Abstract
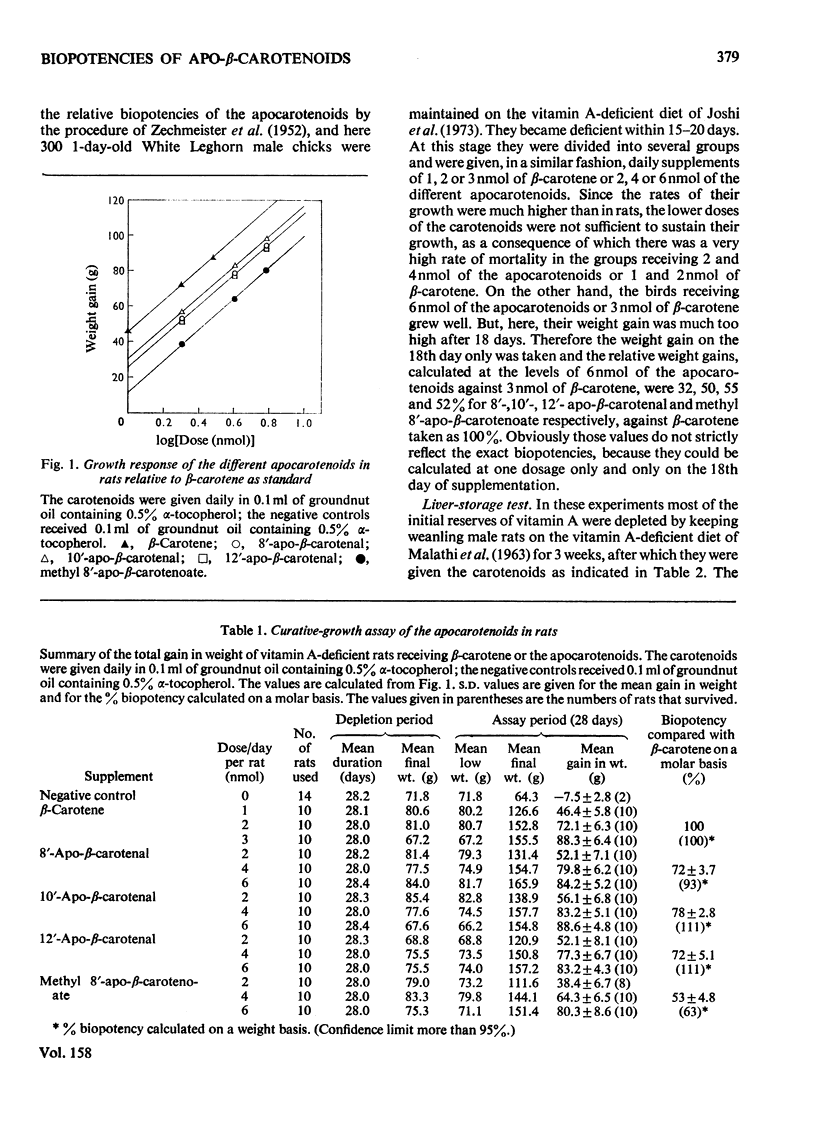
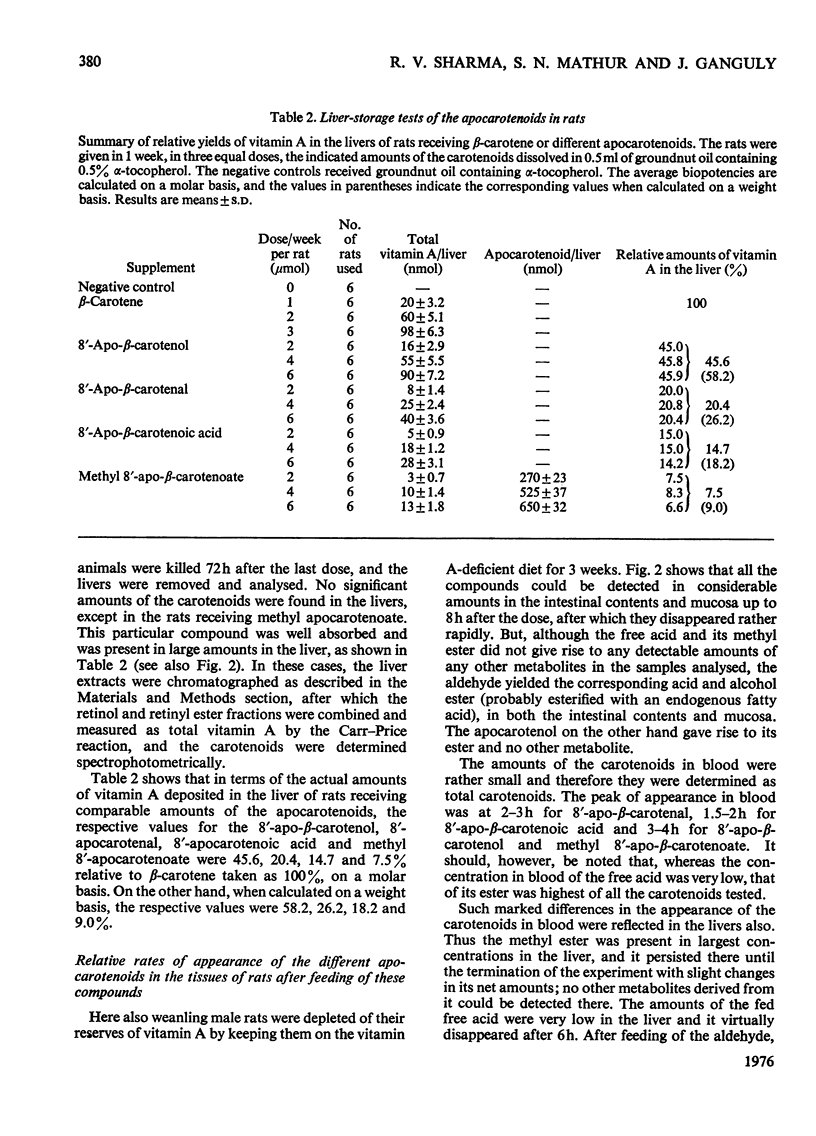
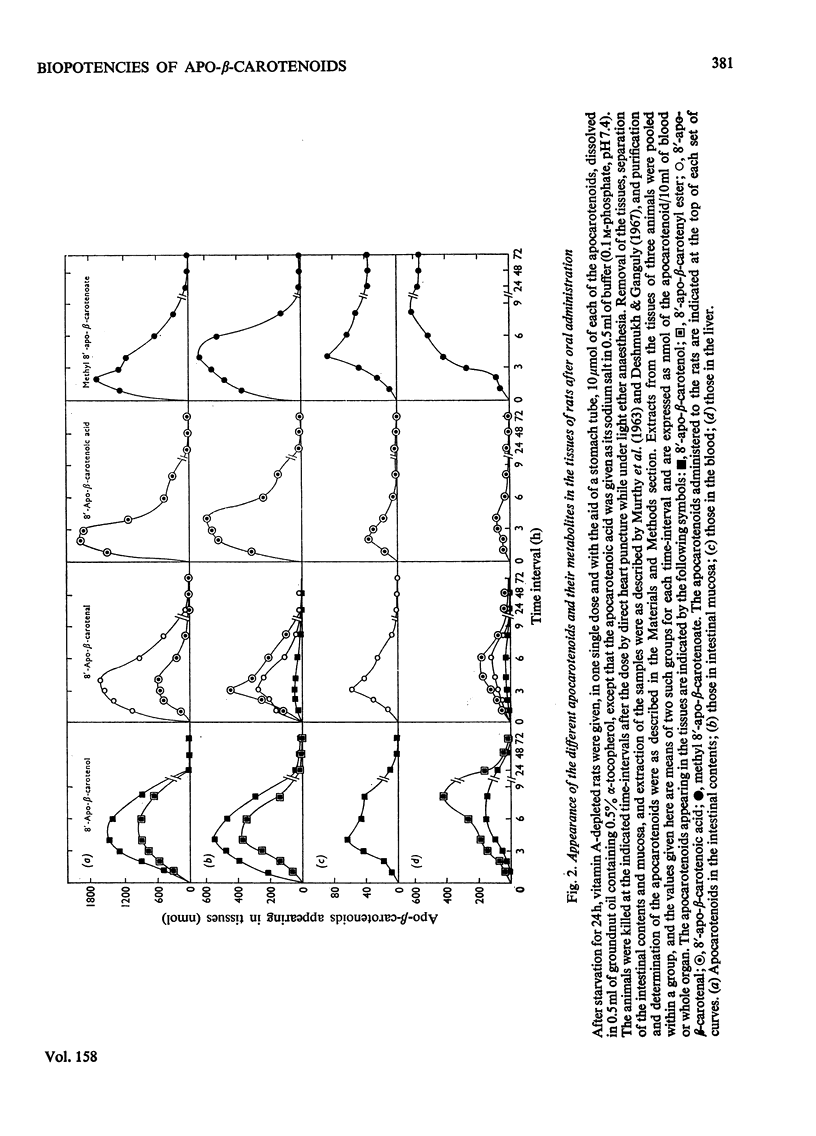
1. The biopotencies relative to beta-carotene of several apocarotenoids, such as 8'-, 10'- and 12'-apo-beta-carotenal and methyl 8'-apo-beta-carotenoate, were investigated in rats, on a molar basis, by both curative-growth assay and liver-storage tests. 2. In the curative-growth assays, on a molar basis the biopotencies of 8'-, 10'- and 12'-apo-beta-carotenal and methyl 8'-apo-beta-carotenoate were 72, 78, 72 and 53% respectively, whereas on a weight basis the corresponding values were 93, 111, 111 and 63%, with respect to beta-carotene taken as 100%. In terms of yield of vitamin A, these values were much lower in the liver-storage tests. 3. When 8'-apo-beta-carotenal was fed, the unchanged aldehyde together with small amounts of the corresponding alcohol and larger proportions of the acid rapidly appeared in the tissues of both rats and chickens. The 8'-apocarotenol, 8'-apocarotenoic acid and its methyl ester were absorbed unchanged. The free acid disappeared most rapidly from the tissues, but its methyl ester persisted in the tissues longest. 4. On the basis of these observations it is suggested that most of an apocarotenal is oxidized to the corresponding acid, which, in turn, is mostly degraded to retinoic acid, with small proportions of it being attacked by the dioxygenase system giving retinal.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURNS M. J., HAUGE S. M., QUACKENBUSH F. W. Utilization of vitamin A and carotene by the rat. I. Effects of tocopherol, Tween and dietary fat. Arch Biochem. 1951 Feb;30(2):341–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball S., Goodwin T. W., Morton R. A. Studies on vitamin A: 5. The preparation of retinene(1)-vitamin A aldehyde. Biochem J. 1948;42(4):516–523. doi: 10.1042/bj0420516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barua A. B., Ghosh M. C., Goswami K. Oxidative esterification of retinal and 3-dehydroretinal to methyl esters of retinoic acid and 3-dehydroretinoic acid. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(2):447–447. doi: 10.1042/bj1130447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEUEL H. J., Jr, GANGULY J., WALLCAVE L., ZECHMEISTER L. Provitamin A activity of a structural isomer of cryptoxanthin and its methyl ether. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1953 Dec;47(2):237–240. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(53)90463-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshmukh D. S., Ganguly J. Demonstration of oxidation & reduction of retinal in rat intestine. Indian J Biochem. 1967 Mar;4(1):18–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidge N. H., Smith F. R., Goodman D. S. Vitamin A and carotenoids. The enzymic conversion of beta-carotene into retinal in hog intestinal mucosa. Biochem J. 1969 Oct;114(4):689–694. doi: 10.1042/bj1140689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GANGULY J., KRISHNAMURTHY S., MAHADEVAN S. The transport of carotenoids, vitamin A and cholesterol across the intestines of rats and chickens. Biochem J. 1959 Apr;71(4):756–762. doi: 10.1042/bj0710756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLOVER J. The conversion of beta-carotene into vitamin A. Vitam Horm. 1960;18:371–386. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60869-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLOVER J. The conversion of beta-carotene into vitamin A. Vitam Horm. 1960;18:371–386. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60869-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman D. S., Huang H. S., Shiratori T. Mechanism of the biosynthesis of vitamin A from beta-carotene. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 10;241(9):1929–1932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi P. S., Mathur S. N., Murthy S. K., Ganguly J. Vitamin A economy of the developing chick embryo and of the freshly hatched chick. Biochem J. 1973 Nov;136(3):757–761. doi: 10.1042/bj1360757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmanan M. R., Chansang H., Olson J. A. Purification and properties of carotene 15,15'-dioxygenase of rabbit intestine. J Lipid Res. 1972 Jul;13(4):477–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmanan M. R., Pope J. L., Olson J. A. The specificity of a partially purified carotenoid cleavage enzyme of rabbit intestine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Oct 24;33(2):347–352. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90791-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAHADEVAN S., KRISHNAMURTHY S., GANGULY J. The mode of absorption of vitamin A across the intestine of rats. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Aug;83:371–375. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90045-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAHADEVAN S., MURTHY S. K., KRISHNAMURTHY S., GANGULY J. Studies on vitamin A esterase. 4. The hydrolysis and synthesis of vitamin A esters by rat intestinal mucosae. Biochem J. 1961 May;79:416–424. doi: 10.1042/bj0790416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAHADEVAN S., SASTRY P. S., GANGULY J. STUDIES ON METABOLISM OF VITAMIN A. 3. THE MODE OF ABSORPTION OF VITAMIN A ESTERS IN THE LIVING RAT. Biochem J. 1963 Sep;88:531–534. doi: 10.1042/bj0880531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALATHI P., RAO K. S., SASTRY P. S., GANGULY J. Studies on metabolism of vitamin A. 1. The biological activity of vitamin A acid in rats. Biochem J. 1963 May;87:305–311. doi: 10.1042/bj0870305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURTHY S. K., DAVID J. S., GANGULY J. SOME OBSERVATIONS ON THE MECHANISM OF ABSORPTION OF CHOLESTEROL IN RATS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 27;70:490–492. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90787-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mize C. E., Steinberg D., Avigan J., Fales H. M. A pathway for oxidative degradation of phytanic acid in mammals. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Nov 11;25(3):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90786-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLSON J. A. The conversion of radioactive beta-carotene into vitamin A by the rat intestine in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1961 Feb;236:349–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. A. The alpha and the omega of vitamin A metabolism. Am J Clin Nutr. 1969 Jul;22(7):953–962. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/22.7.953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Cama H. R. Enzymatic cleavage of carotenoids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 25;370(1):49–61. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., John J., Cama H. R. Separation of -apocarotenals and related compounds by reversed-phase paper and thin-layer chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1973 Jan 3;75(1):146–150. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)83428-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Mallia A. K., Cama H. R. Chemistry and metabolism of beta-apocarotenals and their epoxides. Biochem Soc Symp. 1972;(35):219–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON S. Y., BRAUDE R., COATES M. E., COWIE A. T., GANGULY J., KON S. K. Further studies of the conversion of beta-carotene to vitamin A in the intestine. Br J Nutr. 1950;4(4):398–421. doi: 10.1079/bjn19500063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZECHMEISTER L., DEUEL H. J., Jr, INHOFFEN H. H., LEEMANN J., GREENBERG S. M., GANGULY J. Stereochemical configuration and provitamin A activity. X. A comparison of synthetic 15, 15'-monocis-beta-carotene (central monocis-beta-carotene) with all-trans-beta-carotene in the rat and chick. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Mar;36(1):80–88. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90379-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


