Abstract
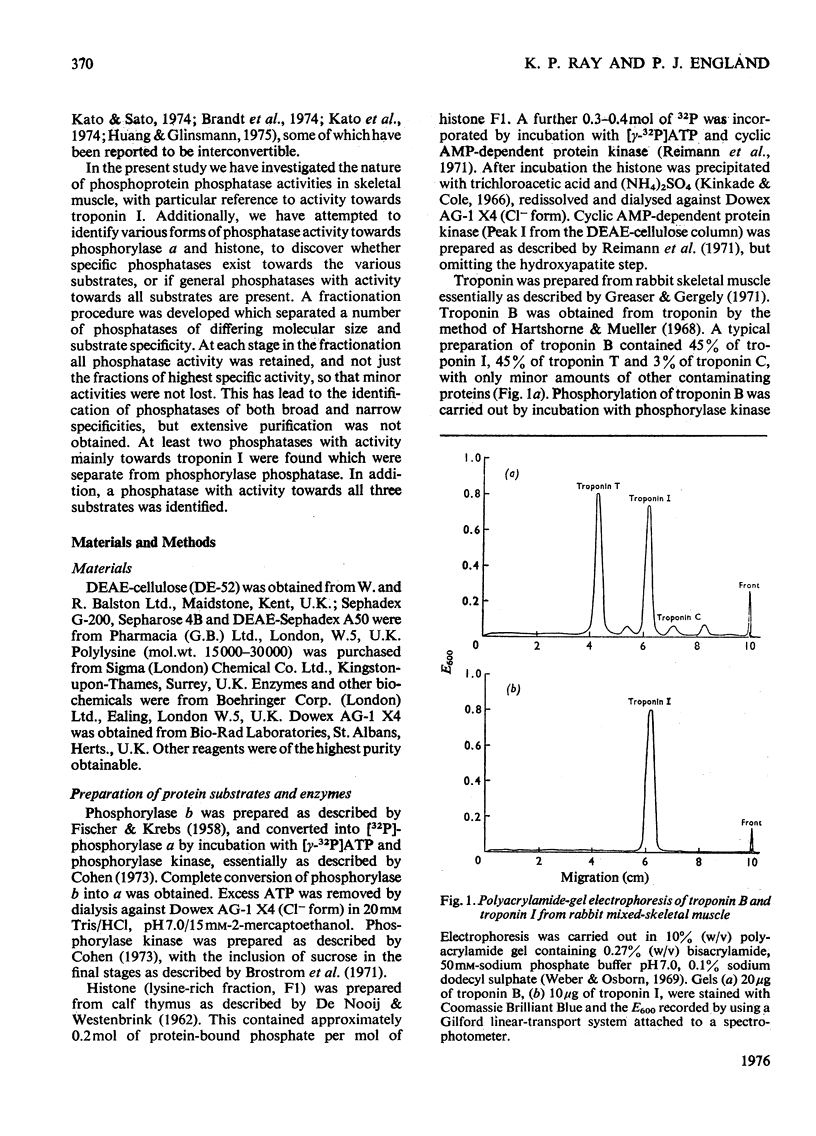
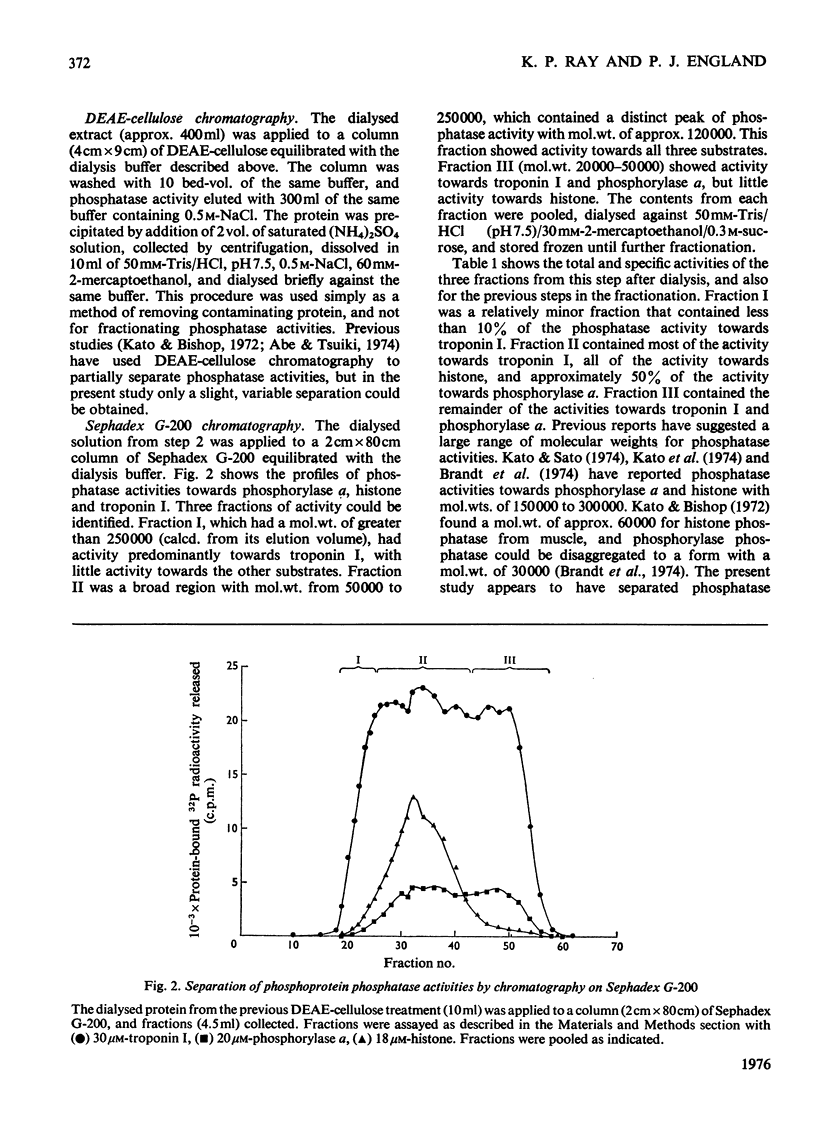
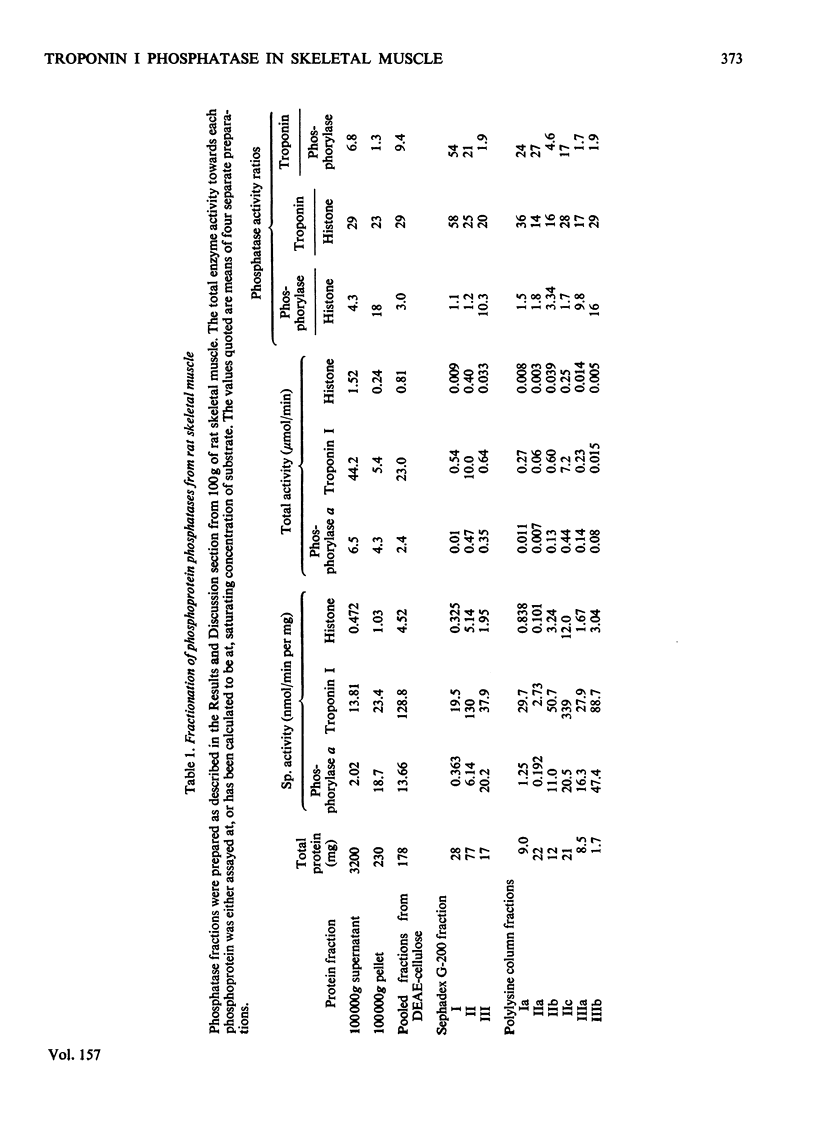
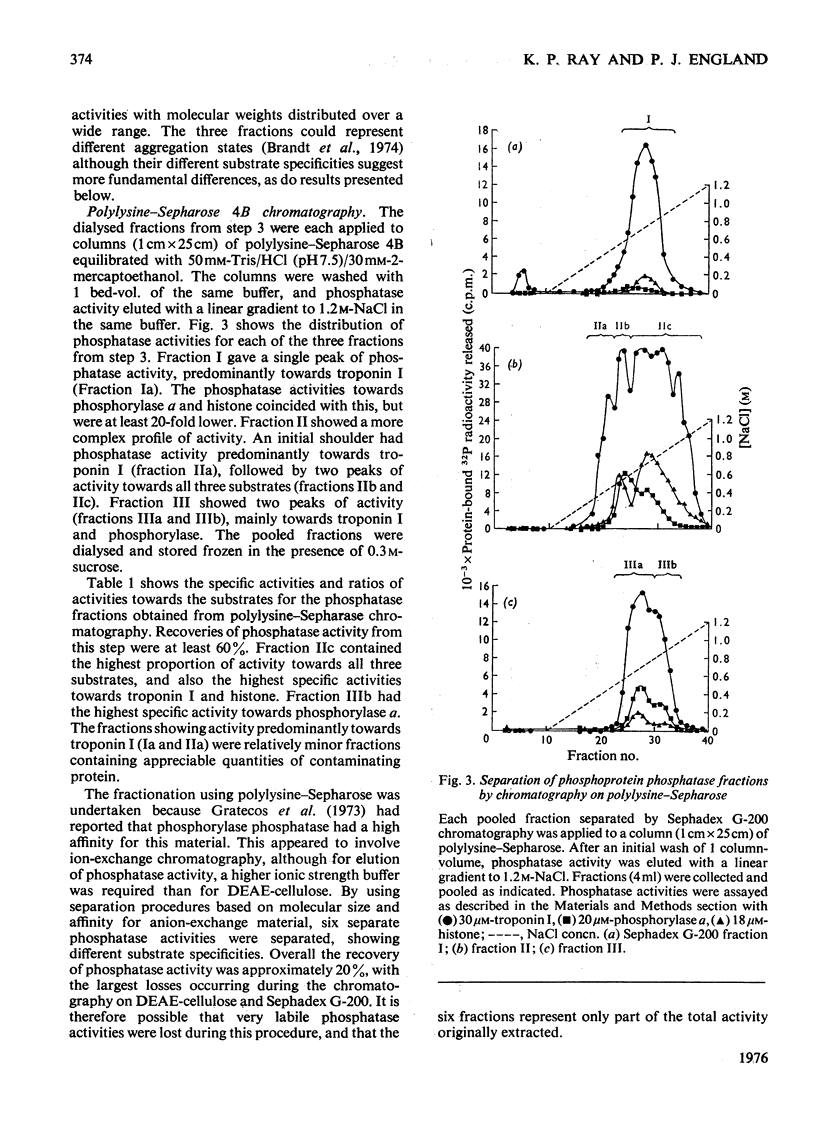
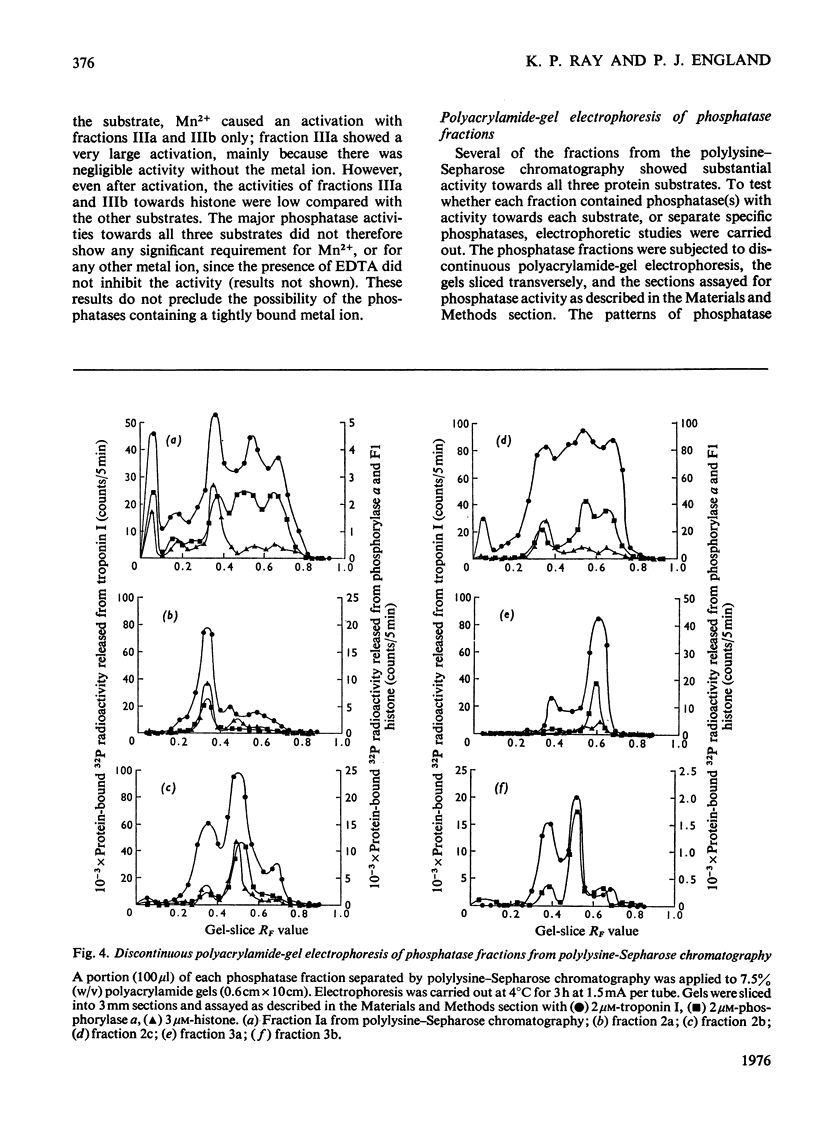
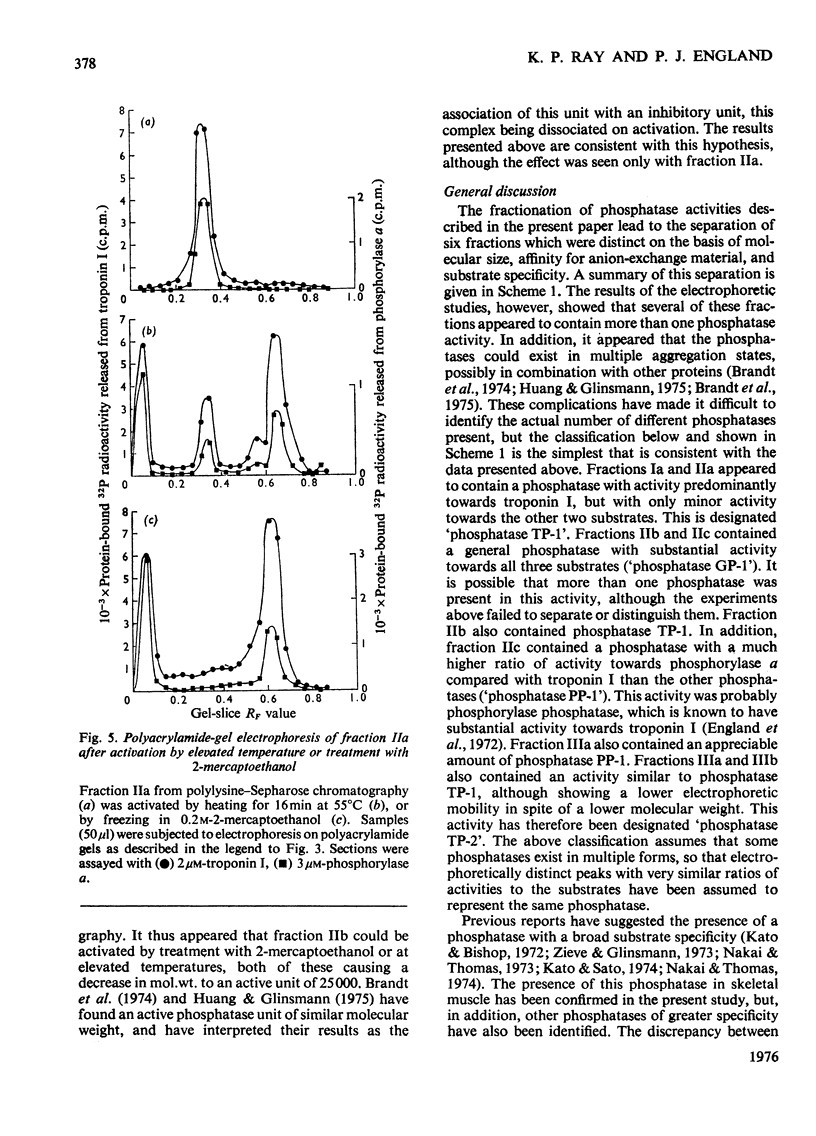
1. Phosphoprotein phosphatases with activity towards the inhibitory subunit of troponin (troponin I), phosphorylase a and lysine-rich histone (fraction F1) have been fractionated from rat skeletal muscle by chromatography on Sephadex G-200 and polylysine-Sepharose. Six separate fractions were identified on the basis of substrate specificity and behaviour during chromatography. 2. All fractions showed similar Km values for any given protein substrate. The Km for troponin I (5 muM) was significantly lower than that previously reported. 3. Phosphatase activities towards troponin I and hosphorylase a did not show a requirement for bivalent-metal ions. Two of the fractions with only minor activity towards histone were activated by Mn2+. 4. Discontinuous polyacrylamide-gel-electrophoresis studies indicated that several of the fractions contained more than one phosphatase activity, and additionally showed that several of the activities could exist in different aggregation states. On the basis of these studies at least two phosphatases with activity only towards troponin I were identified. In addition, phosphorylase phosphatase (which has considerable activity towards troponin I) and a general phosphatase with activity towards all three substrates were found. 5. A fraction with mol.wt. of 150000 could be activated by freezing with 2-mercaptoethanol or by heating to 55 degrees C. This activation was accompanied by a decrease in mol.wt. to 25000. 6. The total amount of phosphatase with activity towards troponin I which was extracted would be sufficient to dephosphorylate all the troponin I present in skeletal muscle in approximately 10s.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe N., Tsuiki S. Studies on glycogen synthase D phosphatase of rat liver--multiple nature. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jun 18;350(2):383–391. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90512-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antoniw J. F., Cohen P. Separation of two phosphorylase kinase phosphatase activities in rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochem Soc Trans. 1975;3(1):83–84. doi: 10.1042/bst0030083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt H., Killilea S. D., Lee E. Y. Activation of phosphorylase phosphatase by a novel procedure: evidence for a regulatory mechanism involving the release of a catalytic subunit from enxyme-inhibitor complex(es) of higher molecular weight. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Nov 27;61(2):598–604. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90999-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt H., Lee E. Y., Killilea S. D. A protein inhibitor of rabbit liver phosphorylase phosphatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Apr 21;63(4):950–956. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90661-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostrom C. O., Hunkeler F. L., Krebs E. G. The regulation of skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase by Ca2+. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):1961–1967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland W. W. The statistical analysis of enzyme kinetic data. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1967;29:1–32. doi: 10.1002/9780470122747.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The subunit structure of rabbit-skeletal-muscle phosphorylase kinase, and the molecular basis of its activation reactions. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Apr 2;34(1):1–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole H. A., Perry S. V. The phosphorylation of troponin I from cardiac muscle. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;149(3):525–533. doi: 10.1042/bj1490525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England P. J. Correlation between contraction and phosphorylation of the inhibitory subunit of troponin in perfused rat heart. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jan 15;50(1):57–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)81040-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England P. J., Stull J. T., Krebs E. G. Dephosphorylation of the inhibitor component of troponin by phosphorylase phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5275–5277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISCHER E. H., KREBS E. G. The isolation and crystallization of rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase b. J Biol Chem. 1958 Mar;231(1):65–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Chappell J. B. A simple method for the preparation of 32-P-labelled adenosine triphosphate of high specific activity. Biochem J. 1964 Jan;90(1):147–149. doi: 10.1042/bj0900147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaser M. L., Gergely J. Reconstitution of troponin activity from three protein components. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4226–4233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne D. J., Mueller H. Fractionation of troponin into two distinct proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jun 10;31(5):647–653. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90610-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haschke R. H., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr, Meyer F., Fischer E. H. Control of phosphorylase activity in a muscle glycogen particle. 3. Regulation of phosphorylase phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1970 Dec 25;245(24):6657–6663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang F. L., Glinsmann W. H. Inactivation of rabbit muscle phosphorylase phosphatase by cyclic AMP-dependent kinas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3004–3008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. S., Bylund D. B., Stull J. T., Krebs E. G. The amino acid sequences of the phosphorylated sites in troponin-I from rabbit skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1974 Jun 15;42(3):249–252. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80738-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itaya K., Ui M. A new micromethod for the colorimetric determination of inorganic phosphate. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Sep;14(3):361–366. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K., Bishop J. S. Glycogen synthetase-D phosphatase. I. Some new properties of the partially purified enzyme from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7420–7429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K., Kobayashi M., Sato S. Multiple molecular forms of phosphoprotein phosphatase. II. Dissociation and activation of phosphorylase phosphatase from rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 5;371(1):89–101. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90158-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinkade J. M., Jr, Cole R. D. The resolution of four lysine-rich histones derived from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 25;241(24):5790–5797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayaski M., Kato K., Sato S. Multiple molecular forms of phosphoprotein phosphatase. III. Phosphorylase phosphatase and phosphohistone phosphatase of rabbit liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 19;377(2):343–355. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90315-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer F., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr, Haschke R. H., Fischer E. H. Control of phosphorylase activity in a muscle glycogen particle. I. Isolation and characterization of the protein-glycogen complex. J Biol Chem. 1970 Dec 25;245(24):6642–6648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moir A. J., Wilkinson J. M., Perry S. V. The phosphorylation sites of troponin I from white skeletal muscle of the rabbit. FEBS Lett. 1974 Jun 15;42(3):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80739-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai C., Thomas J. A. Properties of a phosphoprotein phosphatase from bovine heart with activity on glycogen synthase, phosphorylase, and histone. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 25;249(20):6459–6467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai C., Thomas J. A. Substrate specificity of glycogen synthase phosphatase from bovine heart: action on phosphorylase a and histone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 15;52(2):530–536. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90744-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry S. V., Cole H. A. Phosphorylation of the "37000 component" of the troponin complex (troponin-t). Biochem J. 1973 Feb;131(2):425–428. doi: 10.1042/bj1310425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porath J., Axen R., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of proteins to agarose. Nature. 1967 Sep 30;215(5109):1491–1492. doi: 10.1038/2151491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratje E., Heilmeyer L. M.G. Phosphorylation of rabbit muscle troponin and actin by a 3', 5'-c-AMP-dependent protein kinase. FEBS Lett. 1972 Oct 15;27(1):89–93. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80416-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy Y. S., Ballard D., Giri N. Y., Schwartz A. Phosphorylation of cardiac native tropomyosin and troponin: inhibitory effect of actomyosin and possible presence of endogenous myofibrillar-located cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1973 Oct;5(5):461–471. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(73)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimann E. M., Walsh D. A., Krebs E. G. Purification and properties of rabbit skeletal muscle adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):1986–1995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull J. T., Brostrom C. O., Krebs E. G. Phosphorylation of the inhibitor component of troponin by phosphorylase kinase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5272–5274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve F. J., Glinsmann W. H. Activation of glycogen synthetase and inactivation of phosphorylase kinase by the same phosphoprotein phosphatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Feb 5;50(3):872–878. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91326-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de NOOIJ E., WESTENBRINK H. G. Isolation of a homogeneous lysine-rich histone from calf thymus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Aug 27;62:608–609. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90254-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


