Abstract
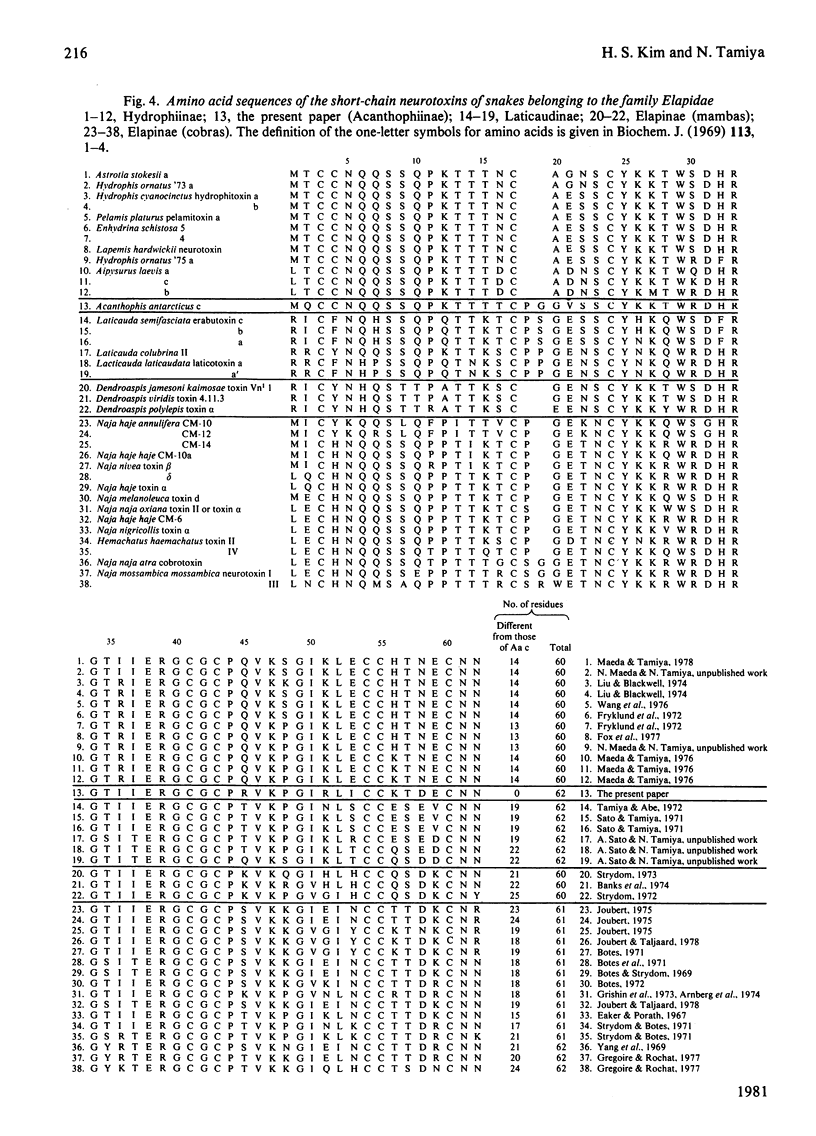
The amino acid sequence of a short-chain neurotoxin Acanthophis antarcticus c (toxin Aa c) from the venom of an Australian elapid snake, the common death adder (Acanthophis antarcticus, subfamily Acanthophiinae) was elucidated. Toxin Aa c is composed of 62 amino acid residues, including eight half-cystine residues and a cysteine residue. The amino acid sequence of toxin Aa c is homologous with those of other short-chain neurotoxins found in snakes of the family Elapidae, especially with those from snakes of the subfamily Hydrophiinae. The single cysteine residue was located in position 4. Toxin Aa c has a lethal dose (LD50) of 0.08 micrograms/g body weight of mouse on intramuscular injection.
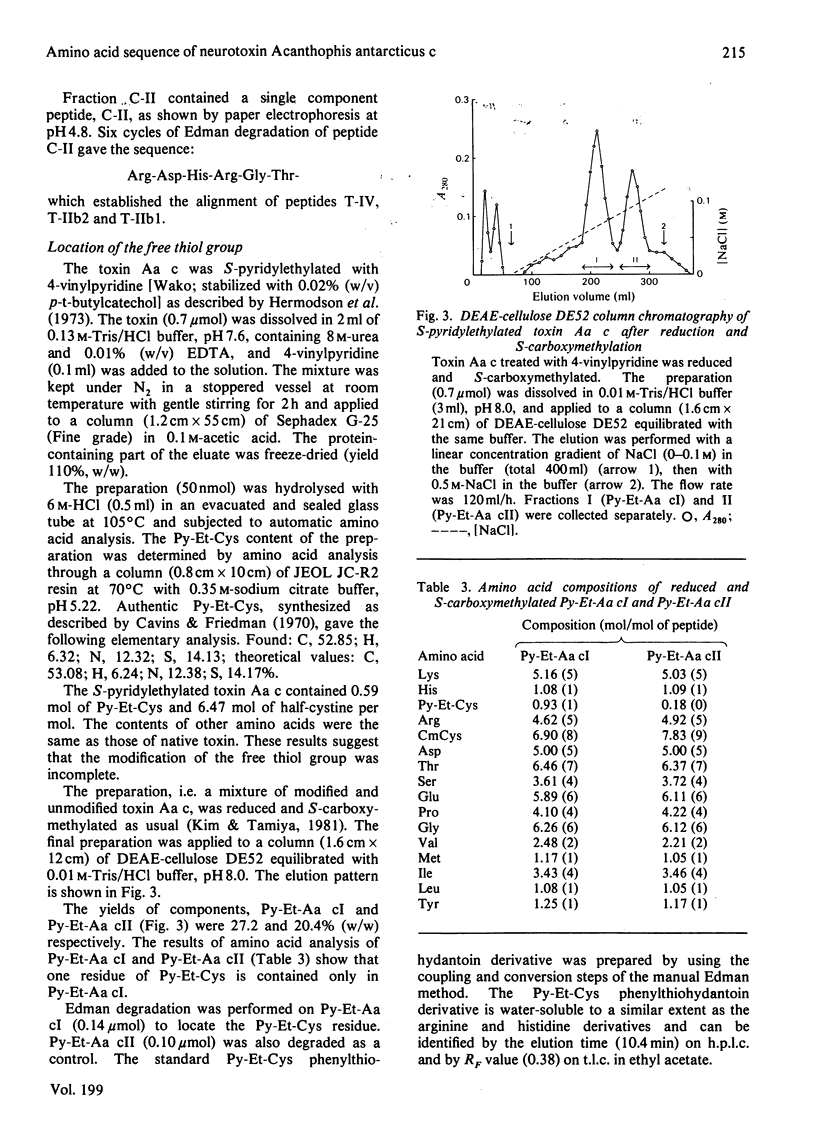
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnberg H., Eaker D., Fryklund L., Karlsson E. Amino acid sequence of oxiana alpha, the main neurotoxin of the venom of Naja naja oxiana. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 8;359(2):222–232. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90217-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks B. E., Miledi R., Shipolini R. A. The primary sequences and neuromuscular effects of three neurotoxic polypeptides from the venom of Dendroaspis viridis. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jun 15;45(2):457–468. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03570.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botes D. P. Snake venom toxins. The amino acid sequences of toxins b and d from Naja melanoleuca venom. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2866–2871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botes D. P., Strydom D. J. A neurotoxin, toxin alpha, from Egyptian cobra (Naja haje haje) venom. I. Purification, properties, and complete amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 10;244(15):4147–4157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botes D. P., Strydom D. J., Anderson C. G., Christensen P. A. Snake venom toxins. Purification and properties of three toxins from Naja nivea (Linnaeus) (Cape cobra) venom and the amino acid sequence of toxin delta. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3132–3139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavins J. F., Friedman M. An internal standard for amino acid analyses: S-beta-(4-pyridylethyl)-L-cysteine. Anal Biochem. 1970 Jun;35(2):489–493. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90211-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. W., Elzinga M., Tu A. T. Amino acid sequence of a snake neurotoxin from the venom of Lapemis hardwickii and the detection of a sulfhydryl group by laser Raman spectroscopy. FEBS Lett. 1977 Aug 1;80(1):217–220. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80443-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryklund L., Eaker D., Karlsson E. Amino acid sequences of the two principal neurotoxins of Enhydrina schistosa venom. Biochemistry. 1972 Nov 21;11(24):4633–4640. doi: 10.1021/bi00774a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoire J., Rochat H. Amino acid sequences of neurotoxins I and III of the elapidae snake Naja mossambica massambica. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Oct 17;80(1):283–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grishin E. V., Sukhikh A. P., Lukyanchuk N. N., Slobodyan L. N., Lipkin V. M., Ovchinnikov YuA, Sorokin V. M. Amino acid sequence of neurotoxin II from Naja naja oxiana venom. FEBS Lett. 1973 Oct 1;36(1):77–78. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80340-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki F., Tamiya N., Miyazawa T. Molecular conformation and function of erabutoxins as studied by nuclear magnetic resonance. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Aug;109(1):129–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04777.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joubert F., Taljaard N. Purification, some properties and the primary structures of three reduced and S-carboxymethylated toxins (CM-5, CM-6 and CM-10a) from Naje haje haje (Egyptian cobra) venom. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 20;537(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90597-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. S., Tamiya N. Isolation, properties and amino acid sequence of a long-chain neurotoxin, Acanthophis antarcticus b, from the venom of an Australian snake (the common death adder, Acanthophis antarcticus). Biochem J. 1981 Mar 1;193(3):899–906. doi: 10.1042/bj1930899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimball M. R., Sato A., Richardson J. S., Rosen L. S., Low B. W. Molecular conformation of erabutoxin b; atomic coordinates at 2.5 A resolution. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jun 13;88(3):950–959. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91500-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kortt A. A., Liu T. Y. On the mechanism of action of streptococcal proteinase. I. Active-site titration. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 16;12(2):320–327. doi: 10.1021/bi00726a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. S., Blackwell R. Q. Hydrophitoxin b from Hydrophis cyanocinctus venom. Toxicon. 1974 Oct;12(5):543–546. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(74)90047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. S., Wang C. L., Blackwell R. Q. Isolation and partial characterization of pelamitoxin A from Pelamis platurus venom. Toxicon. 1975 Feb;13(1):31–36. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(75)90155-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low B. W., Preston H. S., Sato A., Rosen L. S., Searl J. E., Rudko A. D., Richardson J. S. Three dimensional structure of erabutoxin b neurotoxic protein: inhibitor of acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):2991–2994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.2991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Tamiya N. Isolation, properties and amino acid sequences of three neurotoxins from the venom of a sea snake, Aipysurus laevis. Biochem J. 1976 Jan 1;153(1):79–87. doi: 10.1042/bj1530079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Tamiya N. Three neurotoxins from the venom of a sea snake Astrotia stokesii, including two long-chain neurotoxic proteins with amidated C-termini. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 1;175(2):507–517. doi: 10.1042/bj1750507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omichi K., Nagura N., Ikenaka T. The reactive site of Streptomyces subtilisin inhibitor. J Biochem. 1980 Feb;87(2):483–489. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato S., Tamiya N. The amino acid sequences of erabutoxins, neurotoxic proteins of sea-snake (Laticauda semifasciata) venom. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):453–461. doi: 10.1042/bj1220453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strydom A. J., Botes D. P. Snake venom toxins. Purification, properties, and complete amino acid sequence of two toxins from Ringhals (Hemachatus haemachatus) venom. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1341–1349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strydom A. J. Snake venom toxins. The amino acid sequences of two toxins from Dendroaspis jamesoni kaimosae (Jameson's mamba) venom. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 6;328(2):491–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strydom D. J. Snake venom toxins. The amino acid sequences of two toxins from Dendroaspis polylepis polylepis (black mamba) venom. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):4029–4042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamiya N., Abe H. The isolation, properties and amino acid sequence of erabutoxin c, a minor neurotoxic component of the venom of a sea snake Katicauda semifasciata. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(2):547–555. doi: 10.1042/bj1300547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsernoglou D., Petsko G. A. The crystal structure of a post-synaptic neurotoxin from sea snake at A resolution. FEBS Lett. 1976 Sep 15;68(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80390-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsernoglou D., Petsko G. A. Three-dimensional structure of neurotoxin a from venom of the Philippines sea snake. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):971–974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. C., Yang H. J., Huang J. S. The amino acid sequence of cobrotoxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Aug 12;188(1):65–77. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


