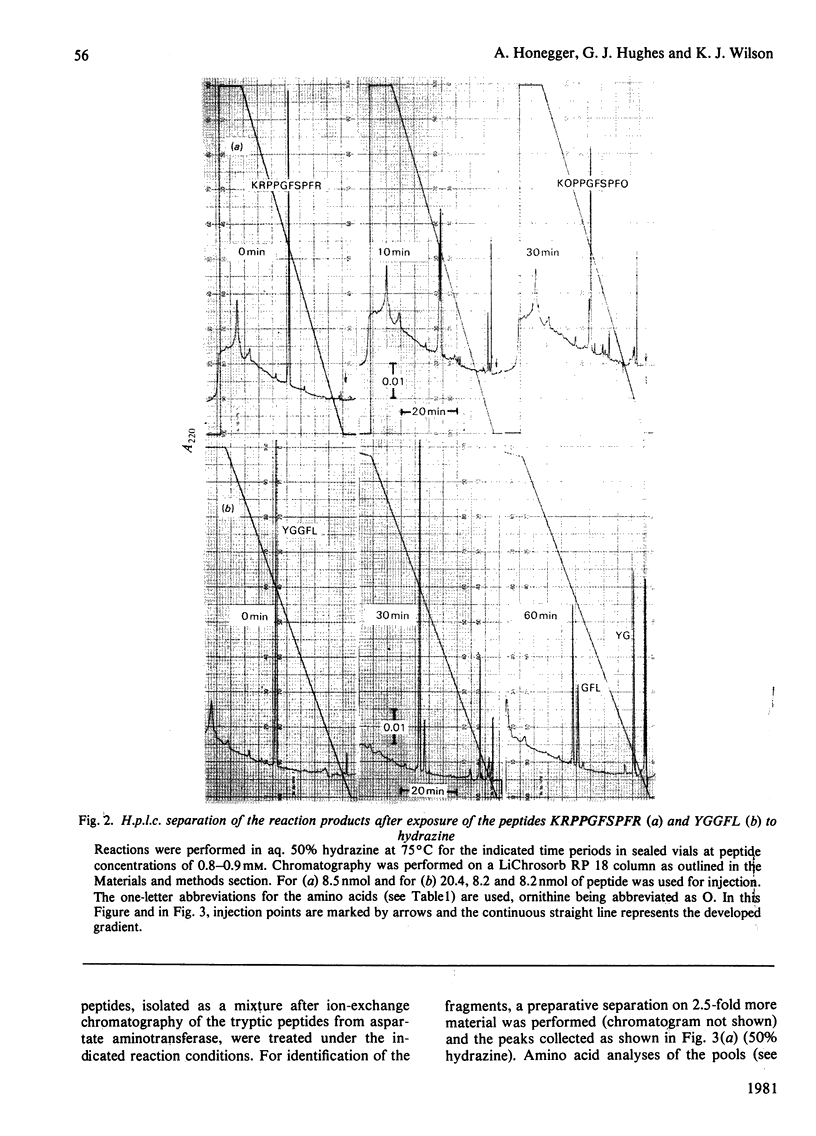

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRADBURY J. H. The kinetics of hydrazinolysis of simple peptides in anhydrous hydrazine. Biochem J. 1958 Mar;68(3):475–482. doi: 10.1042/bj0680475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., Balian G. Cleavage at Asn-Gly bonds with hydroxylamine. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:132–145. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn M. J., Laursen R. A. Solid-phase edman degradation: attachment of carboxyl-terminal homoserine peptides to an insoluble resin. FEBS Lett. 1973 Nov 1;36(3):285–288. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80392-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes G. J., de Jong C., Fischer R. W., Winterhalter K. H., Wilson K. J. Modification by simetryn sulphoxide of a specific thiol group in rat haemoglobin. Biochem J. 1981 Oct 1;199(1):61–67. doi: 10.1042/bj1990061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunziker P. E., Hughes G. J., Wilson K. J. Peptide fragmentation suitable for solid-phase microsequencing. Use of N-bromosuccinimide and BNPS-skatole (3-bromo-3-methyl-2-[(2-nitrophenyl)thio]-3H-indole). Biochem J. 1980 May 1;187(2):515–519. doi: 10.1042/bj1870515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laursen R. A., Horn M. J., Bonner A. G. Solid-phase Edman degradation. The use of p-phenyl diisothiocyanate to attach lysine- and arginine-containing peptides to insoluble resins. FEBS Lett. 1972 Mar;21(1):67–70. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80165-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laursen R. A., Machleidt W. Solid-phase methods in protein sequence analysis. Methods Biochem Anal. 1980;26:201–284. doi: 10.1002/9780470110461.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laursen R. A. Solid-phase Edman degradation. An automatic peptide sequencer. Eur J Biochem. 1971 May 11;20(1):89–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01366.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiltz E., Reinbolt J. Determination of the complete amino-acid sequence of protein S4 from Escherichia coli ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):467–481. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02253.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Synge R. L. The kinetics of low temperature acid hydrolysis of gramicidin and of some related dipeptides. Biochem J. 1945;39(4):351–355. doi: 10.1042/bj0390351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachter E., Machleidt W., Hofner H., Otto J. Aminopropyl glass and its p-phenylene diisothiocyanate derivative, a new support in solid-phase Edman degradation of peptides and proteins. FEBS Lett. 1973 Sep 1;35(1):97–102. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. J., Honegger A., Hughes G. J. Comparison of buffers and detection systems for high-pressure liquid chromatography of peptide mixtures. Biochem J. 1981 Oct 1;199(1):43–51. doi: 10.1042/bj1990043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]