Abstract
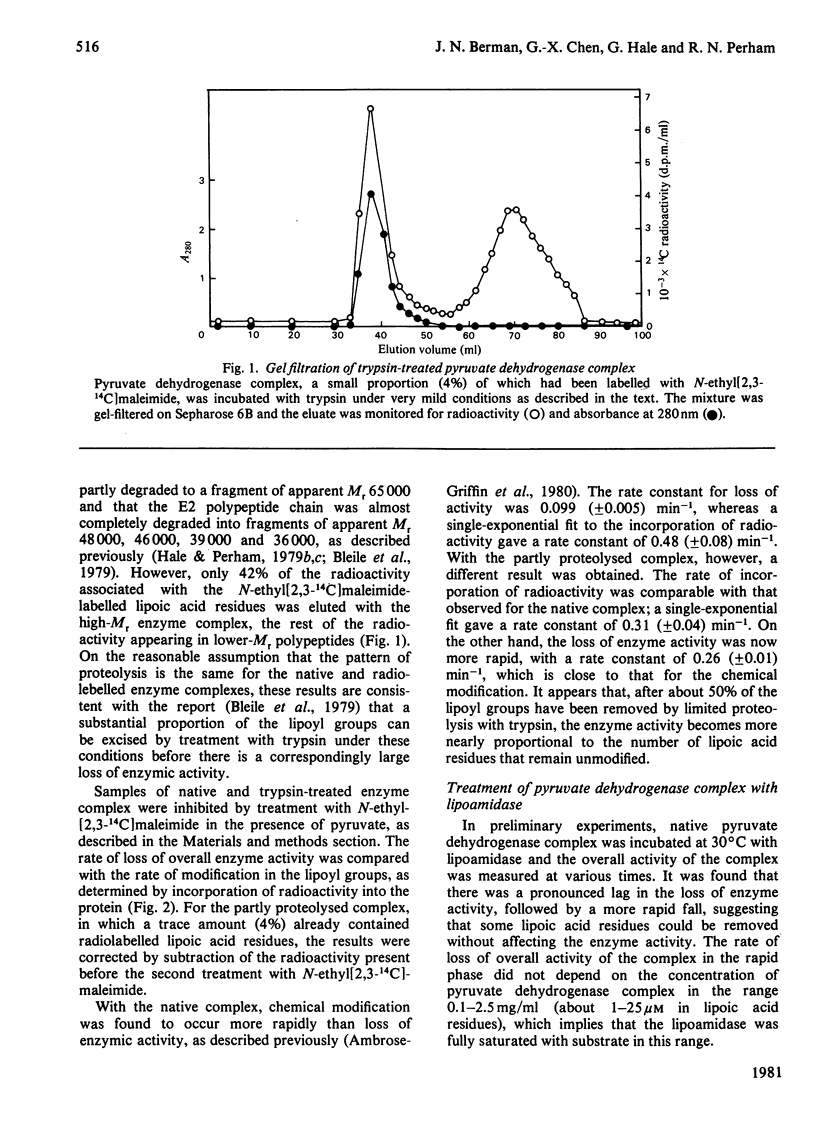
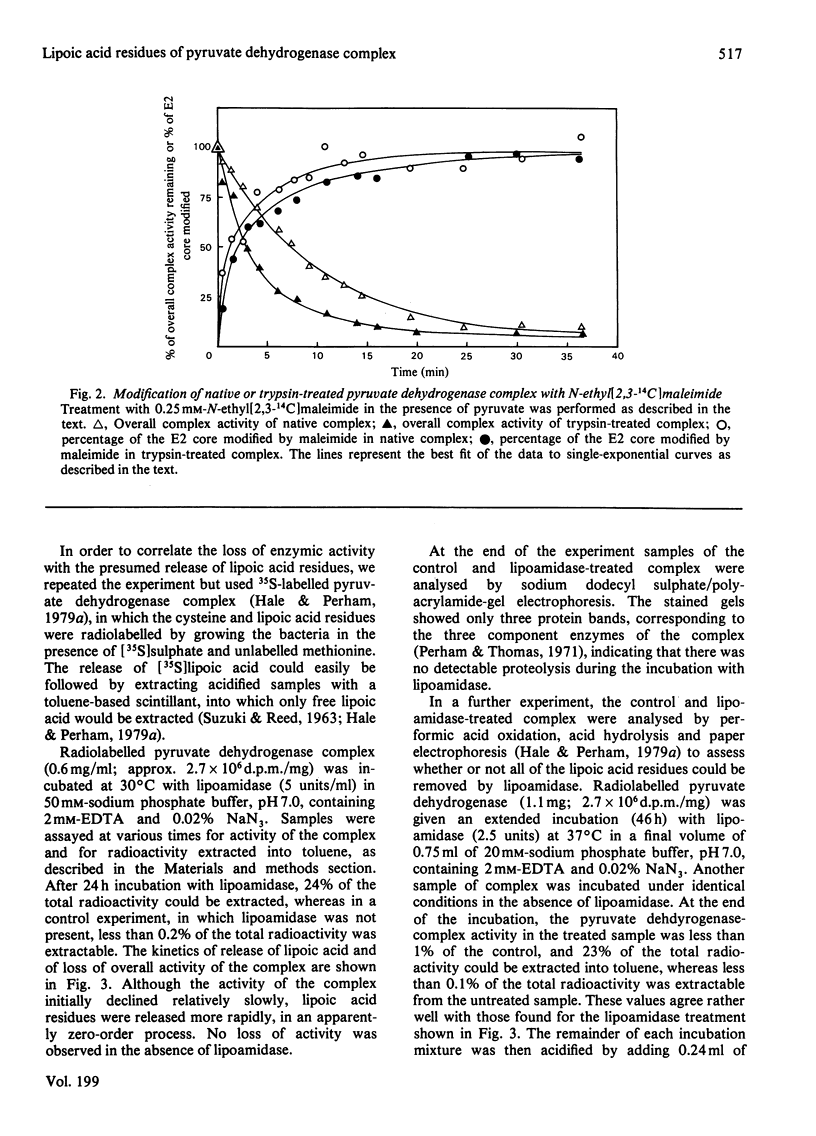
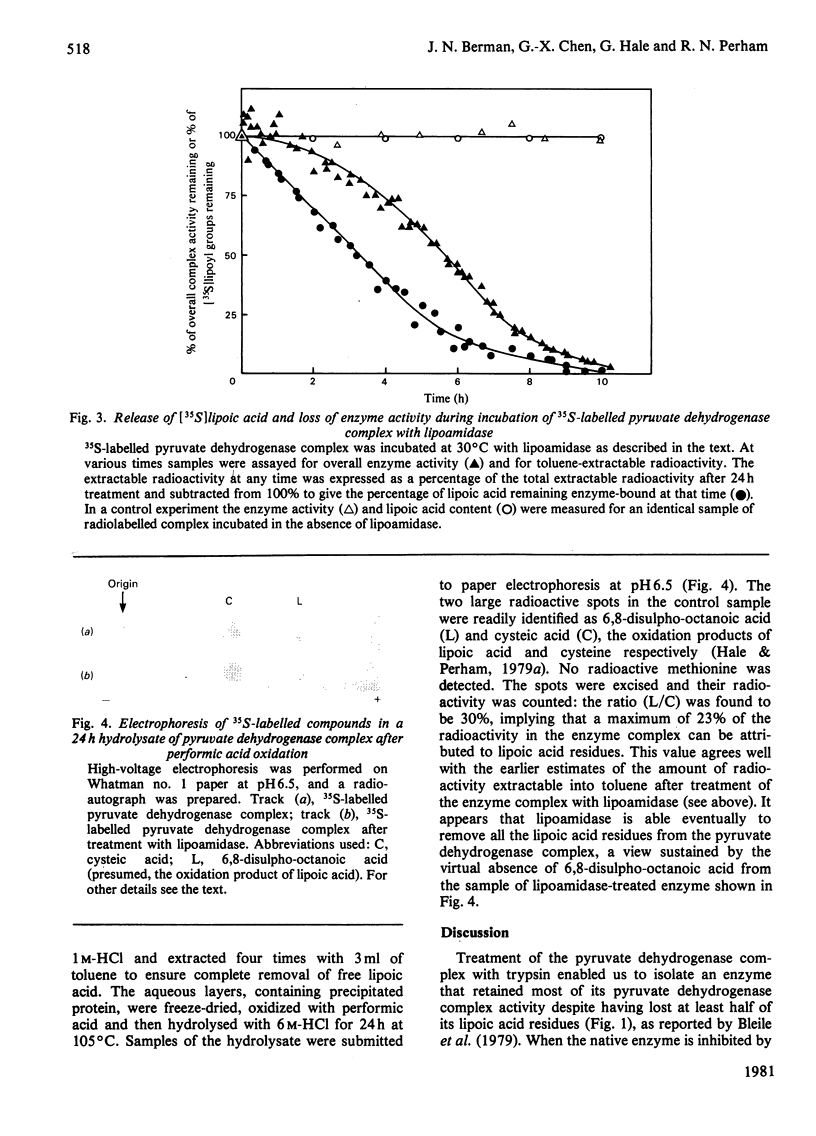
The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Escherichia coli contains two lipoic acid residues per dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase chain, and these are known to engage in the part-reactions of the enzyme. The enzyme complex was treated with trypsin at pH 7.0, and a partly proteolysed complex was obtained that had lost almost 60% of its lipoic acid residues although it retained 80% of its pyruvate dehydrogenase-complex activity. When this complex was treated with N-ethylmaleimide in the presence of pyruvate and the absence of CoASH, the rate of modification of the remaining S-acetyldihydrolipoic acid residues was approximately equal to the accompanying rate of loss of enzymic activity. This is in contrast with the native pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, where under the same conditions modification proceeds appreciably faster than the loss of enzymic activity. The native pyruvate dehydrogenase complex was also treated with lipoamidase prepared from Streptococcus faecalis. The release of lipoic acid from the complex followed zero-order kinetics for most of the reaction, whereas the accompanying loss of pyruvate dehydrogenase-complex activity lagged substantially behind. These results eliminate a model for the enzyme mechanism in which specifically one of the two lipoic acid residues on each dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase chain is essential for the reaction. They are consistent with a model in which the dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase component contains more lipoic acid residues than are required to serve the pyruvate decarboxylase subunits under conditions of saturating substrates, enabling the function of an excised or inactivated lipoic acid residue to be taken over by another one. Unusual structural properties of the enzyme complex might permit this novel feature of the enzyme mechanism.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama S. K., Hammes G. G. Elementary steps in the reaction mechanism of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex from Escherichia coli: kinetics of acetylation and deacetylation. Biochemistry. 1980 Sep 2;19(18):4208–4213. doi: 10.1021/bi00559a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambrose-Griffin M. C., Danson M. J., Griffin W. G., Hale G., Perham R. N. Kinetic analysis of the role of lipoic acid residues in the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1980 May 1;187(2):393–401. doi: 10.1042/bj1870393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambrose M. C., Perham R. N. Spin-label study of the mobility of enzyme-bound lipoic acid in the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1976 May 1;155(2):429–432. doi: 10.1042/bj1550429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates D. L., Danson M. J., Hale G., Hooper E. A., Perham R. N. Self-assembly and catalytic activity of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1977 Jul 28;268(5618):313–316. doi: 10.1038/268313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates D. L., Harrison R. A., Perham R. N. The stoichiometry of polypeptide chains in the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of E. coli determined by a simple novel method. FEBS Lett. 1975 Dec 15;60(2):427–430. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80764-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleile D. M., Munk P., Oliver R. M., Reed L. J. Subunit structure of dihydrolipoyl transacetylase component of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4385–4389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. P., Perham R. N. Selective inactivation of the transacylase components of the 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase multienzyme complexes of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1976 May 1;155(2):419–427. doi: 10.1042/bj1550419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cate R. L., Roche T. E., Davis L. C. Rapid intersite transfer of acetyl groups and movement of pyruvate dehydrogenase component in the kidney pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7556–7562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cate R. L., Roche T. E. Function and regulation of mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Acetylation, interlipoyl acetyl transfer, and migration of the pyruvate dehydrogenase component. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1659–1665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. H., Reed L. J. Acyl group and electron pair relay system: a network of interacting lipoyl moieties in the pyruvate and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complexes from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4223–4227. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danson M. J., Fersht A. R., Perham R. N. Rapid intramolecular coupling of active sites in the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Escherichia coli: mechanism for rate enhancement in a multimeric structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5386–5390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danson M. J., Hale G., Johnson P., Perham R. N., Smith J., Spragg P. Molecular weight and symmetry of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 25;129(4):603–617. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90471-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danson M. J., Hale G., Perham R. N. The role of lipoic acid residues in the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 1;199(3):505–511. doi: 10.1042/bj1990505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danson M. J., Hooper E. A., Perham R. N. Intramolecular coupling of active sites in the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1978 Oct 1;175(1):193–198. doi: 10.1042/bj1750193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danson M. J., Perham R. N. Evidence for two lipoic acid residues per lipoate acetyltransferase chain in the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 1;159(3):677–682. doi: 10.1042/bj1590677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey P. A., Ikeda B. H., Gavino G. R., Speckhard D. C., Wong S. S. Escherichia coli pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Site coupling in electron and acetyl group transfer pathways. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7234–7241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUNSALUS I. C., DOLIN M. I., STRUGLIA L. Pyruvic acid metabolism. III. A manometric assay for pyruvate oxidation factor. J Biol Chem. 1952 Feb;194(2):849–857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert G. A., Gilbert L. M. Detection in the ultracentrifuge of protein heterogeneity by computer modelling, illustrated by pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex. J Mol Biol. 1980 Dec 15;144(3):405–408. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90099-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grande H. J., Van Telgen H. J., Veeger C. Symmetry and asymmetry of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complexes from Azotobacter vinelandii and Escherichia coli as reflected by fluorescence and spin-label studies. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Dec 11;71(2):509–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRS C. H. The oxidation of ribonuclease with performic acid. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):611–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale G., Perham R. N. Limited proteolysis of the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Feb 15;94(1):119–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12878.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale G., Perham R. N. Polypeptide-chain stoicheiometry and lipoic acid content of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 1;177(1):129–136. doi: 10.1042/bj1770129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale G., Perham R. N. Primary structure of the swinging arms of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1979 Sep 15;105(2):263–266. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80625-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOIKE M., REED L. J., CARROLL W. R. alpha-Keto acid dehydrogenation complexes. IV. Resolution and reconstitution of the Escherichia coli pyruvate dehydrogenation complex. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jan;238:30–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kresze G. B., Ronft H. Bovine kidney pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Limited proteolysis and molecular structure of the lipoate acetyltransferase component. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Dec;112(3):589–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perham R. N., Duckworth H. W., Roberts G. C. Mobility of polypeptide chain in the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex revealed by proton NMR. Nature. 1981 Jul 30;292(5822):474–477. doi: 10.1038/292474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perham R. N. Self-assembly of biological macromolecules. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Nov 6;272(915):123–136. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perham R. N., Thomas J. O. The subunit molecular weights of the alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase multienzyme complexes from E. coli. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jun 2;15(1):8–12. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUZUKI K., REED L. J. LIPOAMIDASE. J Biol Chem. 1963 Dec;238:4021–4025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt B., Cohen R. The structure of the Escherichia coli pyruvate dehydrogenase complex is probably not unique. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Apr 14;93(3):709–712. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91135-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speckhard D. C., Ikeda B. H., Wong S. S., Frey P. A. Acetylation stoichiometry of Escherichia coli pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 25;77(2):708–713. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley C. J., Packman L. C., Danson M. J., Henderson C. E., Perham R. N. Intramolecular coupling of active sites in the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complexes from bacterial and mammalian sources. Biochem J. 1981 Jun 1;195(3):715–721. doi: 10.1042/bj1950715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wawrzynczak E. J., Perham R. N., Roberts G. C. Conformational mobility of polypeptide chains in the 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase complexes from ox heart revealed by proton NMR spectroscopy. FEBS Lett. 1981 Aug 17;131(1):151–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80908-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



