Abstract
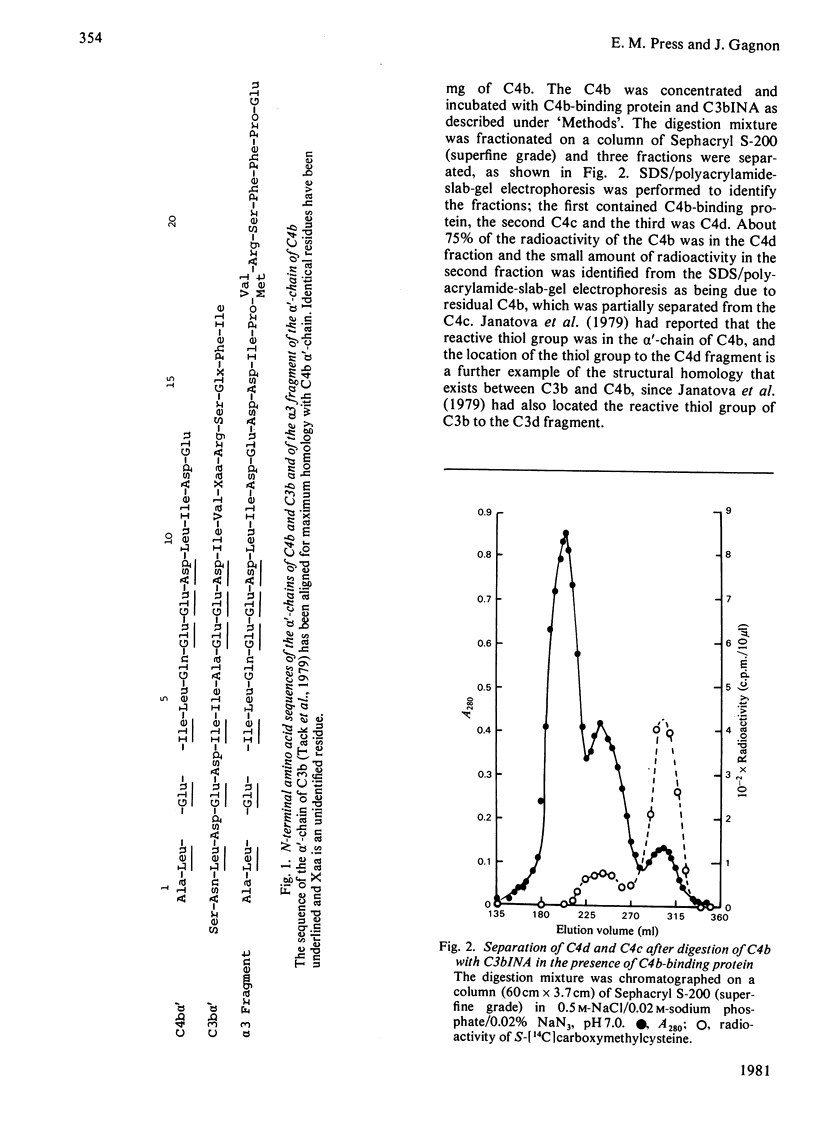
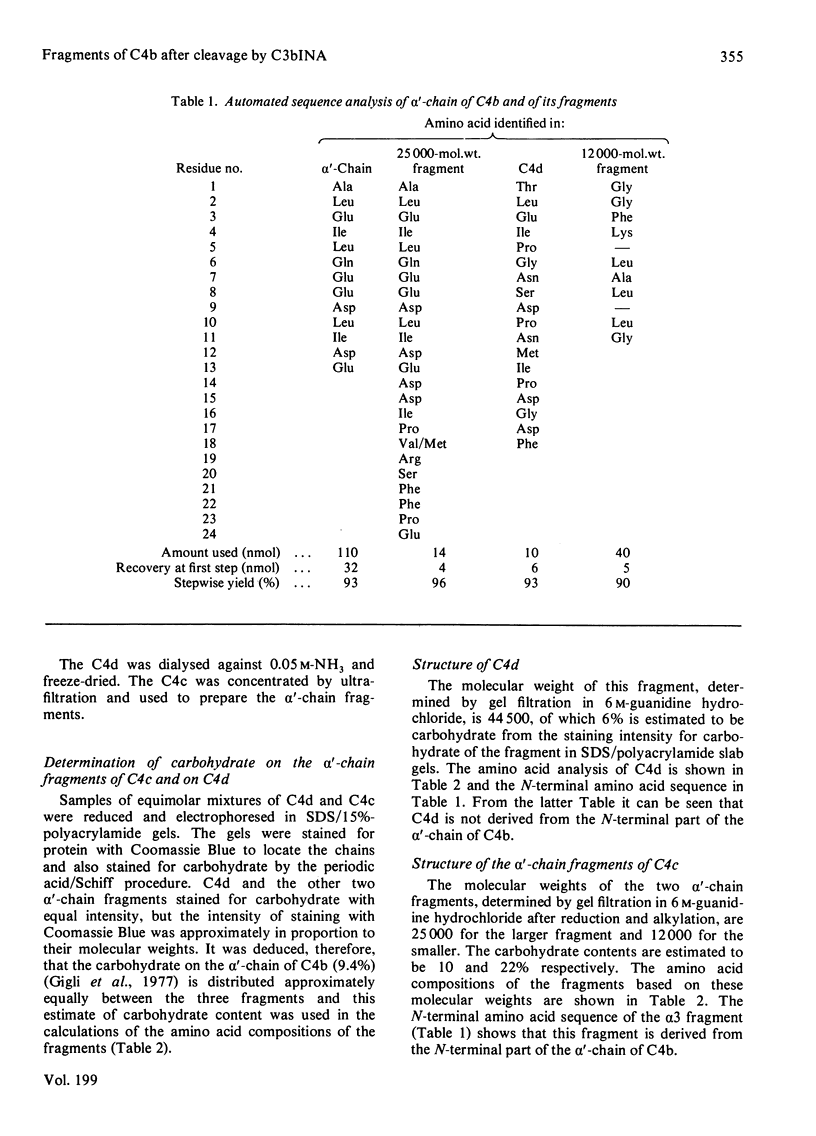
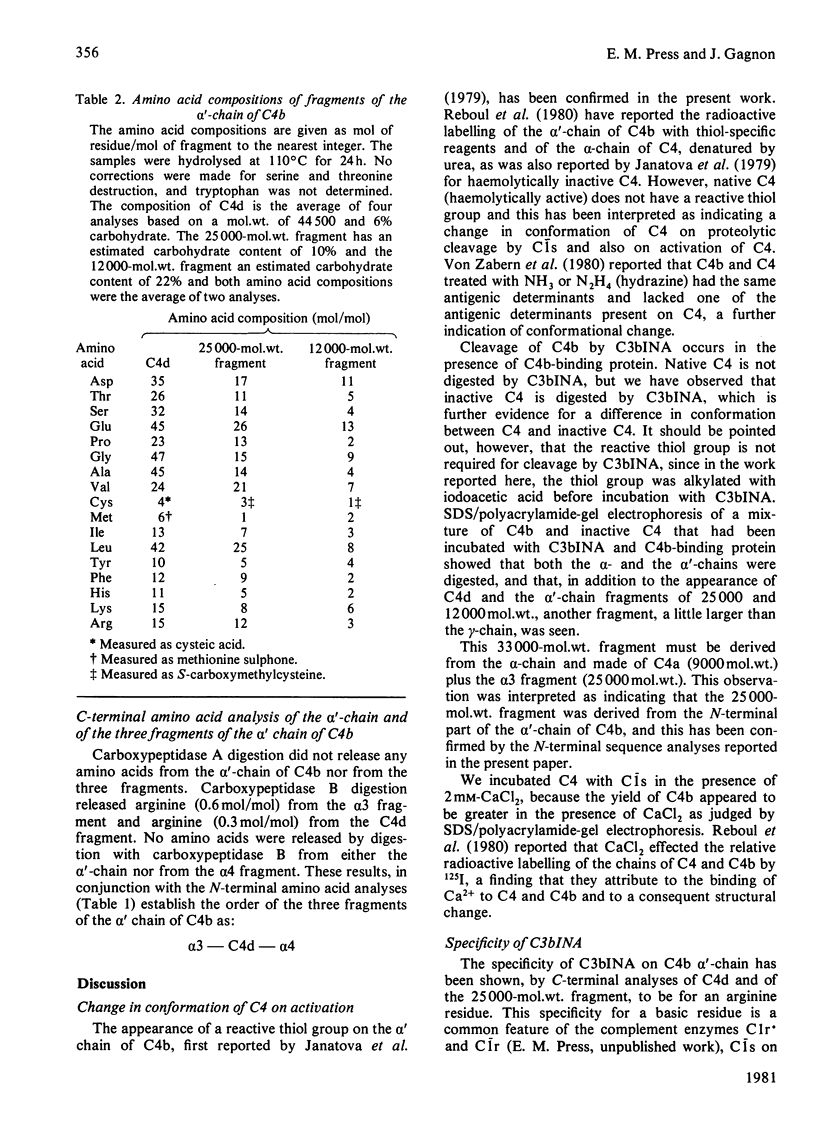
1. One of the activation products of C4, C4b, was prepared, and the reactive thiol group on the alpha'-chain was radioactively labelled with iodo[2-14C]acetic acid. The alpha'-chain was isolated and the N-terminal amino acid sequence of the first 13 residues was determined. 2. C4b was cleaved by C3bINA in the presence of C4b-binding protein and C4d and C4c isolated. The radioactive label and therefore the reactive thiol group were located to C4d. 3. C4c was reduced and alkylated and the two alpha'-chain fragments of C4c were separated. 3. The molecular weights, amino acid analyses and carbohydrate content of the three alpha'-chain fragments were determined. C4d has a mol.wt. of 44500 and a carbohydrate content of 6%. The two alpha'-chain fragments of C4c have mol.wts. of 25000 (alpha 3) and 12000 (alpha 4) and carbohydrate contents of 10 and 22% respectively. 4. The N-terminal amino acid sequences of C4d, the alpha 3 and the alpha 4 fragments were determined for 18, 24 and 11 residues respectively and, by comparison with the N-terminal sequence of the C4b alpha'-chain, the 25000-mol.wt. fragment (alpha 3) was shown to be derived from the N-terminal part of the alpha'-chain. 5. C-Terminal analyses were done on the alpha'-chain and its three fragments. Arginine was found to be the C-terminal residue of C4d and of the alpha 3 fragment. The C-terminal residue of the alpha'-chain and of the alpha 4 fragment could not be identified. The order of the three fragments of the alpha'-chain is therefore: alpha 3(25000)--C4d(44500)--alpha 4(12000). The specificity of C3bINA is for an Arg--Xaa peptide bond.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campbell R. D., Dodds A. W., Porter R. R. The binding of human complement component C4 to antibody-antigen aggregates. Biochem J. 1980 Jul 1;189(1):67–80. doi: 10.1042/bj1890067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie D. L., Gagnon J., Porter R. R. Partial sequence of human complement component factor B: novel type of serine protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4923–4927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossley L. G., Porter R. R. Purification of the human complement control protein C3b inactivator. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 1;191(1):173–182. doi: 10.1042/bj1910173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodds A. W., Sim R. B., Porter R. R., Kerr M. A. Activation of the first component of human complement (C1) by antibody-antigen aggregates. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 1;175(2):383–390. doi: 10.1042/bj1750383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez H. N., Hugli T. E. Primary structural analysis of the polypeptide portion of human C5a anaphylatoxin. Polypeptide sequence determination and assignment of the oligosaccharide attachment site in C5a. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6955–6964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Gigli I., Nussenzweig V. Human C4-binding protein. II. Role in proteolysis of C4b by C3b-inactivator. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):1044–1051. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Porter R. R., Sim R. B. The unactivated form of the first component of human complement, C1. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 1;157(3):541–548. doi: 10.1042/bj1570541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., von Zabern I., Porter R. R. The isolation and structure of C4, the fourth component of human complement. Biochem J. 1977 Sep 1;165(3):439–446. doi: 10.1042/bj1650439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goers J. W., Porter R. R. The assembly of early components of complement on antibody-antigen aggregates and on antibody-coated erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 1;175(2):675–684. doi: 10.1042/bj1750675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski J. P., Hugli T. E., Müller-Eberhard H. J. C4a: the third anaphylatoxin of the human complement system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5299–5302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRS C. H. The oxidation of ribonuclease with performic acid. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):611–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugli T. E. Human anaphylatoxin (C3a) from the third component of complement. Primary structure. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 10;250(21):8293–8301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. M., Gagnon J., Reid K. B. Factor D of the alternative pathway of human complement. Purification, alignment and N-terminal amino acid sequences of the major cyanogen bromide fragments, and localization of the serine residue at the active site. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 1;187(3):863–874. doi: 10.1042/bj1870863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapitany R. A., Zebrowski E. J. A high resolution PAS stain for polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr M. A. Limited proteolysis of complement components C2 and factor B. Structural analogy and limited sequence homology. Biochem J. 1979 Dec 1;183(3):615–622. doi: 10.1042/bj1830615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Fearon D. T., Levine R. P. Action of the C3b-inactivator on the cell-bound C3b. J Immunol. 1979 Mar;122(3):759–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Levine R. P. Interaction between the third complement protein and cell surface macromolecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2701–2705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Lichtenberg N. A., Levine R. P. Evidence for an ester linkage between the labile binding site of C3b and receptive surfaces. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1388–1394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa S., Ichihara C., Stroud R. M. Cleavage of C4b by C3b inactivator: production of a nicked form of C4b, C4b', as an intermediate cleavage product of C4b by C3b inactivator. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):578–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K., Schreiber R. D., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Human complement C3b inactivator: isolation, characterization, and demonstration of an absolute requirement for the serum protein beta1H for cleavage of C3b and C4b in solution. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):257–270. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reboul A., Thielens N., Villiers M. B., Colomb M. G. Structural changes in C4 produced by cleavage with C1-s. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jun 16;115(1):118–122. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80739-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharfstein J., Ferreira A., Gigli I., Nussenzweig V. Human C4-binding protein. I. Isolation and characterization. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):207–222. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim R. B., Porter R. R. Isolation and comparison of the proenzyme and activated forms of the human serum complement subcomponents C1r and C1s. Biochem Soc Trans. 1976;4(1):127–129. doi: 10.1042/bst0040127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack B. F., Harrison R. A., Janatova J., Thomas M. L., Prahl J. W. Evidence for presence of an internal thiolester bond in third component of human complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5764–5768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack B. F., Morris S. C., Prahl J. W. Third component of human complement: structural analysis of the polypeptide chains of C3 and C3b. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 17;18(8):1497–1503. doi: 10.1021/bi00575a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


