Abstract
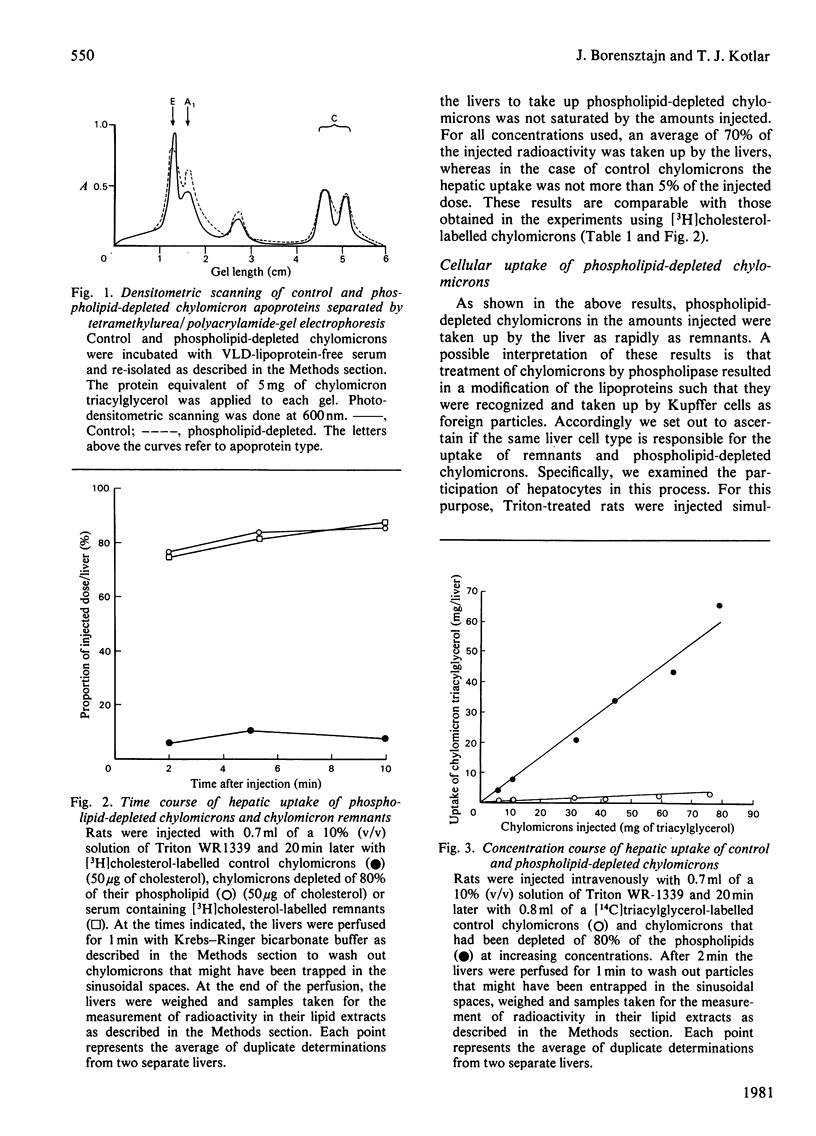
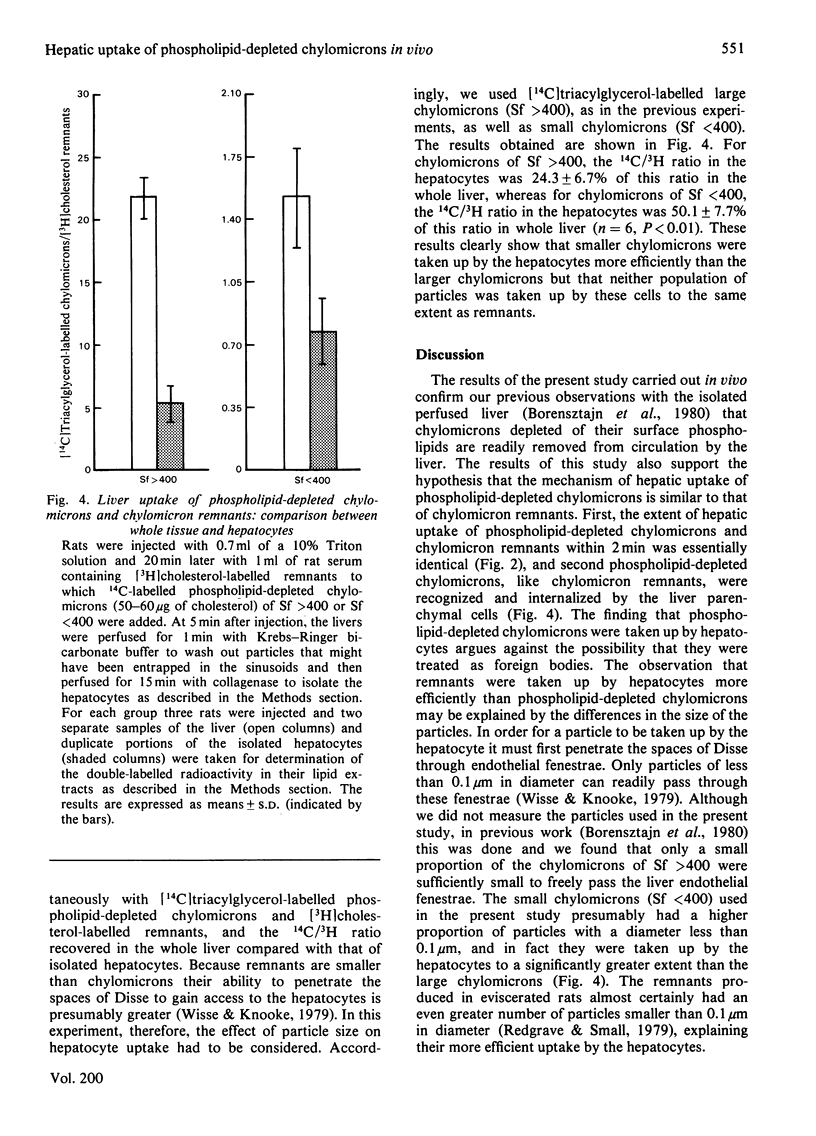
1. Rats pretreated with Triton WR-1339 to prevent the formation of remnants were injected with [3H]cholesterol-labelled remnants, intact chylomicrons or chylomicrons depleted of most of their surface phospholipids by treatment with phospholipase A2. Within 5 min about 80% of the injected label of remnants and phospholipid-depleted chylomicrons was incorporated into the livers compared with less than 10% of the injected radioactivity of intact chylomicrons. A similar rapid hepatic uptake of radioactivity occurred when rats not pretreated with Triton were injected with [3H]cholesterol-labelled phospholipid-depleted chylomicrons. This rapid hepatic uptake of phospholipid-depleted chylomicrons occurred apparently without any alteration in the apoprotein composition of the particles. 2. The participation of hepatocytes in the uptake of remnants and phospholipid-depleted chylomicrons was examined. Both types of particles were taken up by the hepatocytes. However, small chylomicrons (Sf less than 400) were taken up more efficiently than were large chylomicrons (Sf greater than 400), but neither was taken up as efficiently as the remnants. 3. The results of this study lend support to the hypothesis that phospholipid-depleted chylomicrons and chylomicron remnants are taken up by the liver by a similar mechanism, which depends on the loss of surface phospholipids.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borensztajn J., Kotlar T. J., McNeill B. J. Uptake of phospholipid-depleted chylomicrons by the perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1980 Dec 15;192(3):845–851. doi: 10.1042/bj1920845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borensztajn J., Rone M. S., Kotlar T. J. The inhibition in vivo of lipoprotein lipase (clearing-factor lipase) activity by triton WR-1339. Biochem J. 1976 Jun 15;156(3):539–543. doi: 10.1042/bj1560539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrella M., Cooper A. D. High affinity binding of chylomicron remnants to rat liver plasma membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):338–342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. D., Yu P. Y. Rates of removal and degradation of chylomicron remnants by isolated perfused rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1978 Jul;19(5):635–643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S. Hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine by phospholipase A2 does not cause dissociation of apolipoprotein C from rat plasma very low density lipoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 24;489(2):337–342. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90153-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elovson J., Huang Y. O., Baker N., Kannan R. Apolipoprotein B is structurally and metabolically heterogeneous in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):157–161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felts J. M., Itakura H., Crane R. T. The mechanism of assimilation of constituents of chylomicrons, very low density lipoproteins and remnants - a new theory. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Oct 27;66(4):1467–1475. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90524-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher M. J. A colorimetric method for estimating serum triglycerides. Clin Chim Acta. 1968 Nov;22(3):393–397. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(68)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R. S., Mayes P. A. Comparison of the metabolism of chylomicrons and chylomicron remnants by the perfused liver. Biochem J. 1978 Jan 15;170(1):47–55. doi: 10.1042/bj1700047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa T., Fidge N. Changes in the concentration of plasma lipoproteins and apoproteins following the administration of Triton WR 1339 to rats. J Lipid Res. 1979 Feb;20(2):254–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. P. A rapid electrophoretic technique for identification of subunit species of apoproteins in serum lipoproteins. Anal Biochem. 1973 Jun;53(2):350–364. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotlar T. J., Borensztajn J. Hydrolysis of chylomicron triacylglycerol by endothelium-bound lipoprotein lipase. Effect of decreased apoprotein C-II/C-III ratio. Biochem J. 1979 Oct 1;183(1):171–174. doi: 10.1042/bj1830171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kris-Etherton P. M., Cooper A. D. Studies on the etiology of the hyperlipemia in rats fed an atherogenic diet. J Lipid Res. 1980 May;21(4):435–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnaiah K. V., Walker L. F., Borensztajn J., Schonfeld G., Getz G. S. Apolipoprotein B variant derived from rat intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3806–3810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mjos O. D., Faergeman O., Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J. Characterization of remnants produced during the metabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins of blood plasma and intestinal lymph in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):603–615. doi: 10.1172/JCI108130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson A., Ehnholm C., Florén C. H. Uptake and degradation of rat chylomicron remnants, produced in vivo and in vitro, in rat hepatocyte monolayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 23;663(2):408–420. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90170-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson M., Berg T. Uptake and degradation of formaldehyde-treated 125I-labelled human serum albumin in rat liver cells in vivo and in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 29;497(1):171–182. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90150-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel S. P., Dolphin P. J., Rubinstein D. An in vitro model for the catabolism of rat chylomicrons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Apr 7;63(3):764–772. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80449-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redgrave T. G. Formation of cholesteryl ester-rich particulate lipid during metabolism of chylomicrons. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):465–471. doi: 10.1172/JCI106255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redgrave T. G., Small D. M. Quantitation of the transfer of surface phospholipid of chylomicrons to the high density lipoprotein fraction during the catabolism of chylomicrons in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jul;64(1):162–171. doi: 10.1172/JCI109435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOTZ M. C., SCANU A., PAGE I. H. Effect of triton on lipoprotein lipase of rat plasma. Am J Physiol. 1957 Feb;188(2):399–402. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1957.188.2.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scow R. O., Egelrud T. Hydrolysis of chylomicron phosphatidylcholine in vitro by lipoprotein lipase, phospholipase A2 and phospholipase C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 22;431(3):538–549. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelburne F., Hanks J., Meyers W., Quarfordt S. Effect of apoproteins on hepatic uptake of triglyceride emulsions in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):652–658. doi: 10.1172/JCI109710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrill B. C., Dietschy J. M. Characterization of the sinusoidal transport process responsible for uptake of chylomicrons by the liver. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):1859–1867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrill B. C., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Rapid hepatic clearance of the canine lipoproteins containing only the E apoprotein by a high affinity receptor. Identity with the chylomicron remnant transport process. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1804–1807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparks C. E., Marsh J. B. Metabolic heterogeneity of apolipoprotein B in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1981 Mar;22(3):519–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tall A. R., Green P. H., Glickman R. M., Riley J. W. Metabolic fate of chylomicron phospholipids and apoproteins in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1979 Oct;64(4):977–989. doi: 10.1172/JCI109564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windler E., Chao Y., Havel R. J. Regulation of the hepatic uptake of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins in the rat. Opposing effects of homologous apolipoprotein E and individual C apoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8303–8307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Tol A., van Berkel T. J. Uptake and degradation of rat and human very low density (remnant) apolipoprotein by parenchymal and non-parenchymal rat liver cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul 14;619(1):156–166. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(80)90251-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


