Abstract
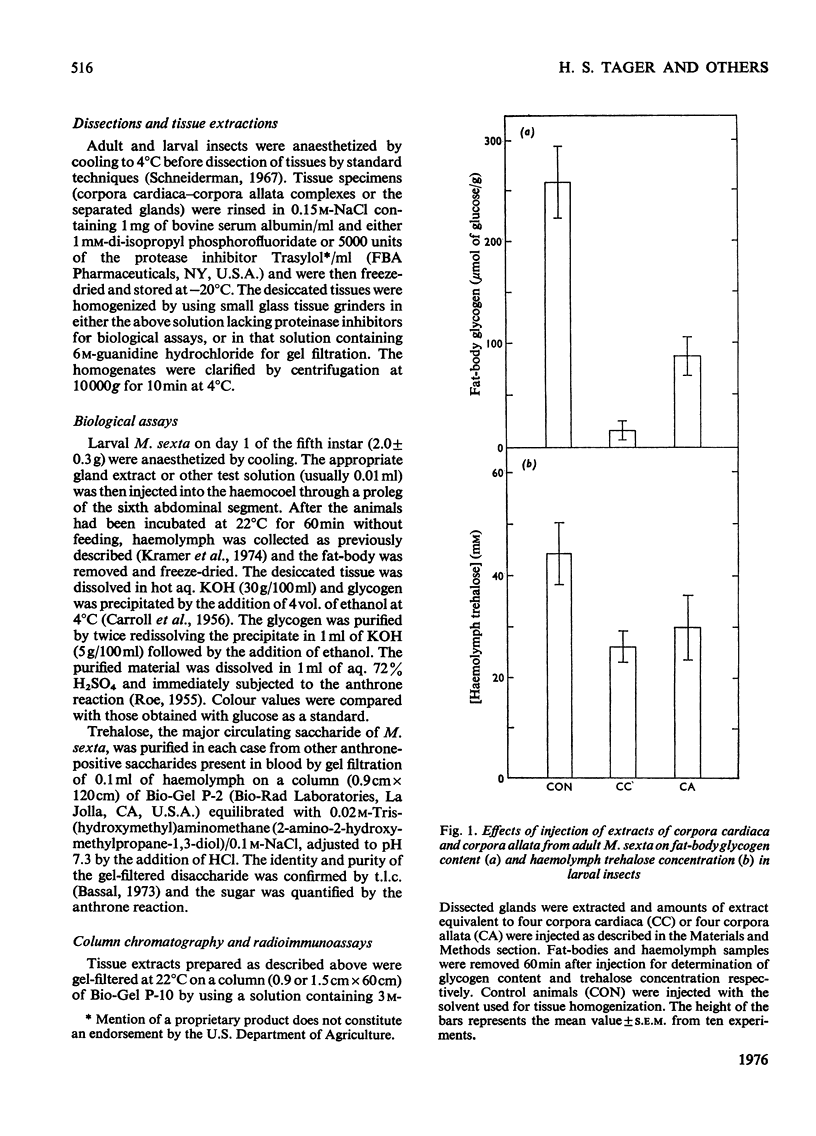
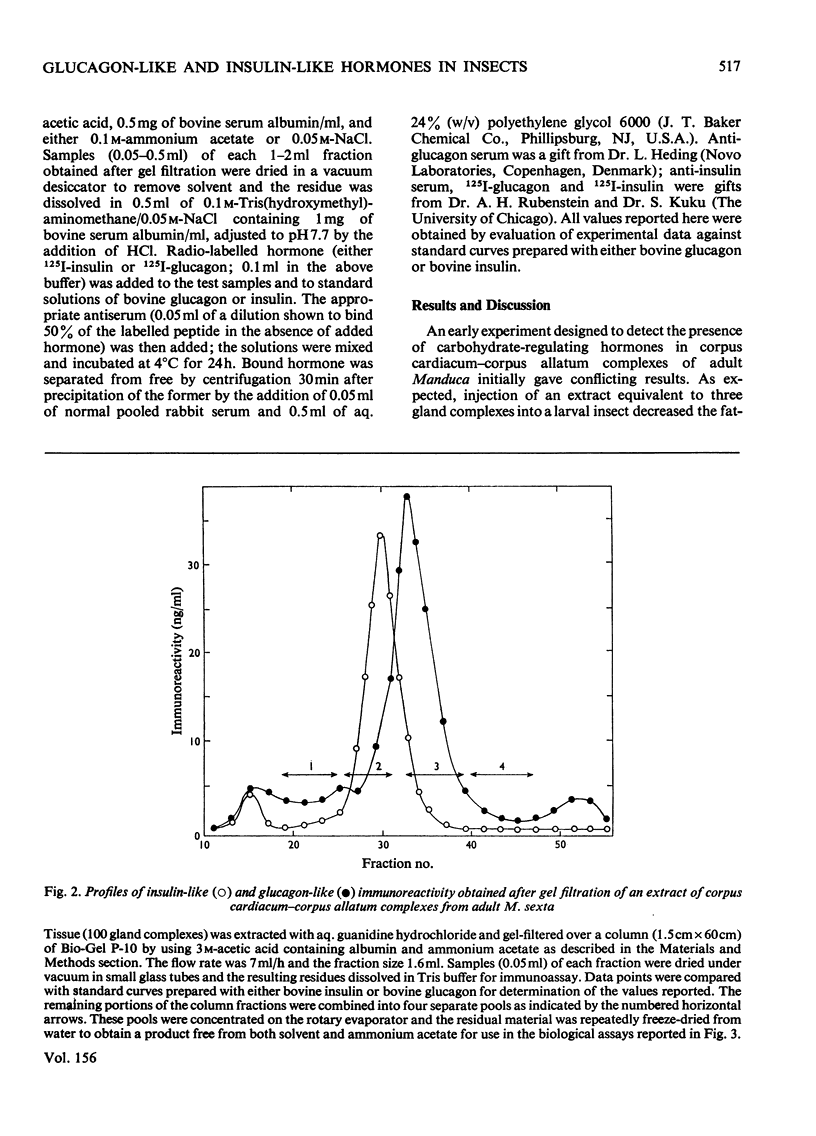
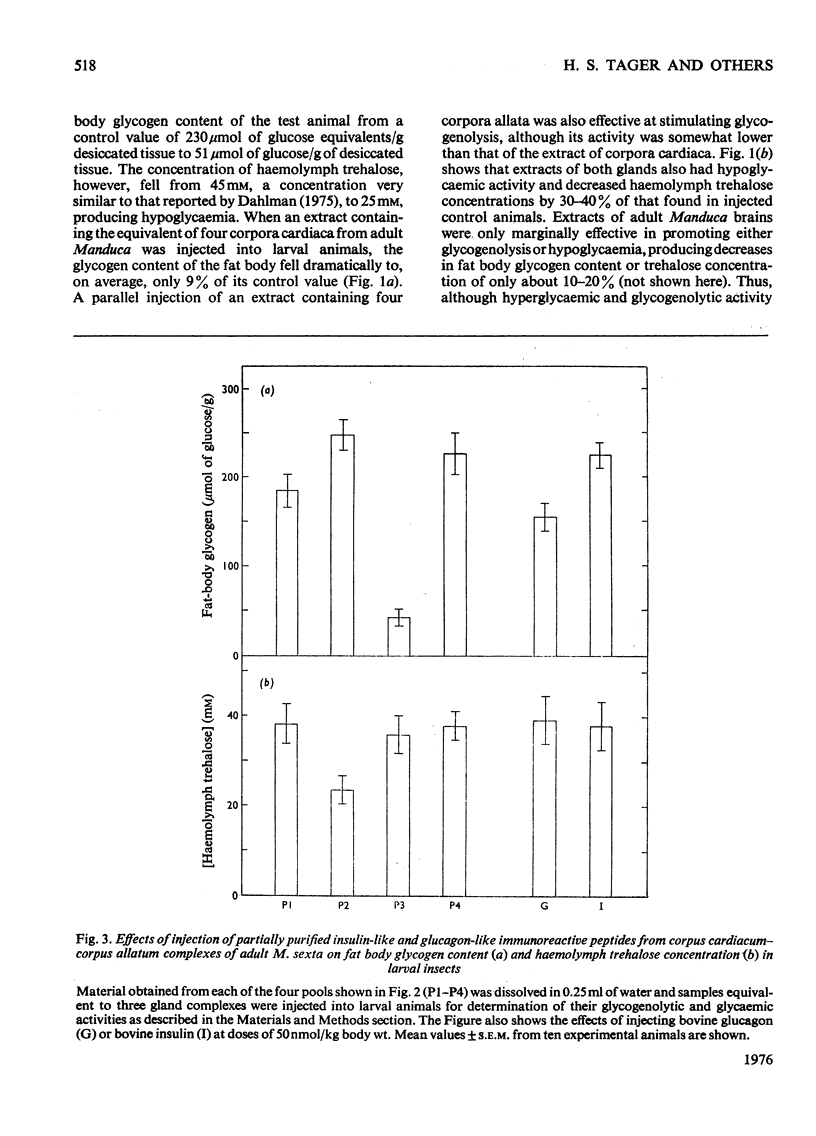
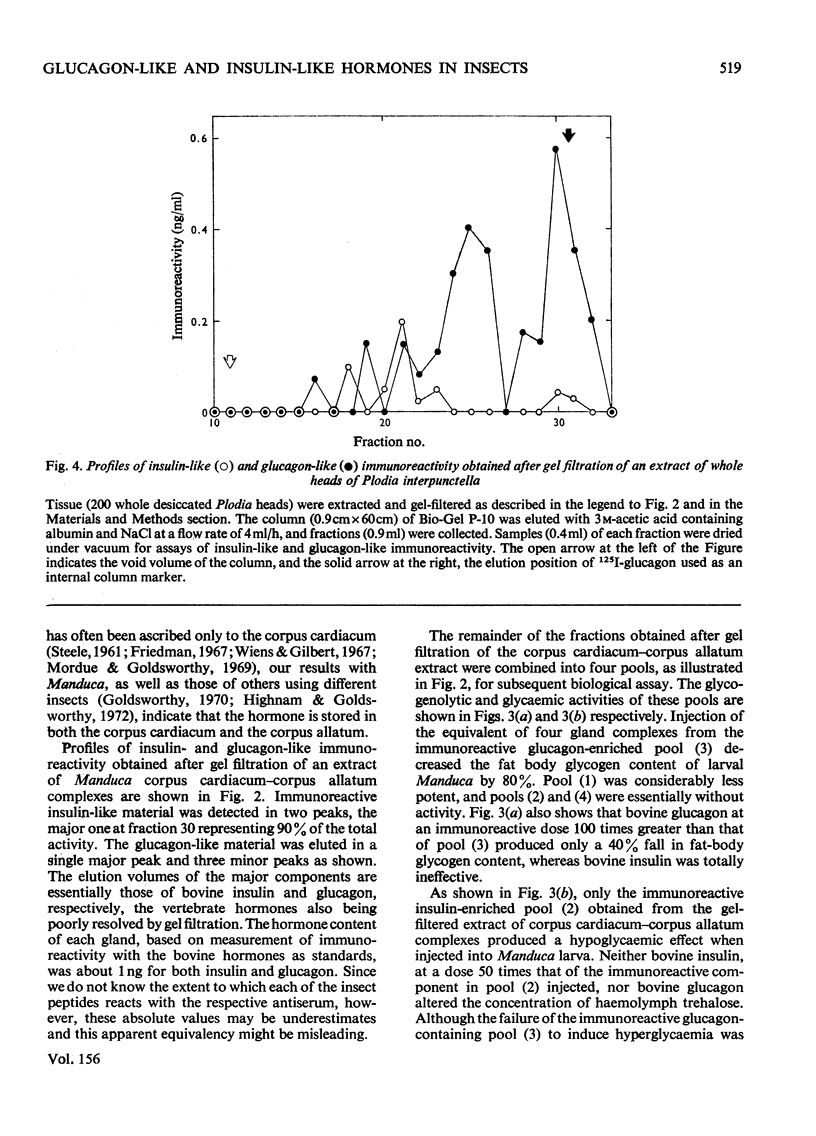
Aqueous extracts of corpus cardiacum-corpus allatum complexes of the adult tobacco hornworm Manduca sexta produced both glycogenolysis and hypoglycaemia when injected into the larval form of the same species. Application of specific radioimmuno assays to similar extracts showed also that these gland complexes contain both glucagon-like and insulin-like peptides. Further, the partially purified immunoreactive peptides had the expected biological activities. The former decreased the glycogen content of the fatbody and the latter the circulating trehalose levels in recipient animals. These results suggest the existence of hormones in these invertebrates having both biological and structural similarities to vertebrate insulin and glucagon.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bassal T. T. Detection on silicic acid chromatograms of trehalose and other sugars in arthropod fluids. J Med Entomol. 1973 Apr 25;10(2):228–228. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/10.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. E. Pharmacologically active constituents of the cockroach corpus cardacum: resolution and some characteristics. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1965 Aug;5(4):387–401. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(65)90099-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARROLL N. V., LONGLEY R. W., ROE J. H. The determination of glycogen in liver and muscle by use of anthrone reagent. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jun;220(2):583–593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXIT P. K., PATEL N. G. INSULIN-LIKE ACTIVITY IN LARVAL FOODS OF THE HONEYBEE. Nature. 1964 Apr 11;202:189–190. doi: 10.1038/202189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlman D. L. Trehalose and glucose levels in hemolymph of diet-reared, tobacco leaf-reared and parasitized tobacco hornworm larvae. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1975 Jan 1;50(1A):165–167. doi: 10.1016/s0010-406x(75)80220-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S. The control of trehalose synthesis in the blowfly, Phormia regina Meig. J Insect Physiol. 1967 Jan;13(3):397–405. doi: 10.1016/0022-1910(67)90080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsworthy G. J., Mordue W. Neurosecretory hormones in insects. J Endocrinol. 1974 Mar;60(3):529–558. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0600529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsworthy G. J. The action of hyperglycaemic factors from the corpus cardiacum of Locusta migratoria on glycogen phosphorylase. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1970 Feb;14(1):78–85. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(70)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highnam K. C., Goldsworthy G. J. Regenerated corpora cardiaca and hyperglycemic factor in Locusta migratoria. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1972 Feb;18(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(72)90083-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer K. J., Sanburg L. L., Kézdy F. J., Law J. H. The Juvenile Hormone Binding Protein in the Hemolymph of Manduca sexta Johannson (Lepidoptera: Sphingidae). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):493–497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meneses P., De Los Angeles Ortíz M. A protein extract from Drosophila melanogaster with insulin-like activity. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1975 Jun 1;51(2):483–485. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(75)90398-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mordue W., Goldsworthy G. J. The physiological effects of corpus cardiacum extracts in locusts. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1969 Apr;12(2):360–369. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(69)90208-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normann T. C., Duve H. Experimentally induced release of a neurohormone influencing hemolymph trehalose level in Calliphora erythrocephala (Diptera). Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1969 Jun;12(3):449–459. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(69)90161-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normann T. C. Neurosecretory cells in insect brain and production of hypoglycaemic hormone. Nature. 1975 Mar 20;254(5497):259–261. doi: 10.1038/254259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROE J. H. The determination of sugar in blood and spinal fluid with anthrone reagent. J Biol Chem. 1955 Jan;212(1):335–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seecof R. L., Dewhurst S. Insulin is a Drosophila hormone and acts to enhance the differentiation of embryonic Drosophila cells. Cell Differ. 1974 Jun;3(1):63–70. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(74)90041-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tager H. S., Markese J., Spiers R. D., Kramer K. J. Glucagon-like immunoreactivity in insect corpus cardiacum. Nature. 1975 Apr 24;254(5502):707–708. doi: 10.1038/254707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vejbjerg K., Normann T. C. Secretion of hyperglycaemic hormone from the corpus cardiacum of flying blowflies, Calliphora erythrocephala. J Insect Physiol. 1974 Jul;20(7):1189–1192. doi: 10.1016/0022-1910(74)90224-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiens A. W., Gilbert L. I. Regulation of carbohydrate mobilization and utilization in Leucophaea maderae. J Insect Physiol. 1967 May;13(5):779–794. doi: 10.1016/0022-1910(67)90126-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


