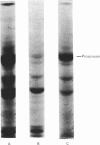
Abstract
Proacrosin, the zymogen precursor of acrosin, was shown to associate with anionic phospholipid membranes through apparent electrostatic charge interactions. This association was diminished by elevated cation concentrations and was dependent on membrane composition, as shown both by direct binding assays and by following the phospholipid stimulation of conversion of proacrosin into acrosin.
Full text
PDF
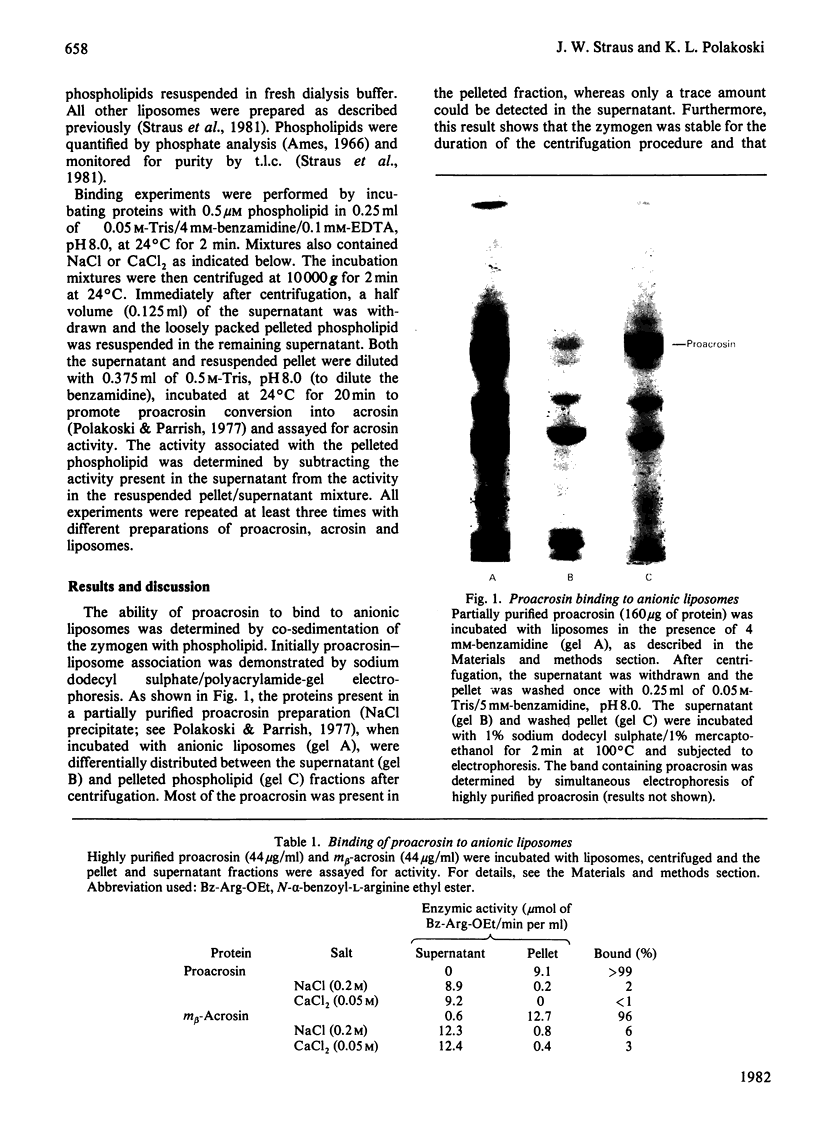
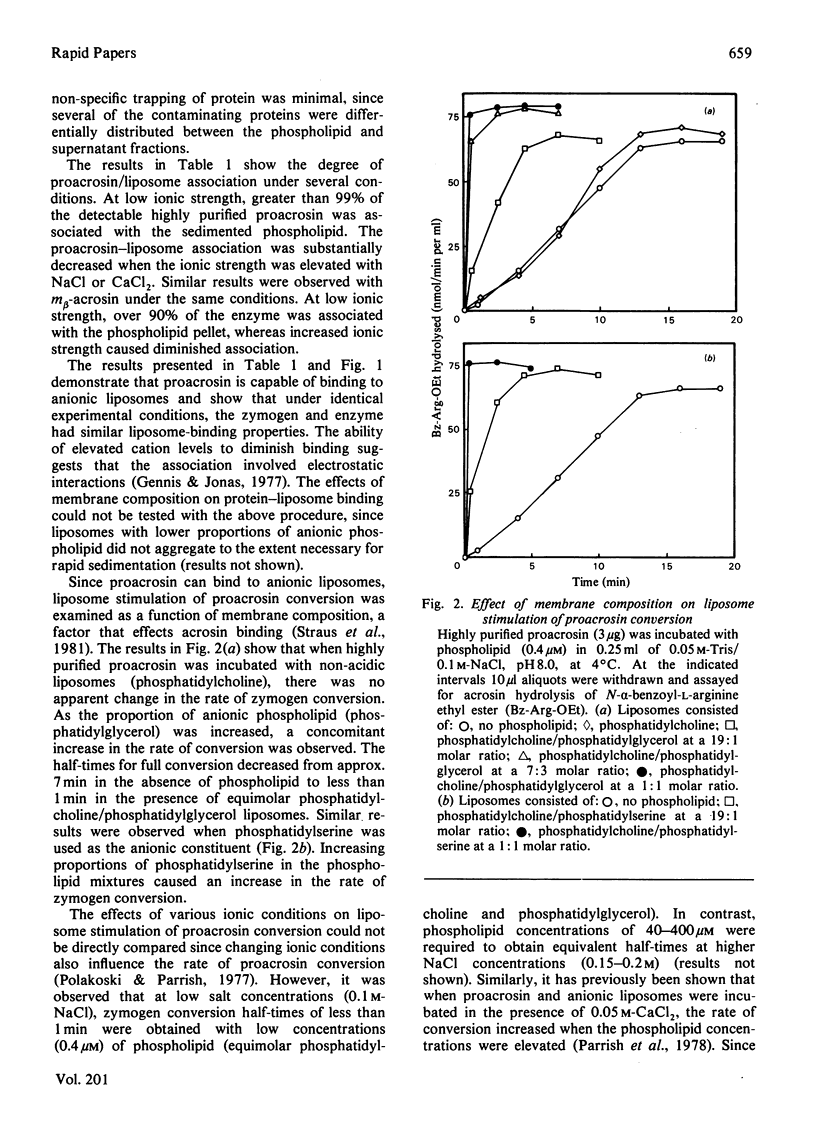

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown C. R., Hartree E. F. Effects of acrosin inhibitors on the soluble and membrane-bound forms of ram acrosin, and a reappraisal of the role of the enzyme in fertilization. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1976 Jan;357(1):57–65. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1976.357.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gennis R. B. Protein-lipid interactions. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1977;6:195–238. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.06.060177.001211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nohmi M., Kuriyama H. Topical difference of myosin B. extracted from smooth muscle of the rabbit stomach, in ATPase activity and rate of superprecipitation. Int J Biochem. 1979;10(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(79)90136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D., Vail W. J., Pangborn W. A., Poste G. Studies on membrane fusion. II. Induction of fusion in pure phospholipid membranes by calcium ions and other divalent metals. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 5;448(2):265–283. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90241-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrish R. F., Polakoski K. L. Effect of polyamines on the activity of acrosin and the activation of proacrosin. Biol Reprod. 1977 Oct;17(3):417–422. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod17.3.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrish R. F., Straus W., Polakoski K. L., Dombrose F. A. Phospholipid vesicle stimulation of proacrosin activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):149–152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polakoski K. L., Parrish R. F. Boar proacrosin. Purification and preliminary activation studies of proacrosin isolated from ejaculated boar sperm. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):1888–1894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus J. W., Parrish R. F., Polakoski K. L. Boar acrosin. Association of an endogenous membrane proteinase with phospholipid membranes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5662–5668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahler W. L., Polakoski K. L. Benzamidine as an inhibitor of proacrosin activation in bull sperm. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Feb 9;480(2):461–468. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]