Abstract
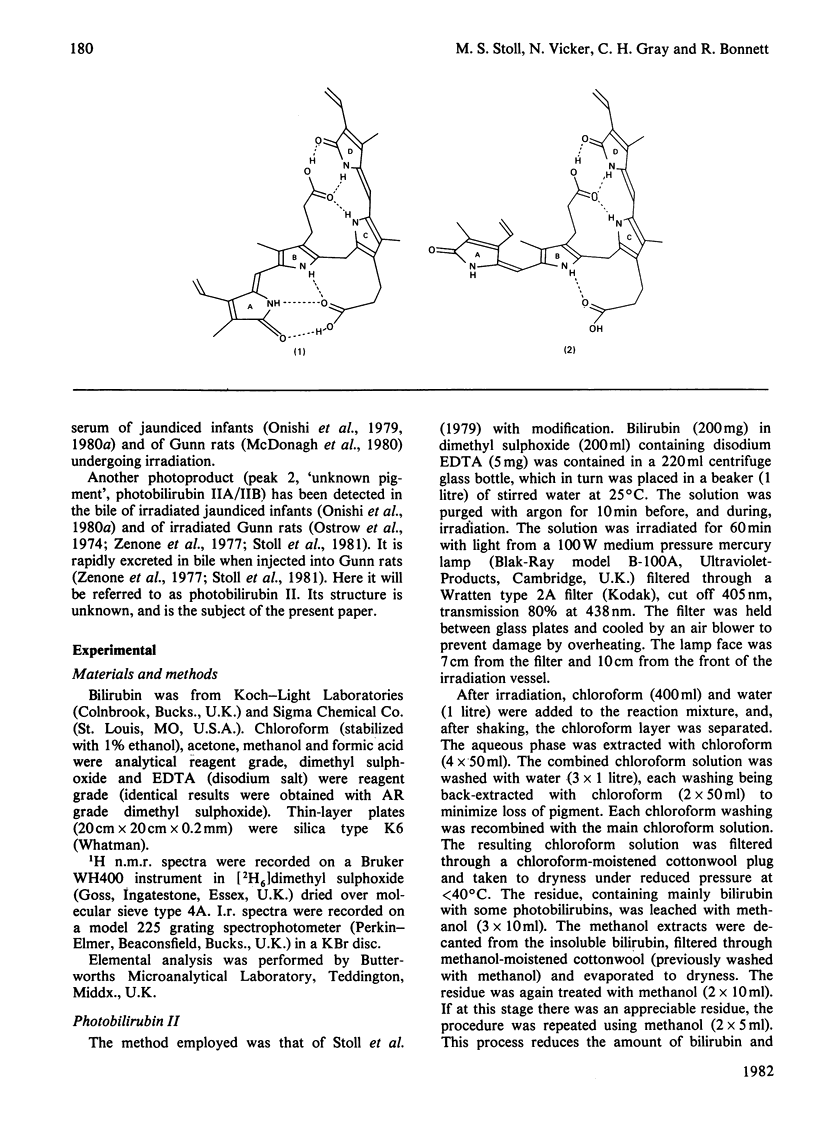
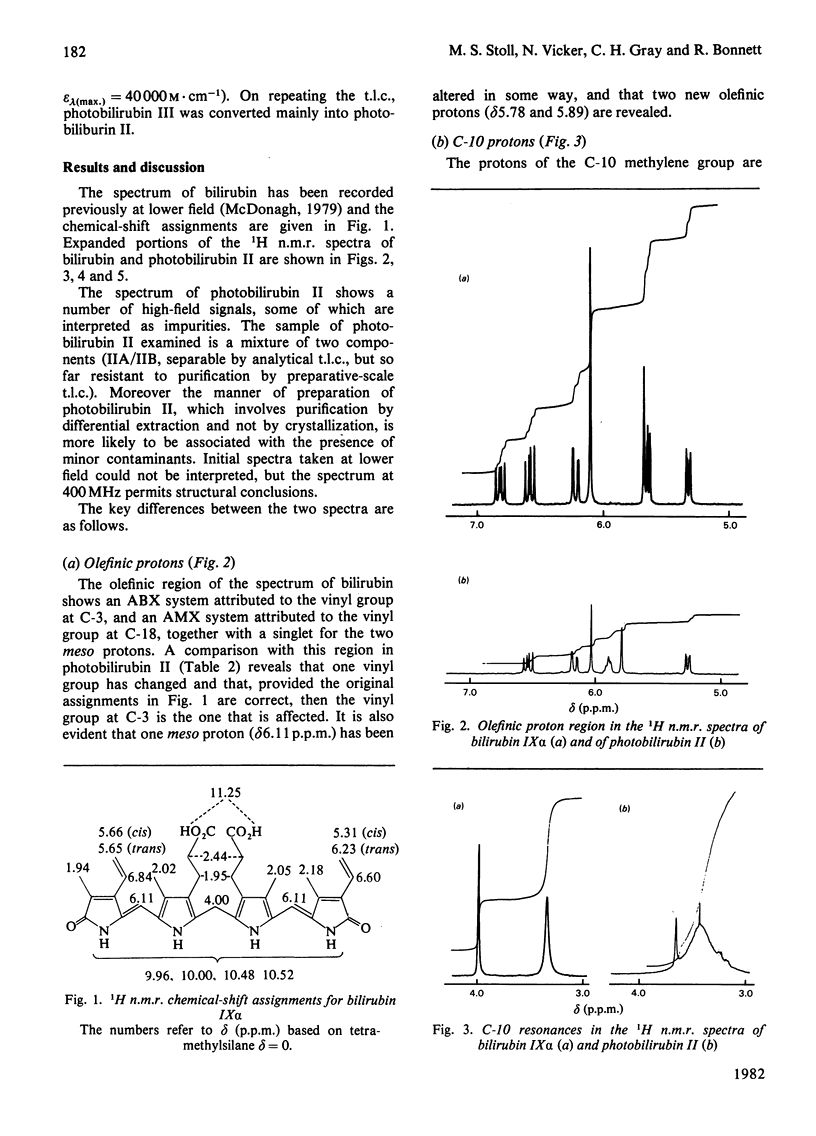
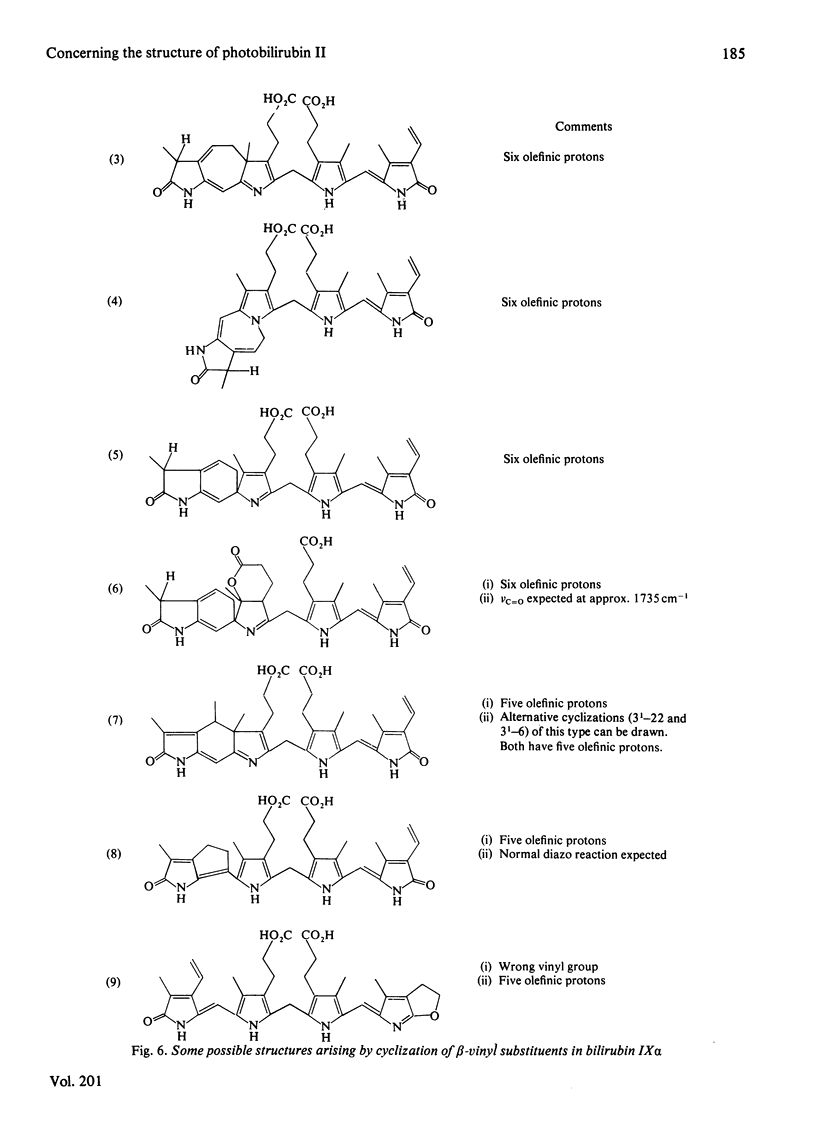
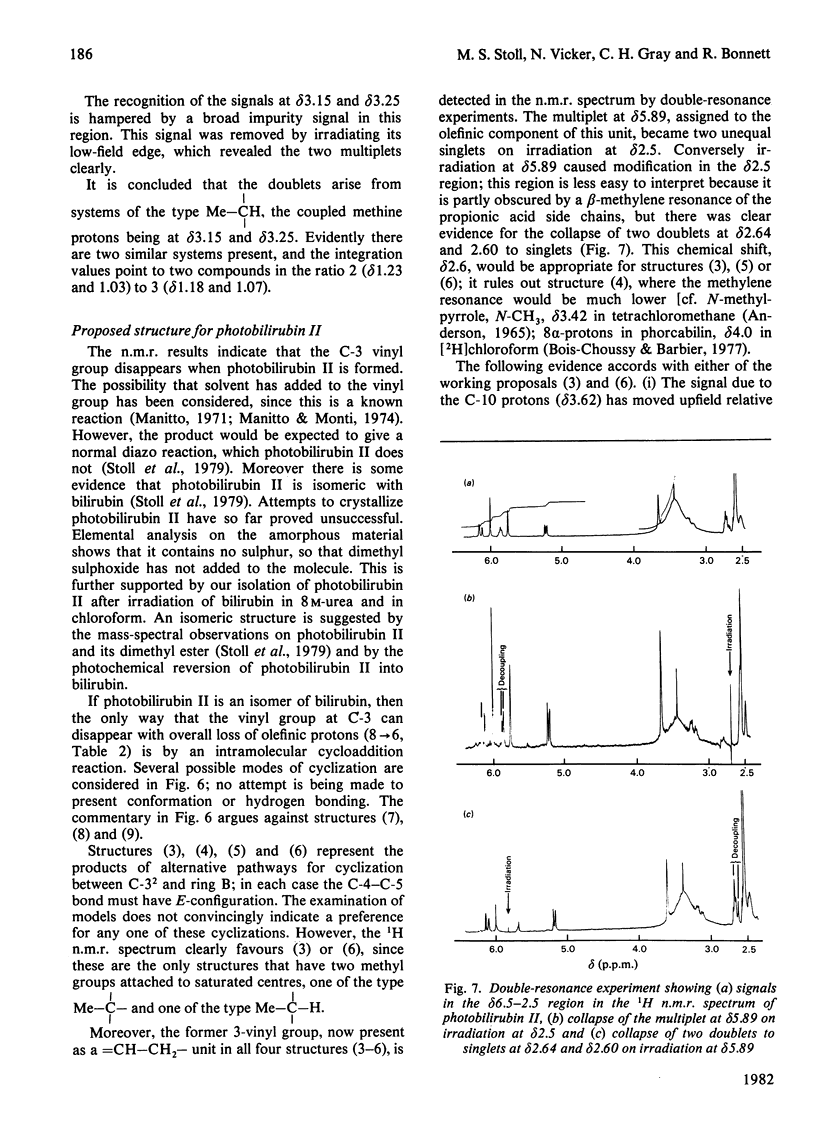
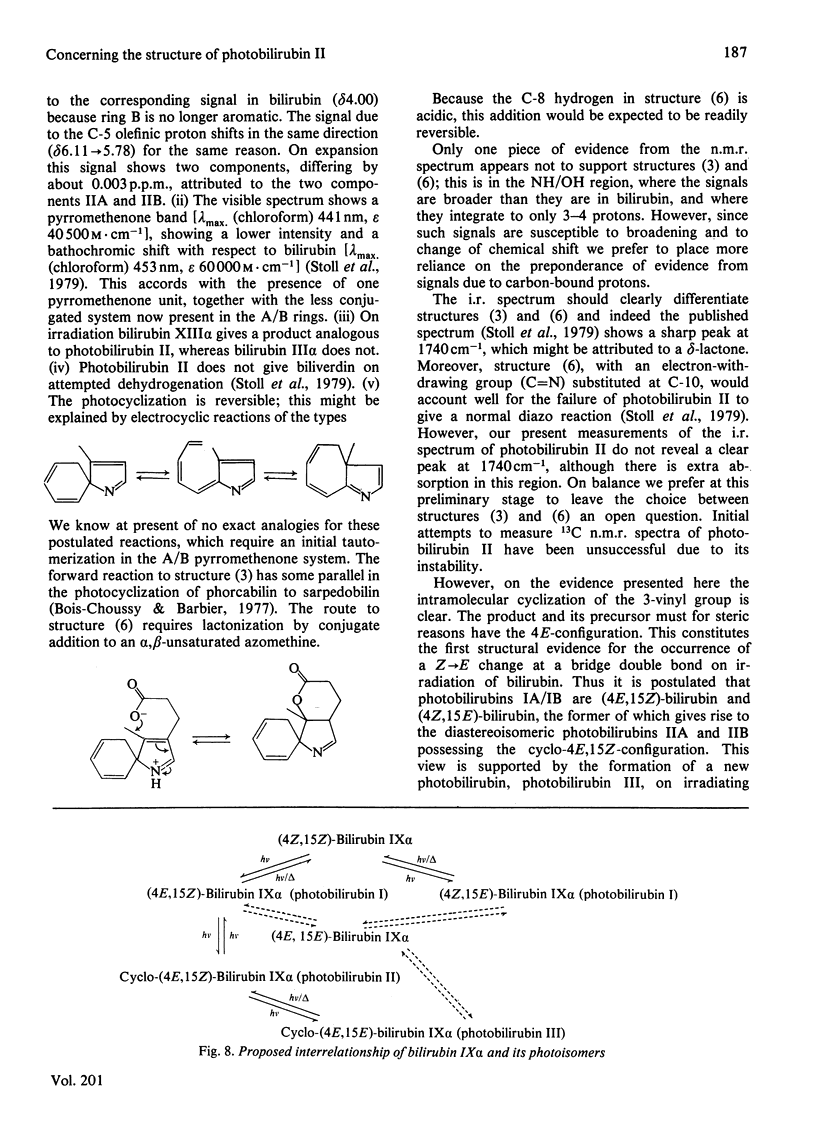
Evidence is presented which supports the postulate that the photobilirubins IIA and IIB are diastereoisomers in which the C-3 vinyl group has cyclized intramolecularly. The evidence comes principally from proton n.m.r. spectroscopy at 400 MHz and from chemical considerations. The cyclic structures require the E-configuration at the C-4 double bond in the precursor; this is the first structural evidence for the Z leads to E isomerization in bilirubin and supports the view that the precursor (photobilirubin IA or IB) is (4E, 15Z)-bilirubin. Brief irradiation of photobilirubin II gives bilirubin, a new compound (photobilirubin III) and unchanged starting material. The various photoisomers are discussed in terms of their inter-relationships and biological fates.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonnett R., Davies J. E., Hursthouse M. B., Sheldrick G. M. The structure of bilirubin. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1978 Jun 23;202(1147):249–268. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1978.0066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnett R., Davies J. E., Hursthouse M. B. Structure of bilirubin. Nature. 1976 Jul 22;262(5566):327–328. doi: 10.1038/262326a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREMER R. J., PERRYMAN P. W., RICHARDS D. H. Influence of light on the hyperbilirubinaemia of infants. Lancet. 1958 May 24;1(7030):1094–1097. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(58)91849-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isobe K., Onishi S. Kinetics of the photochemical interconversion among geometric photoisomers of bilirubin. Biochem J. 1981 Mar 1;193(3):1029–1031. doi: 10.1042/bj1931029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightner D. A., Wooldridge T. A., McDonagh A. F. Configurational isomerization of bilirubin and the mechanism of jaundice phototherapy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jan 30;86(2):235–243. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90857-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightner D. A., Wooldridge T. A., McDonagh A. F. Photobilirubin: an early bilirubin photoproduct detected by absorbance difference spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):29–32. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund H. T., Jacobsen J. Influence of phototherapy on unconjugated bilirubin in duodenal bile of newborn infants with hyperbilirubinemia. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1972 Nov;61(6):693–696. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1972.tb15968.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manitto P. Photochemistry of bilirubin. Experientia. 1971 Oct 15;27(10):1147–1149. doi: 10.1007/BF02286889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonagh A. F., Palma L. A., Lightner D. A. Blue light and bilirubin excretion. Science. 1980 Apr 11;208(4440):145–151. doi: 10.1126/science.7361112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonagh A. F. The role of singlet oxygen in bilirubin photo-oxidation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Sep 17;44(6):1306–1311. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80228-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi S., Isobe K., Itoh S., Kawade N., Sugiyama S. Demonstration of a geometric isomer of bilirubin-IX alpha in the serum of a hyperbilirubinaemic newborn infant and the mechanism of jaundice phototherapy. Biochem J. 1980 Sep 15;190(3):533–536. doi: 10.1042/bj1900533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi S., Itoh S., Kawade N., Isobe K., Sugiyama S. The separation of configurational isomers of bilirubin by high pressure liquid chromatography and the mechanism of jaundice phototherapy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Oct 12;90(3):890–896. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91911-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi S., Kawade N., Itoh S., Isobe K., Sugiyama S. High-pressure liquid chromatographic analysis of anaerobic photoproducts of bilirubin-IX alpha in vitro and its comparison with photoproducts in vivo. Biochem J. 1980 Sep 15;190(3):527–532. doi: 10.1042/bj1900527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrow J. D. Photocatabolism of labeled bilirubin in the congenitally jaundiced (Gunn) rat. J Clin Invest. 1971 Mar;50(3):707–718. doi: 10.1172/JCI106541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligman J. W. Recent and changing concepts of hyperbilirubinemia and its management in the newborn. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1977 Aug;24(3):509–527. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)33461-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll M. S., Gray C. H. The preparation and characterization of bile pigments. Biochem J. 1977 Apr 1;163(1):59–101. doi: 10.1042/bj1630059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll M. S., Zenone E. A., Ostrow J. D. Excretion of administered and endogenous photobilirubins in the bile of the jaundice gunn rat. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jul;68(1):134–141. doi: 10.1172/JCI110229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll M. S., Zenone E. A., Ostrow J. D., Zarembo J. E. Preparation and properties of bilirubin photoisomers. Biochem J. 1979 Oct 1;183(1):139–146. doi: 10.1042/bj1830139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


