Abstract
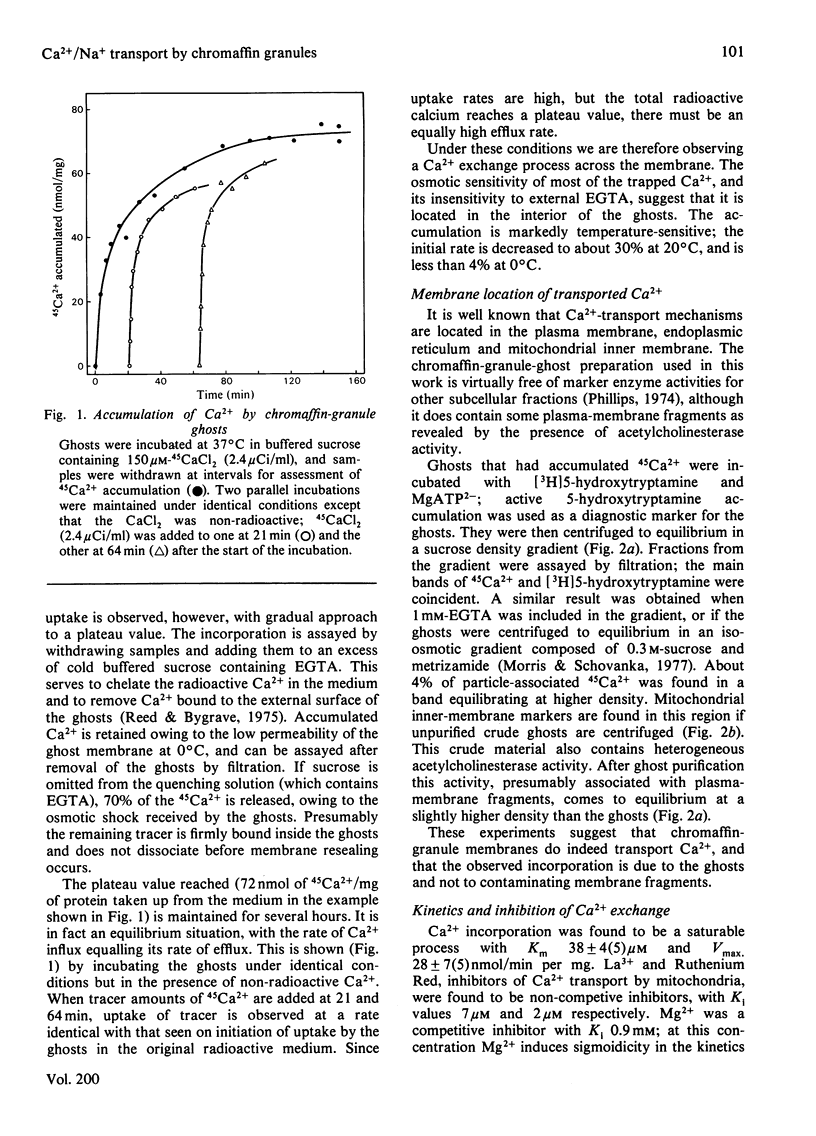
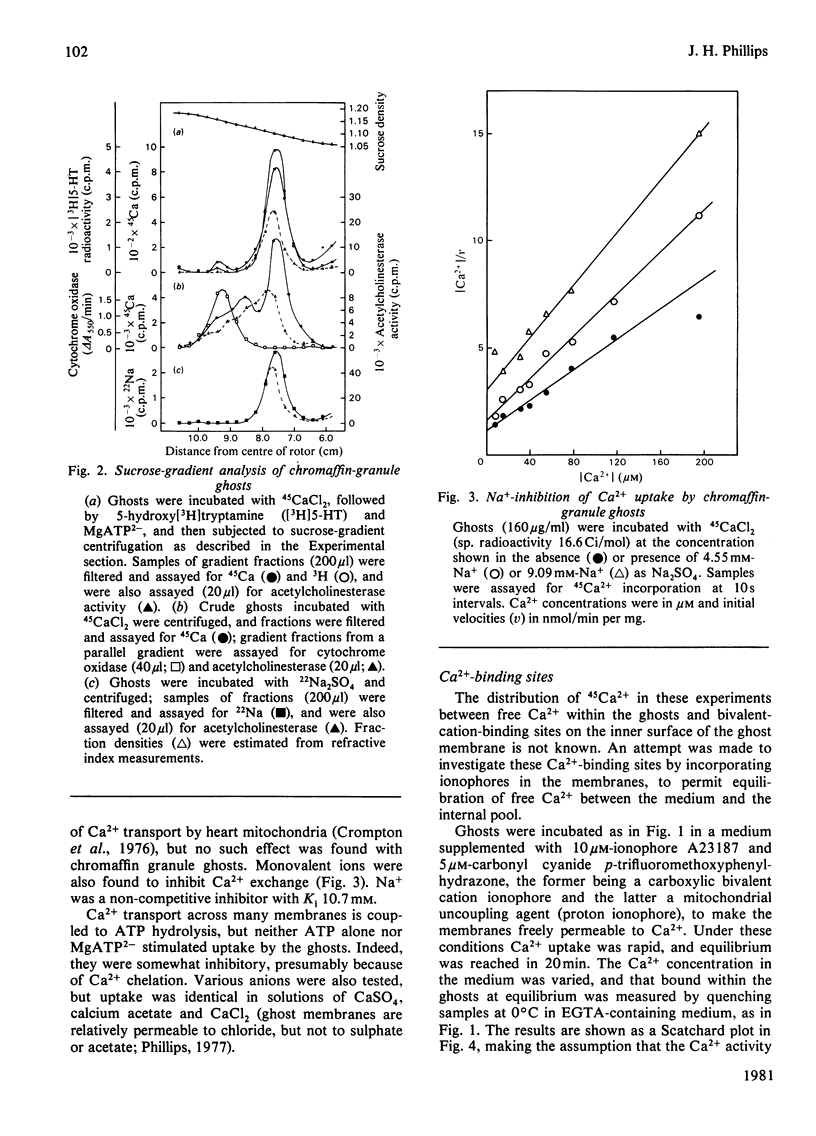
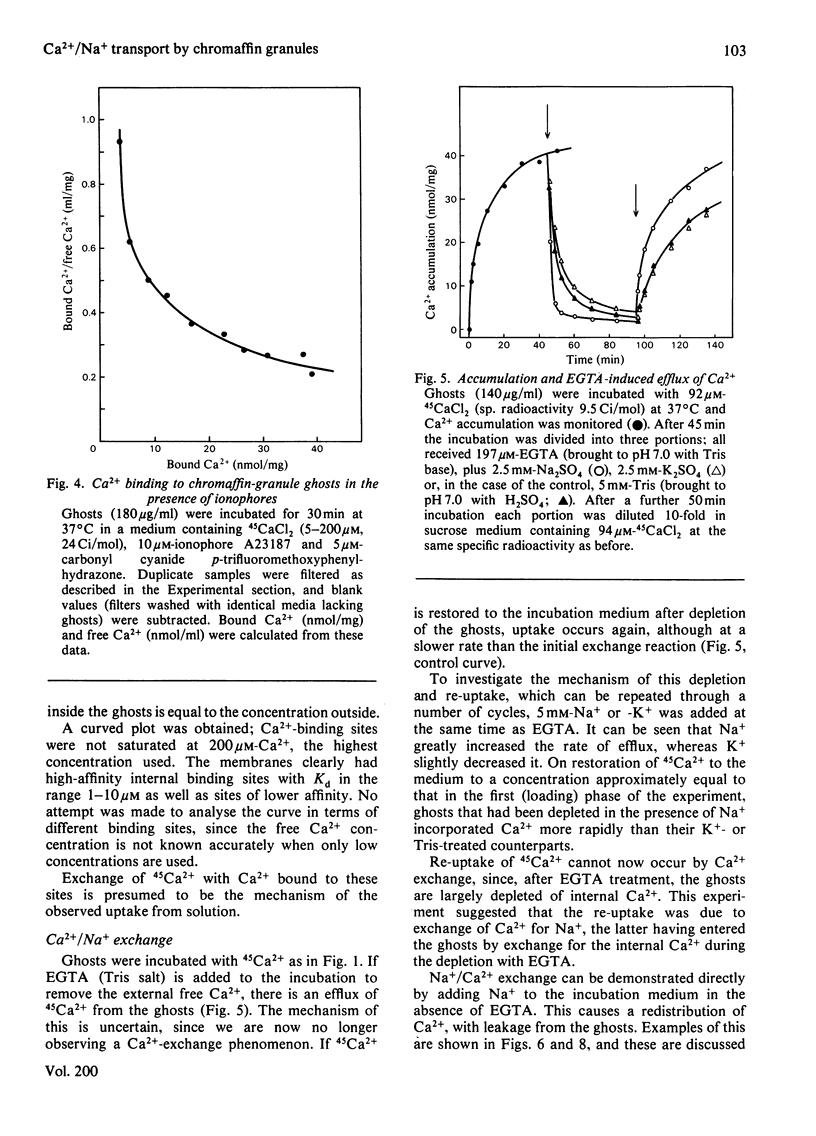
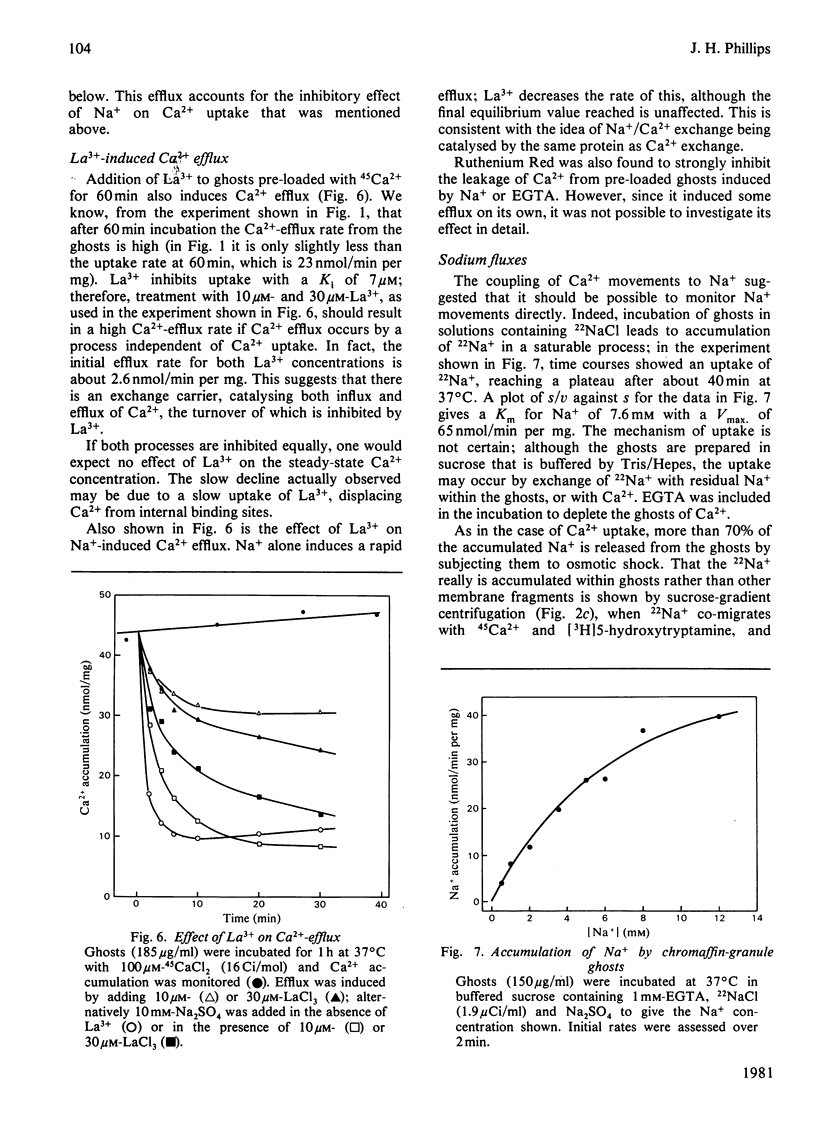
Bovine chromaffin-granule ghosts accumulate 45Ca2+ in a temperature- and osmotic-shock-sensitive process; the uptake is saturable, with Km 38 microM and Vmax. 28 nmol/min per mg at 37 degrees C. Entry occurs by exchange with Ca2+ bound to the inner surface of the membrane. It is inhibited non-competitively by Na+, La3+ and Ruthenium Red (Ki 10.7 mM, 7 microM and 2 microM respectively), and competitively by Mg2+ (ki 0.9 mM). Uptake was not stimulated by ATP. Na+ induces Ca2+ efflux; Ca2+ can re-enter the ghosts by a process of Ca2+/Na+ exchange. La3+ inhibits Ca2+ efflux during Ca2+-exchange, and Ca2+ efflux induced by Na+, suggesting that Ca2+ uptake and efflux, and Ca2+/Na+ exchange, are catalysed by the same protein. Na+ enters ghosts during CA2+ efflux, but the kinetics of its entry are not exactly similar to the kinetics of Ca2+ efflux. Initially 1-2 Na+ enter per Ca2+ lost, but at equilibrium 3-4 Na+ have replaced each Ca2+. There is no evidence that either Ca2+ uptake or efflux by Ca2+/Na+ exchange is electrogenic, suggesting that the stoichiometry of exchange is Ca2+/2Na+. This exchange reaction may have a role in depleting cytoplasmic Ca2+ after depolarization-induced Ca2+ entry through the adrenal medulla plasma membrane; there is some evidence that there may be an additional entry mechanism for Na+ across the granule membrane.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apps D. K., Pryde J. G., Sutton R., Phillips J. H. Inhibition of adenosine triphosphatase, 5-hydroxytryptamine transport and proton-translocation activities of resealed chromaffin-granule 'ghosts'. Biochem J. 1980 Aug 15;190(2):273–282. doi: 10.1042/bj1900273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOROWITZ J. L., FUWA K., WEINER N. DISTRIBUTION OF METALS AND CATECHOLAMINES IN BOVINE ADRENAL MEDULLA SUB-CELLULAR FRACTIONS. Nature. 1965 Jan 2;205:42–43. doi: 10.1038/205042a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Hodgkin A. L., Ridgway E. B. Depolarization and calcium entry in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1971 Nov;218(3):709–755. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P. The ins and outs of calcium transport in squid axons: internal and external ion activation of calcium efflux. Fed Proc. 1976 Dec;35(14):2574–2578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E. The calcium cycle of mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1979 Aug 1;104(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroni P., Reinlib L., Carafoli E. Charge movements during the Na+-Ca2+ exchange in heart sarcolemmal vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6354–6358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemente F., Meldolesi J. Calcium and pancreatic secretion. I. Subcellular distribution of calcium and magnesium in the exocrine pancreas of the guinea pig. J Cell Biol. 1975 Apr;65(1):88–102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.1.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crompton M., Künzi M., Carafoli E. The calcium-induced and sodium-induced effluxes of calcium from heart mitochondria. Evidence for a sodium-calcium carrier. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Oct 3;79(2):549–558. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11839.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton R. M., McCormack J. G. On the role of the calcium transport cycle in heart and other mammalian mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1980 Sep 22;119(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80986-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiskum G., Lehninger A. L. Regulated release of Ca2+ from respiring mitochondria by Ca2+/2H+ antiport. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6236–6239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. G., Scarpa A. Ion permeability of isolated chromaffin granules. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Dec;68(6):601–631. doi: 10.1085/jgp.68.6.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostron H., Winkler H., Geissler D., König P. Uptake of calcium by chromaffin granules in vitro. J Neurochem. 1977 Mar;28(3):487–493. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb10419.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen F. L., Vincenzi F. F. Calcium transport across the plasma membrane: stimulation by calmodulin. Science. 1979 Apr 20;204(4390):306–309. doi: 10.1126/science.155309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft J. H. Ruthenium red and violet. I. Chemistry, purification, methods of use for electron microscopy and mechanism of action. Anat Rec. 1971 Nov;171(3):347–368. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091710302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H., Wong P. T. Isolation of a calcium-sequestering protein from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1231–1235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macintyre J. D., Green J. W. Stimulation of calcium transport in inside-out vesicles of human erythrocyte membranes by a soluble cytoplasmic activator. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 4;510(2):373–377. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason T. L., Poyton R. O., Wharton D. C., Schatz G. Cytochrome c oxidase from bakers' yeast. I. Isolation and properties. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 25;248(4):1346–1354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelson D. M., Ophir I., Angel I. ATP-stimulated Ca2+ transport into cholinergic Torpedo synaptic vesicles. J Neurochem. 1980 Jul;35(1):116–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb12496.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris S. J., Schovanka I. Some physical properties of adrenal medulla chromaffin granules isolated by a new continuous iso-osmotic density gradient method. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 4;464(1):53–64. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90370-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D. G., Crompton M. Mitochondrial calcium transport. FEBS Lett. 1980 Mar 10;111(2):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80806-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D. G., Scott I. D. The regulation of brain mitochondrial calcium-ion transport. The role of ATP in the discrimination between kinetic and membrane-potential-dependent calcium-ion efflux mechanisms. Biochem J. 1980 Mar 15;186(3):833–839. doi: 10.1042/bj1860833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordmann J. J., Chevallier J. The role of microvesicles in buffering [Ca2+]i in the neurohypophysis. Nature. 1980 Sep 4;287(5777):54–56. doi: 10.1038/287054a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panfili E., Crompton M., Sottocasa G. L. Immunochemical evidence of the independence of the Ca2+/Na2+ antiporter and electrophoretic Ca2+ uniporter in heart mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jan 12;123(1):30–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson K. D., Nishimoto A. Y. Na+-Ca2+ exchange is affected by membrane potential in cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6880–6882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. H., Allison V. P. Proton translocation of the bovine chromaffin-granule membrane. Biochem J. 1978 Mar 15;170(3):661–672. doi: 10.1042/bj1700661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. H., Allison Y. P., Morris S. J. The distribution of calcium, magnesium, copper and iron in the bovine adrenal medulla. Neuroscience. 1977;2(1):147–152. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90075-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. H. Passive ion permeability of the chromaffin-granule membrane. Biochem J. 1977 Nov 15;168(2):289–297. doi: 10.1042/bj1680289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. H. Transport of catecholamines by resealed chromaffin-grnaule "ghosts". Biochem J. 1974 Nov;144(2):311–318. doi: 10.1042/bj1440311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitts B. J. Stoichiometry of sodium-calcium exchange in cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles. Coupling to the sodium pump. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6232–6235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pletscher A., Da Prada M., Berneis K. H., Steffen H., Lütold B., Weder H. G. Molecular organization of amine storage organelles of blood platelets and adrenal medulla. Adv Cytopharmacol. 1974;2:257–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter L. T. A radiometric microassay of acetylcholinesterase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1967 Jun;156(3):500–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahamimoff H., Abramovitz E. Ca transport and ATPase activity of synaptosomal vesicles from rat brain. FEBS Lett. 1978 Aug 15;92(2):163–167. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80745-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Bygrave F. L. Methodology for in vitro studies of Ca-2+ transport. Anal Biochem. 1975 Jul;67(1):44–54. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90270-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves J. P., Sutko J. L. Sodium-calcium exchange activity generates a current in cardiac membrane vesicles. Science. 1980 Jun 27;208(4451):1461–1464. doi: 10.1126/science.7384788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott I. D., Akerman K. E., Nicholls D. G. Calcium-ion transport by intact synaptosomes. Intrasynaptosomal compartmentation and the role of the mitochondrial membrane potential. Biochem J. 1980 Dec 15;192(3):873–880. doi: 10.1042/bj1920873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Sharp R. R., Domino L. E., Domino E. F. Composition of the aqueous phase of chromaffin granules. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Sep 20;587(1):75–88. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90222-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serck-Hanssen G., Christiansen E. N. Uptake of calcium in chromaffin granules of bovine adrenal medulla stimulated in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 11;307(2):404–414. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90106-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp R. R., Richards E. P. Molecular mobilities of soluble components in the aqueous phase of chromaffin granules. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 29;497(1):260–271. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90159-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


