Abstract
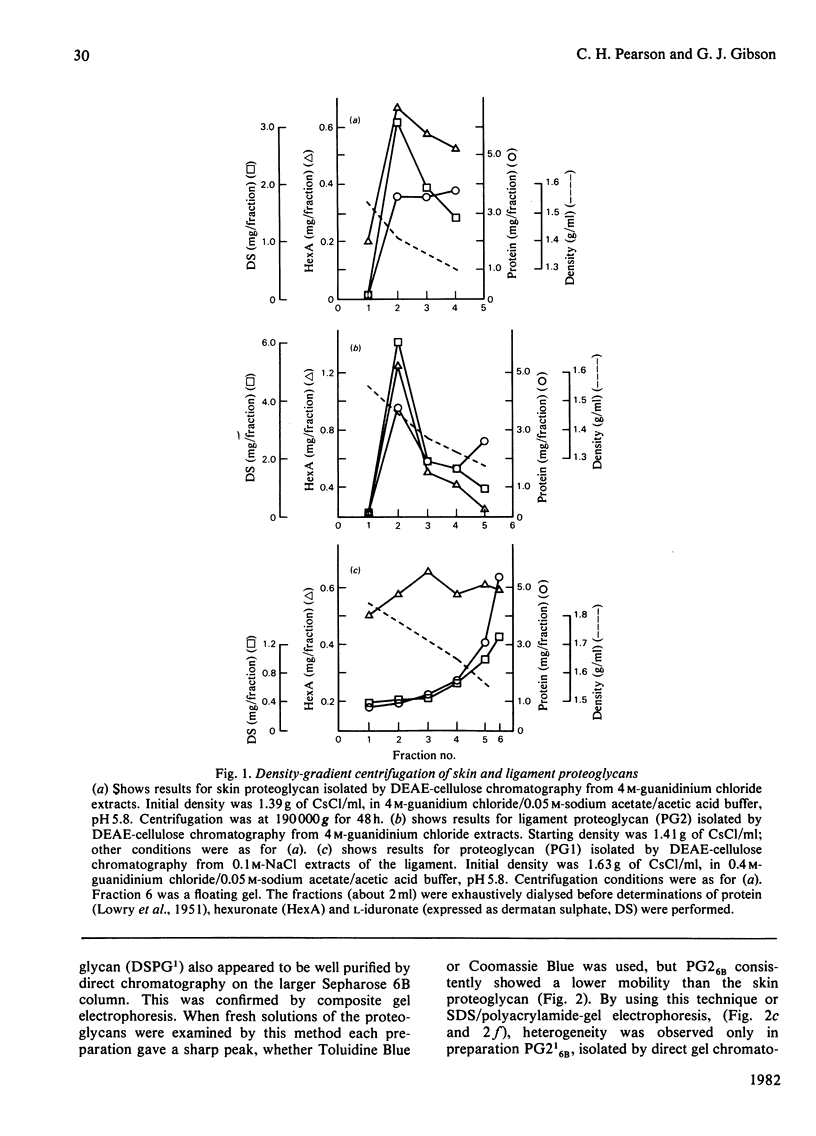
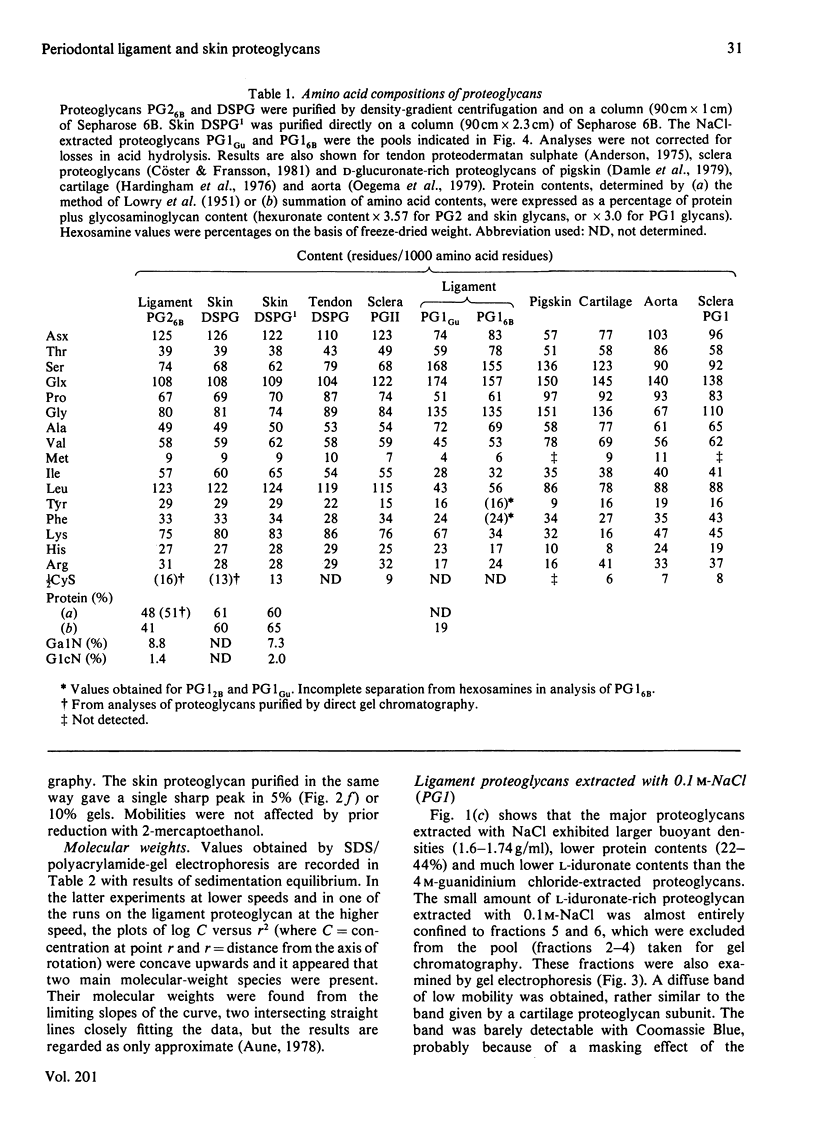
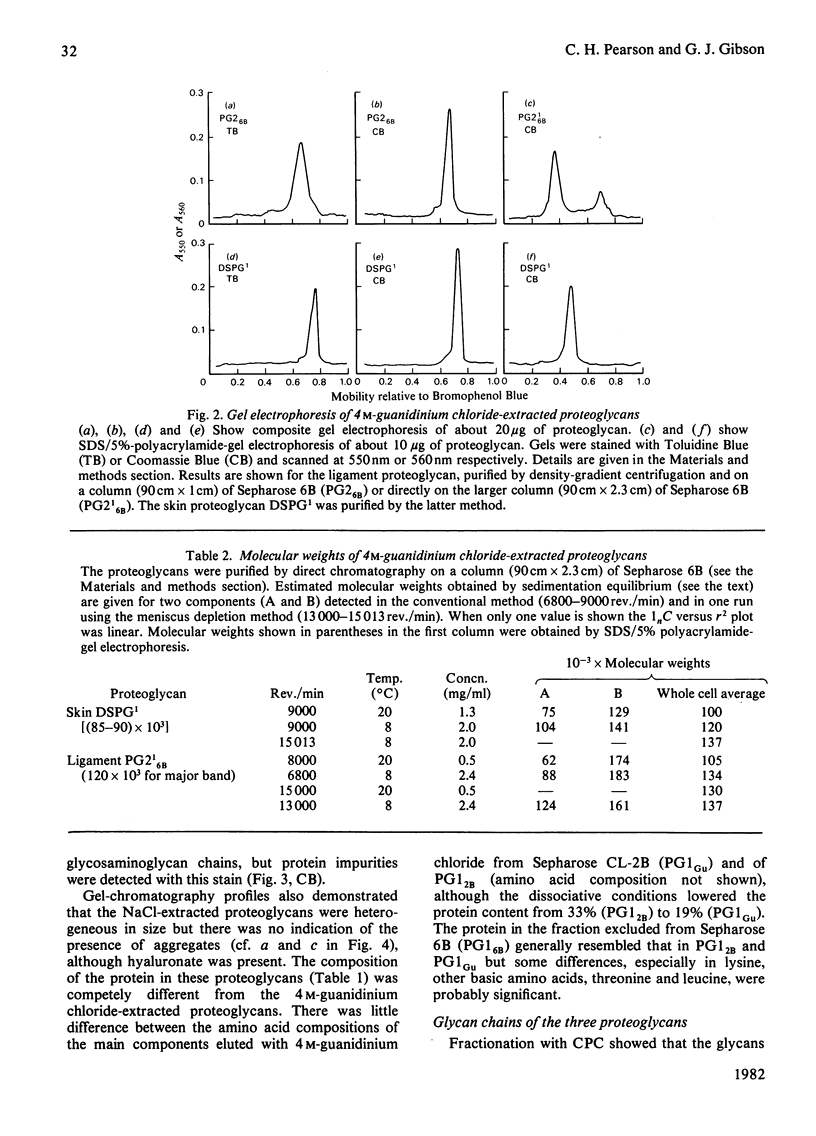
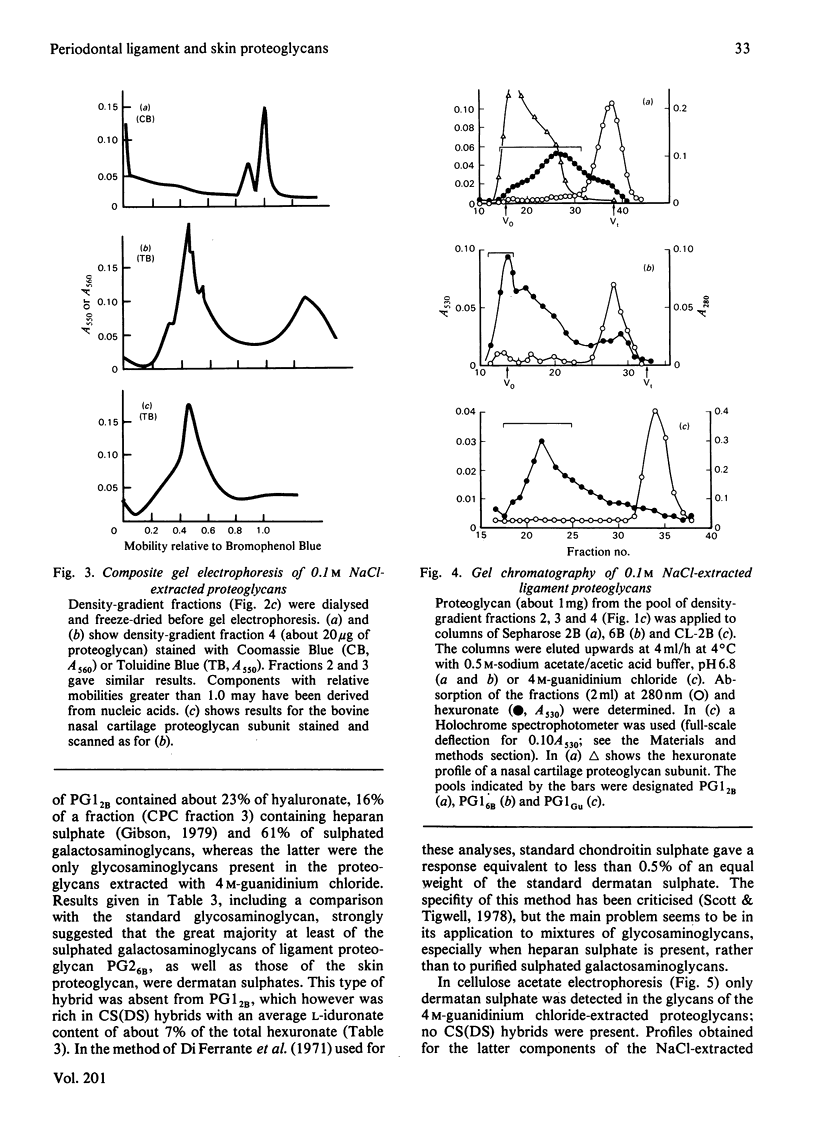
A proteoglycan purified from 4 M-guanidinium chloride extracts of bovine periodontal ligament closely resembled that of bovine skin, except for a rather lower protein content and a higher molecular weight (120 000 compared with about 90 000) by sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. The latter difference was explained by the molecular weights (29 000 and 16 000) of the respective dermatan sulphate components, each of which was rich in L-iduronate (about 75% of the total hexuronate). Significant amounts of other glycosaminoglycans did not occur in these proteoglycans, which were homogenous on gel chromatography and agarose/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Polydispersity was observed in sedimentation equilibrium experiments, but proteolysis or self-association of the proteodermatan sulphates may have affected these results. Ligament proteoglycans that were almost completely extracted with 0.1 M-NaCl contained less protein of a completely different amino acid composition than the proteodermatan sulphates. They were heterogeneous in size but generally smaller than cartilage proteoglycans and L-iduronate was a component, comprising about 7% of the total hexuronate of the sulphated galactosaminoglycan chains. The latter consisted of two fractions differing in molecular weight, but a dermatan sulphate with a high L-iduronate content was not present. These proteoglycans had some resemblance to D-glucuronate-rich proteoglycans of other non-cartilaginous tissues. Such compounds, however, are difficult to categorize at present.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. C. Isolation of a glycoprotein and proteodermatan sulphate from bovine achilles tendon by affinity chromatography on concanavalin A-Sepharose. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 27;379(2):444–455. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90151-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aune K. C. Molecular weight measurements by sedimentation equilibrium: some common pitfalls and how to avoid them. Methods Enzymol. 1978;48:163–185. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)48009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cöster L., Fransson L. A. Isolation and characterization of dermatan sulphate proteoglycans from bovine sclera. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 1;193(1):143–153. doi: 10.1042/bj1930143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIDSON E., HOFFMAN P., LINKER A., MEYER K. The acid mucopolysaccharides of connective tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Sep;21(3):506–518. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90188-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damle S. P., Kieras F. J., Tzeng W. K., Gregory J. D. Isolation and characterization of proteochondroitin sulfate from pig skin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1614–1620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransson L. A., Havsmark B. Structure of dermatan sulfate. VII. The copolymeric structure of dermatan sulfate from horse aorta. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 25;245(18):4770–4783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransson L. A. Interaction between dermatan sulphate chains. I. Affinity chromatography of copolymeric galactosaminioglycans on dermatan sulphate-substituted agarose. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 23;437(1):106–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90351-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransson L. A., Rodén L. Structure of dermatan sulfate. I. Degradation by testicular hyaluronidase. J Biol Chem. 1967 Sep 25;242(18):4161–4169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habuchi H., Yamagata T., Iwata H., Suzuki S. The occurrence of a wide variety of dermatan sulfate-chondroitin sulfate copolymers in fibrous cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):6019–6028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Ewins R. J., Muir H. Cartilage proteoglycans. Structure and heterogeneity of the protein core and the effects of specific protein modifications on the binding to hyaluronate. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 1;157(1):127–143. doi: 10.1042/bj1570127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Sajdera S. W. Proteinpolysaccharide complex from bovine nasal cartilage. The function of glycoprotein in the formation of aggregates. J Biol Chem. 1969 May 10;244(9):2384–2396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood J. J., Robinson H. C. The molecular-weight distribution of glycosaminoglycans. Biochem J. 1973 Dec;135(4):631–637. doi: 10.1042/bj1350631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowther D. A., Preston B. N., Meyer F. A. Isolation and properties of chondroitin sulphates from bovine heart valves. Biochem J. 1970 Jul;118(4):595–601. doi: 10.1042/bj1180595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurão P. A., Machado-Santelli G. M., Toledo O. M. Sulfated glycosaminoglycans of cultured fibroblasts from guinea-pig embryo kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 7;629(2):259–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurtrey J., Radhakrishnamurthy B., Dalferes E. R., Jr, Berenson G. S., Gregory J. D. Isolation of proteoglycan-hyaluronate complexes from bovine aorta. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1621–1626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munemoto K., Iwayama Y., Yoshida M., Sera M., Aono M., Yokomizo I. Isolation and characterization of acid mucopolysaccharides of bovine periodontal membrane. Arch Oral Biol. 1970 May;15(5):369–382. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(70)90065-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrink B. Isolation and partial characterization of a dermatan sulphate proteoglycan from pig skin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 21;264(2):354–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oegema T. R., Jr, Hascall V. C., Eisenstein R. Characterization of bovine aorta proteoglycan extracted with guanidine hydrochloride in the presence of protease inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1312–1318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oike Y., Kimata K., Shinomura T., Nakazawa K., Suzuki S. Structural analysis of chick-embryo cartilage proteoglycan by selective degradation with chondroitin lyases (chondroitinases) and endo-beta-D-galactosidase (keratanase). Biochem J. 1980 Oct 1;191(1):193–207. doi: 10.1042/bj1910193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson C. H., Wohllebe M., Carmichael D. J., Chovelon A. Bovine periodontal ligament. An invesitation of the collagen, glycosaminoglycan and insoluble glycoprotein components at different stages of tissue development. Connect Tissue Res. 1975;3(4):195–206. doi: 10.3109/03008207509152179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson H., Davies J. D., Gibson G. J., Lehocky S., Scott P. G. Degradation of skin dermatan sulphate proteoglycan by cathepsin D [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1978;6(6):1199–1202. doi: 10.1042/bst0061199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston B. N. Physical characterization of dermatan sulphate-protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Sep 10;126(3):974–977. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90500-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radhakrishnamurthy B., Ruiz H. A., Jr, Berenson G. S. Isolation and characterization of proteoglycans from bovine aorta. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4831–4841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Yamagata T., Suzuki S. Enzymatic methods for the determination of small quantities of isomeric chondroitin sulfates. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 10;243(7):1536–1542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. E. Collagen--proteoglycan interactions. Localization of proteoglycans in tendon by electron microscopy. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 1;187(3):887–891. doi: 10.1042/bj1870887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. E., Tigwell M. J. Periodate oxidation and the shapes of glycosaminoglycuronans in solution. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 1;173(1):103–114. doi: 10.1042/bj1730103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toole B. P., Lowther D. A. The organisation of hexosamine-containing compounds in bovine skin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jun 29;121(2):315–325. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90120-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANTIS D. A. EQUILIBRIUM ULTRACENTRIFUGATION OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:297–317. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Ferrante N., Donnelly P. V., Berglund R. K. Colorimetric measurement of dermatan sulphate. Biochem J. 1971 Sep;124(3):549–553. doi: 10.1042/bj1240549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


