Abstract
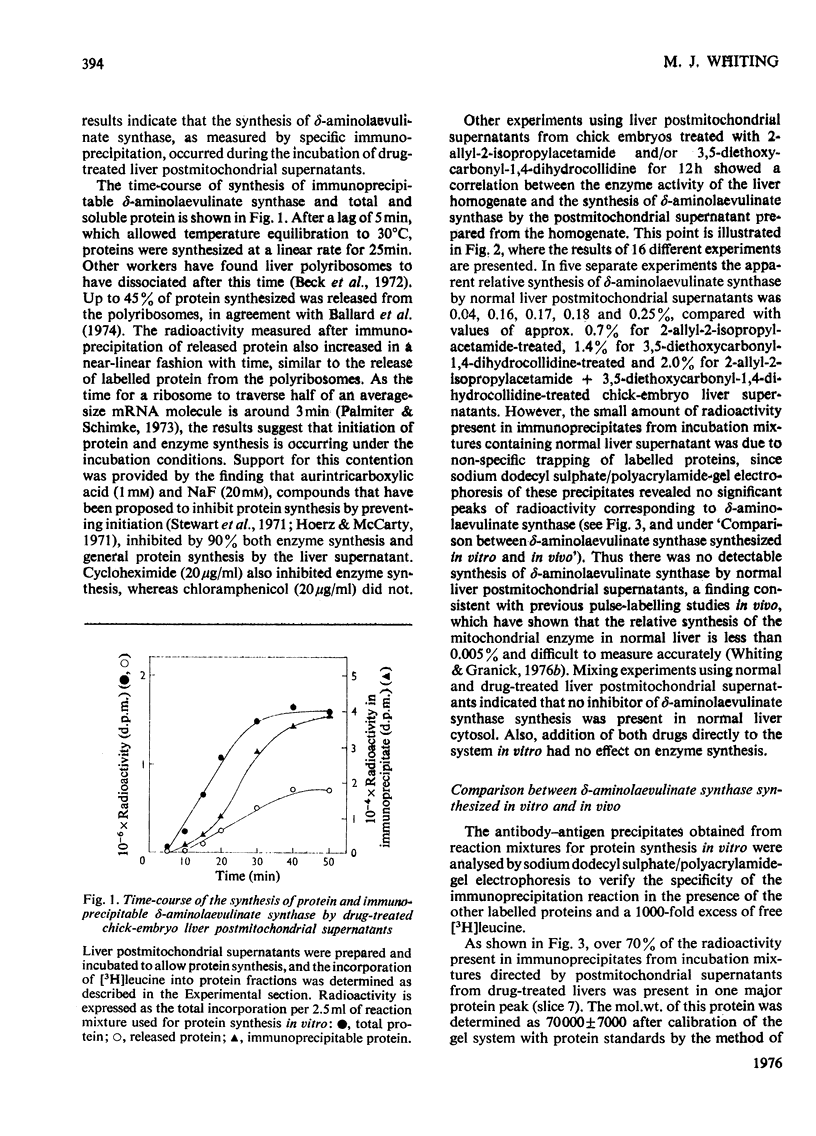
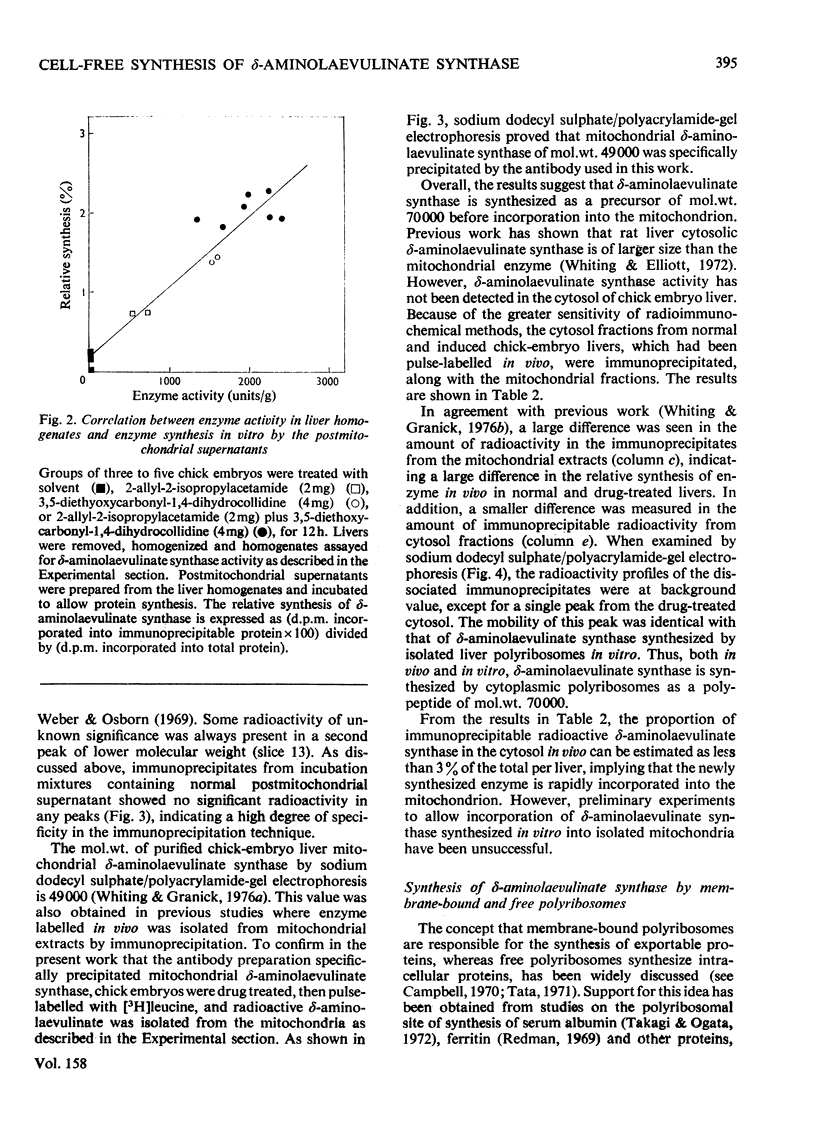
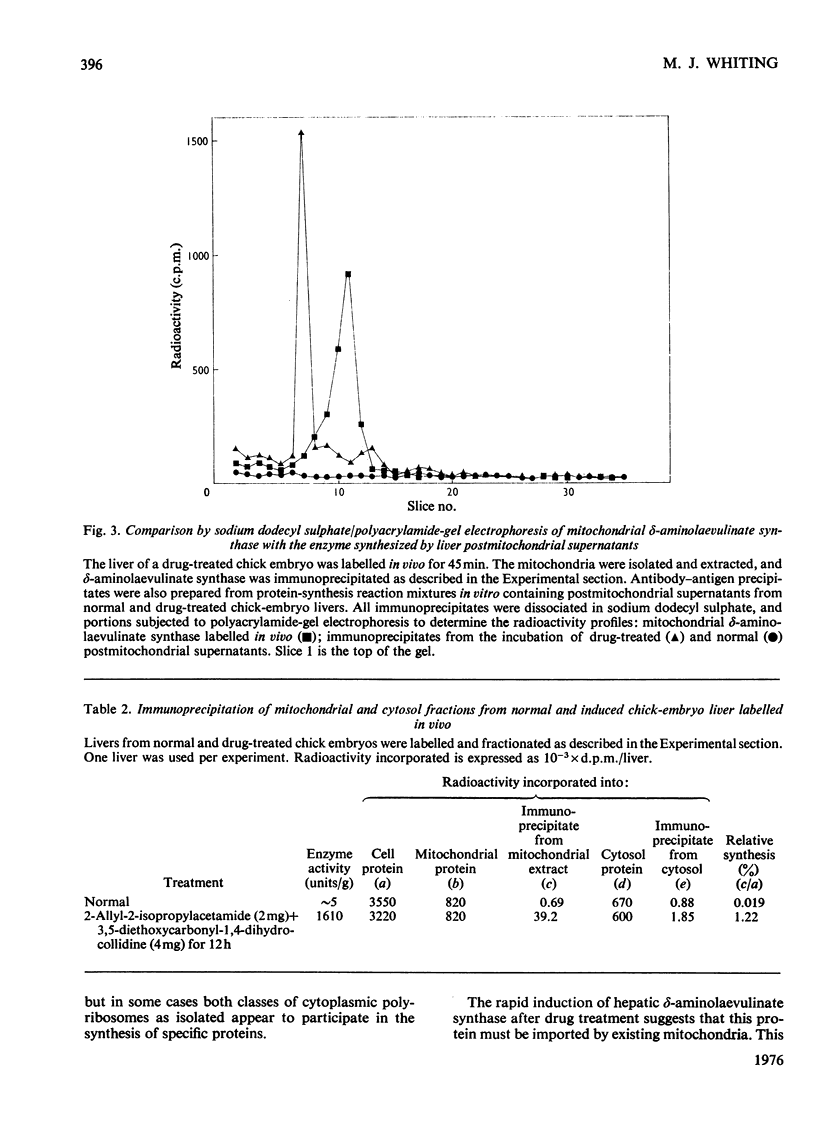
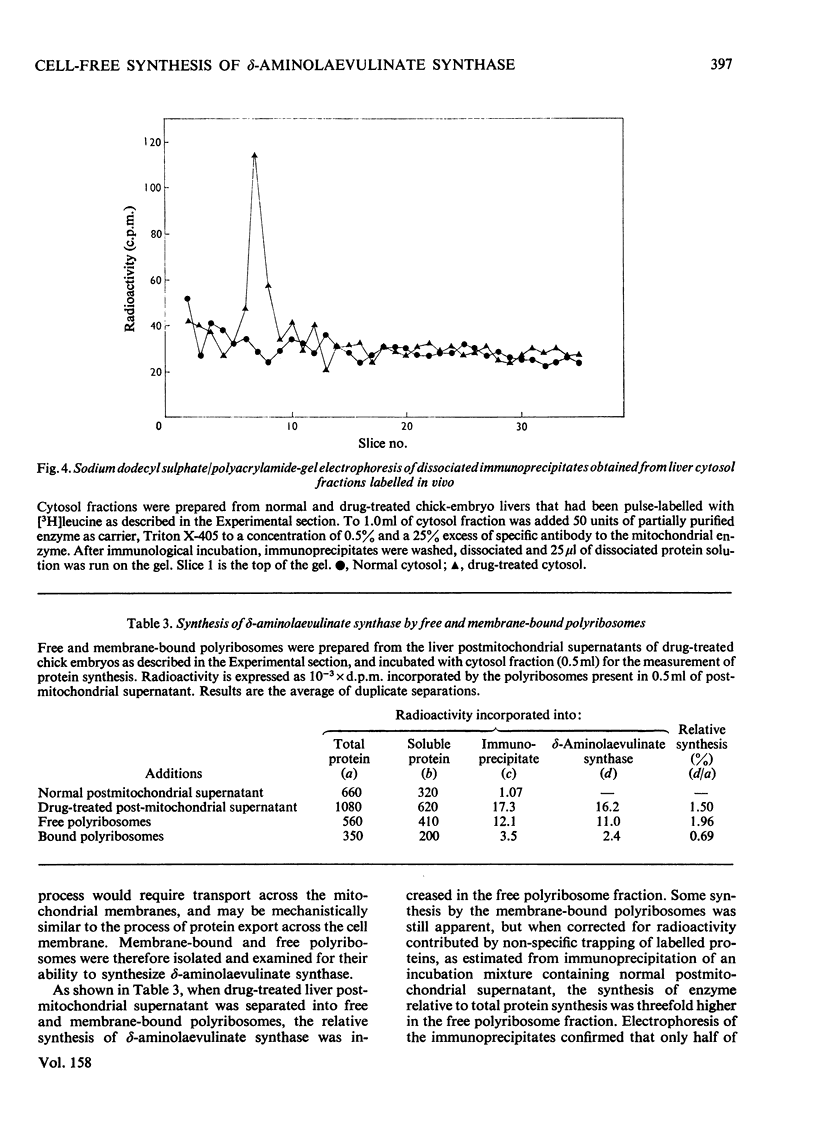
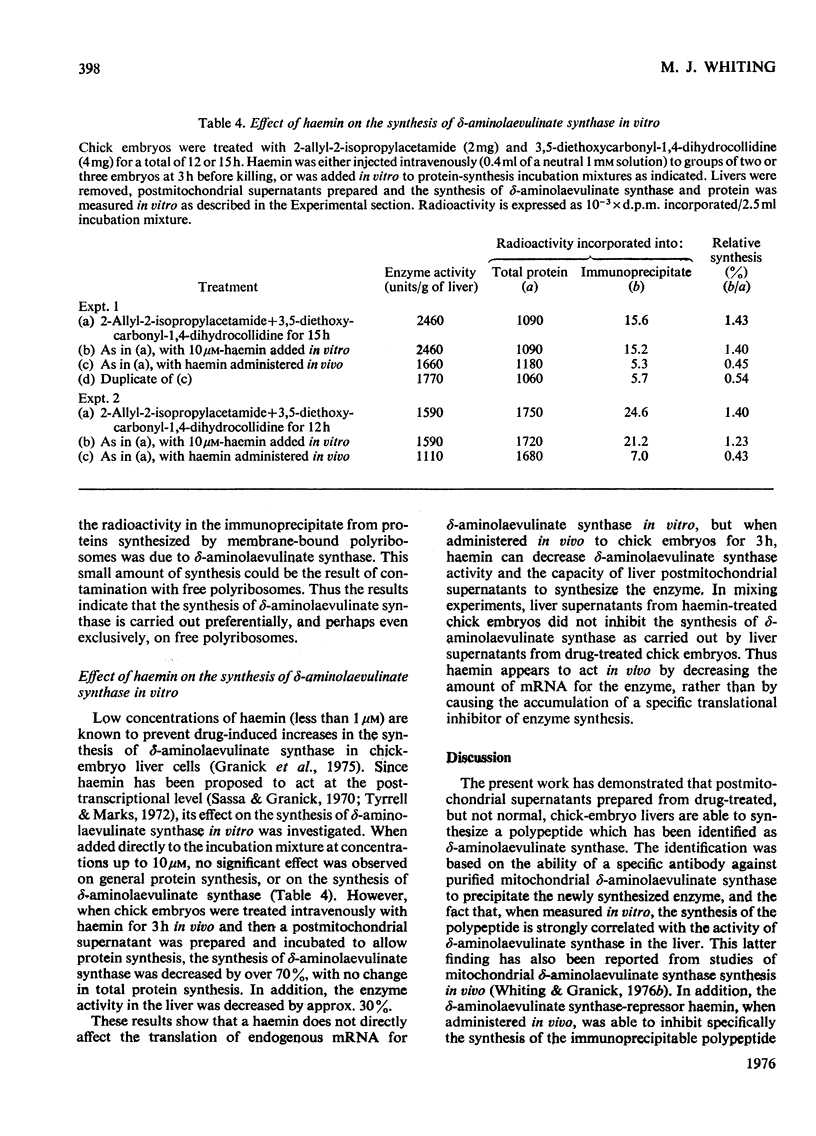
1. Postmitochondrial supernatants were prepared from the livers of chick embryos and were incubated under conditions that supported protein synthesis. delta-Aminolaevulinate synthase (EC 2.3.1.37) was synthesized by supernatants from livers treated with the porphyrinogenic drugs 2-allyl-2-isopropylacetamide and/or 3,5-diethoxycarbonyl-1,4-dihydrocollidine, but synthesis by supernatants from normal livers could not be detected. Synthesis of enzyme released from polyribosomes was measured by immunoprecipitation with specific antibody to the mitochondrial enzyme, and the specificity of the reaction was established by electrophoresis of dissociated immunoprecipitates on sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide gels. 2. The relative synthesis of delta-aminolaevulinate synthase in vitro was comparable with that previously measured in vivo, and was correlated with the enzyme activity of the liver. 3. Enzyme synthesis in vitro occurred predominantly on free rather than membrane-bound polyribosomes. 4. The mol.wt. of the product synthesized in vitro was 7000 +/- 7000 by sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. However, pulse-labelling of the enzyme in vivo confirmed its mol.wt. to be 49000 +/- 5000 when isolated from the mitochondrion. A small amount of immunoprecipitable enzyme of mol.wt. 70000 was detected in the cytosol in vivo. In chick embryo liver, delta-aminolaevulinate synthase therefore appears to be synthesized on cytoplasmic polyribosomes as a polypeptide of mol.wt. 70000, which in vivo is rapidly incorporated into the mitochondrion, and is then extracted as a lower-molecular-weight form. 5. Haemin added to the postmitochondrial supernatant-containing incubation mixture at concentrations up to 10 muM had no effect on general protein synthesis or the synthesis of delta-aminolaevulinate synthase. On the other hand, haemin treatment of induced chick embryo livers in vivo for 3h markedly decreased the relative synthesis of delta-aminolaevulinate synthase in vitro. These results suggest that haemin represses the synthesis of delta-aminolaevulinate synthase by decreasing the amount of mRNA for the enzyme available for translation.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballard F. J., Hanson R. W. Purification of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase from the cytosol fraction of rat liver and the immunochemical demonstration of differences between this enzyme and the mitochondrial phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5625–5630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J., Hopgood M. F., Reshef L., Tilghman S., Hanson R. W. Synthesis of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (guanosine triphosphate) by isolated liver polyribosomes. Biochem J. 1974 Nov;144(2):199–207. doi: 10.1042/bj1440199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck J. P., Beck G., Wong K. Y., Tomkins G. M. Synthesis of inducible tyrosine aminotransferase in a cell-free extract from cultured hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3615–3619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloemendal H., Benedetti E. L., Bont W. S. Preparation and characterization of free and membrane-bound polysomes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:313–327. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30034-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell P. N. Functions of polyribosomes attached to membranes of animal cells. FEBS Lett. 1970 Mar 16;7(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80603-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delta-Aminolevulinic acid synthase from chick embryo liver mitochondria. II. Immunochemical correlation between synthesis and activity in induction and repression. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1347–1353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González-Cadavid N. F., Sáez de Córdova C. Role of membrane-bound and free polyribosomes in the synthesis of cytochrome c in rat liver. Biochem J. 1974 May;140(2):157–167. doi: 10.1042/bj1400157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granick S., Sinclair P., Sassa S., Grieninger G. Effects by heme, insulin, and serum albumin on heme and protein synthesis in chick embryo liver cells cultured in a chemically defined medium, and a spectrofluorometric assay for porphyrin composition. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 25;250(24):9215–9225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granick S. The induction in vitro of the synthesis of delta-aminolevulinic acid synthetase in chemical porphyria: a response to certain drugs, sex hormones, and foreign chemicals. J Biol Chem. 1966 Mar 25;241(6):1359–1375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley E. S., Greenawalt J. W. An assessment of in vivo mitochondrial protein synthesis in Neurospora crassa. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jul 25;245(14):3574–3583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi N., Yoda B., Kikuchi G. Mechanism of allylisopropylacetamide-induced increase of delta-aminolevulinate synthetase in liver mitochondria. II. Effects of hemin and bilirubin on enzyme induction. J Biochem. 1968 Apr;63(4):446–452. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi N., Yoda B., Kikuchi G. Mechanism of allylisopropylacetamide-induced increase of delta-aminolevulinate synthetase in liver mitochondria. IV. Accumulation of the enzyme in the soluble fraction of rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Apr;131(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90107-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoerz W., McCarty K. S. Initiation of protein synthesis in a rabbit reticulocyte lysate system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 28;228(2):526–535. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellems R. E., Allison V. F., Butow R. A. Cytoplasmic type 80S ribosomes associated with yeast mitochondria. IV. Attachment of ribosomes to the outer membrane of isolated mitochondria. J Cell Biol. 1975 Apr;65(1):1–14. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay R., Druyan R., Getz G. S., Rabinowitz M. Intramitochondrial localization of delta-aminolaevulate synthetase and ferrochelatase in rat liver. Biochem J. 1969 Sep;114(3):455–461. doi: 10.1042/bj1140455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nisselbaum J. S., Bodansky O. Kinetics and electrophoretic properties of the isozymes of aspartate aminotransferase from pig heart. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jun 10;241(11):2661–2664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Schimke R. T. Regulation of protein synthesis in chick oviduct. 3. Mechanism of ovalbumin "superinduction" by actinomycin D. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 10;248(5):1502–1512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman C. M. Biosynthesis of serum proteins and ferritin by free and attached ribosomes of rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4308–4315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson A., McGown E., Henderson L. M., Swan P. B. In vitro amino acid incorporation by the post-mitochondrial supernatant from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 30;254(3):468–477. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90881-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassa S., Granick S. Induction of -aminolevulinic acid synthetase in chick embryo liver cells in cluture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):517–522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M. L., Grollman A. P., Huang M. T. Aurintricarboxylic acid: inhibitor of initiation of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):97–101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi M., Ogata K. Isolation of serum albumin-synthesizing polysomes from rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jan 8;42(1):125–131. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90371-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell D. L., Marks G. S. Drug-induced porphyrin biosynthesis. V. Effect of protohemin on the transcriptional and post-transcriptional phases of -aminolevulinic acid synthetase induction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1972 Aug 1;21(15):2077–2093. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(72)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiting M. J., Elliott W. H. Purification and properties of solubilized mitochondrial -aminolevulinic acid synthetase and comparison with the cytosol enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6818–6826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiting M. J., Granick S. Delta-Aminolevulinic acid synthase from chick embryo liver mitochondria. I. Purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1340–1346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


