Abstract
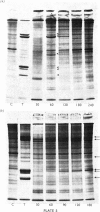
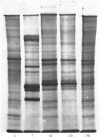
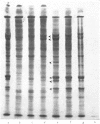
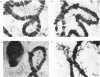
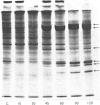
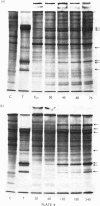
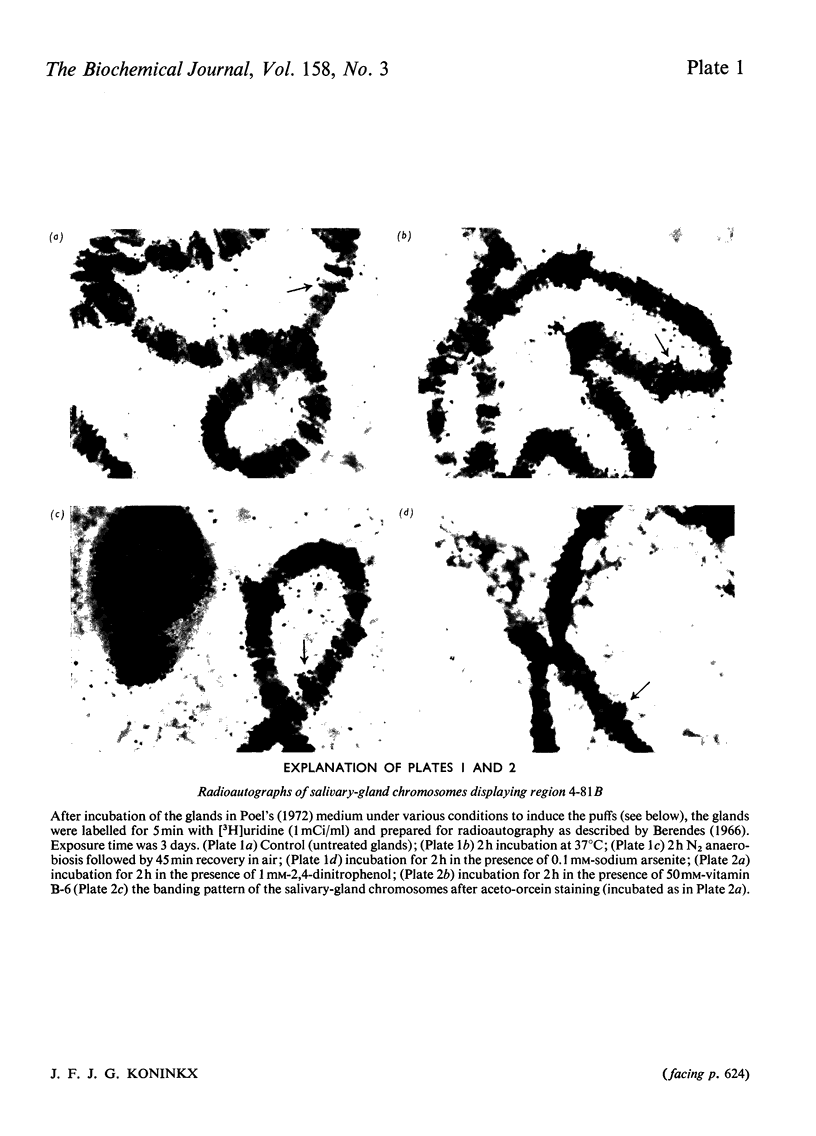
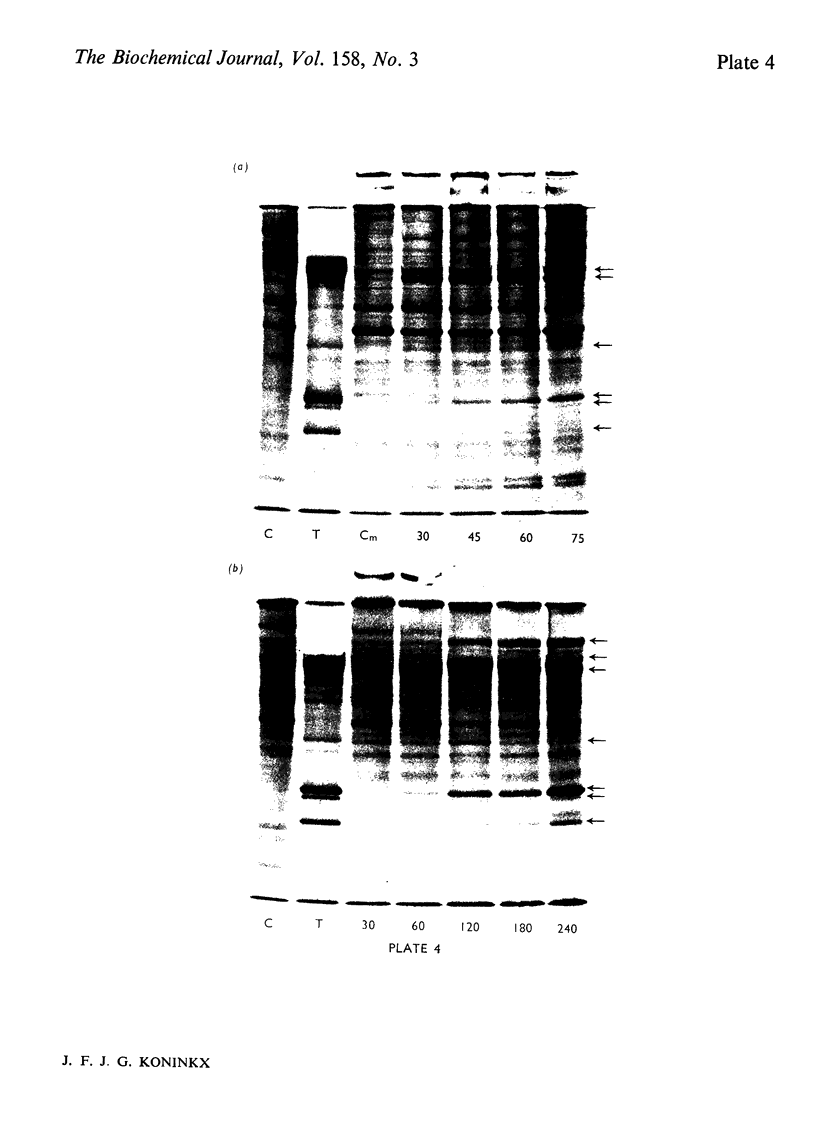
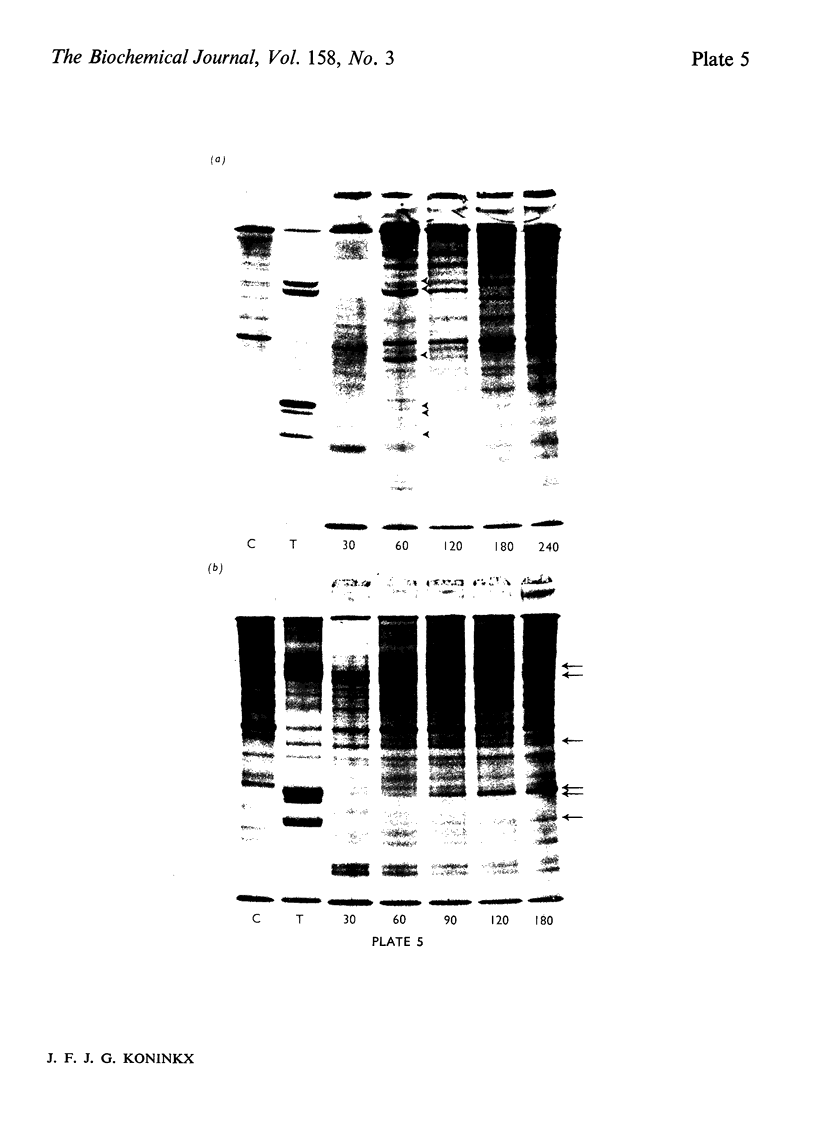
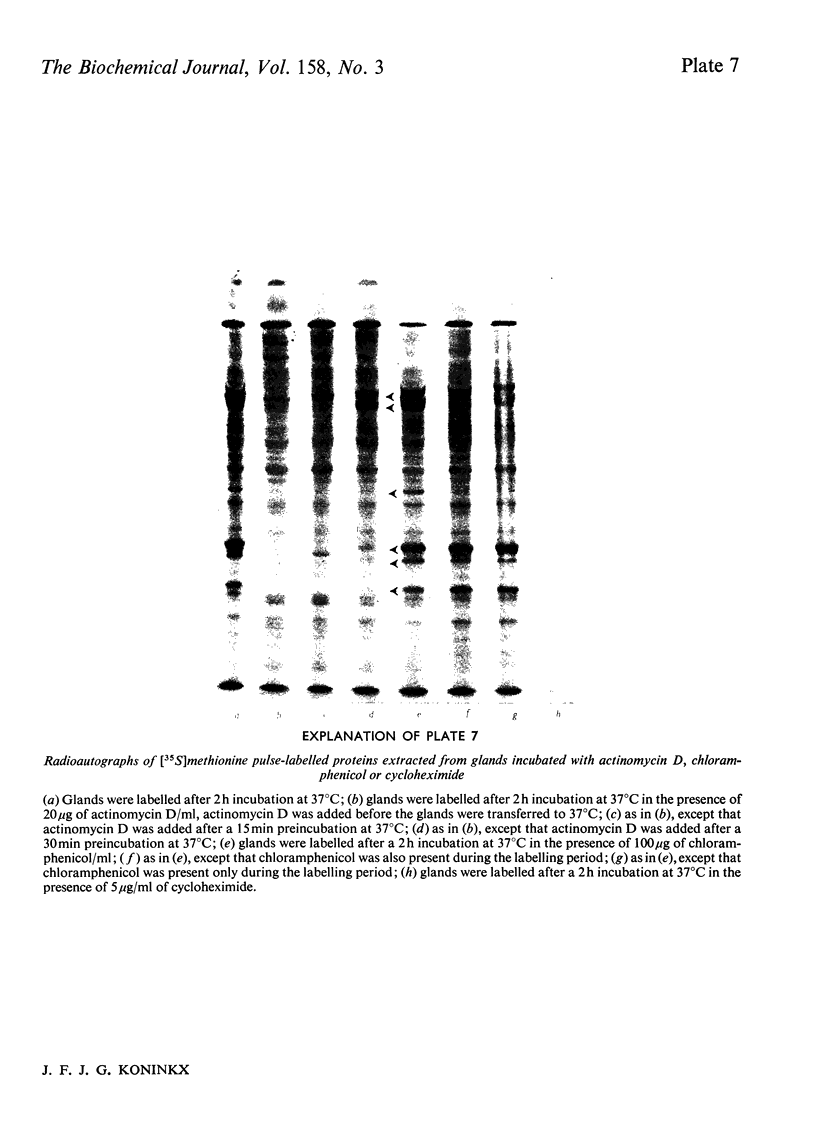
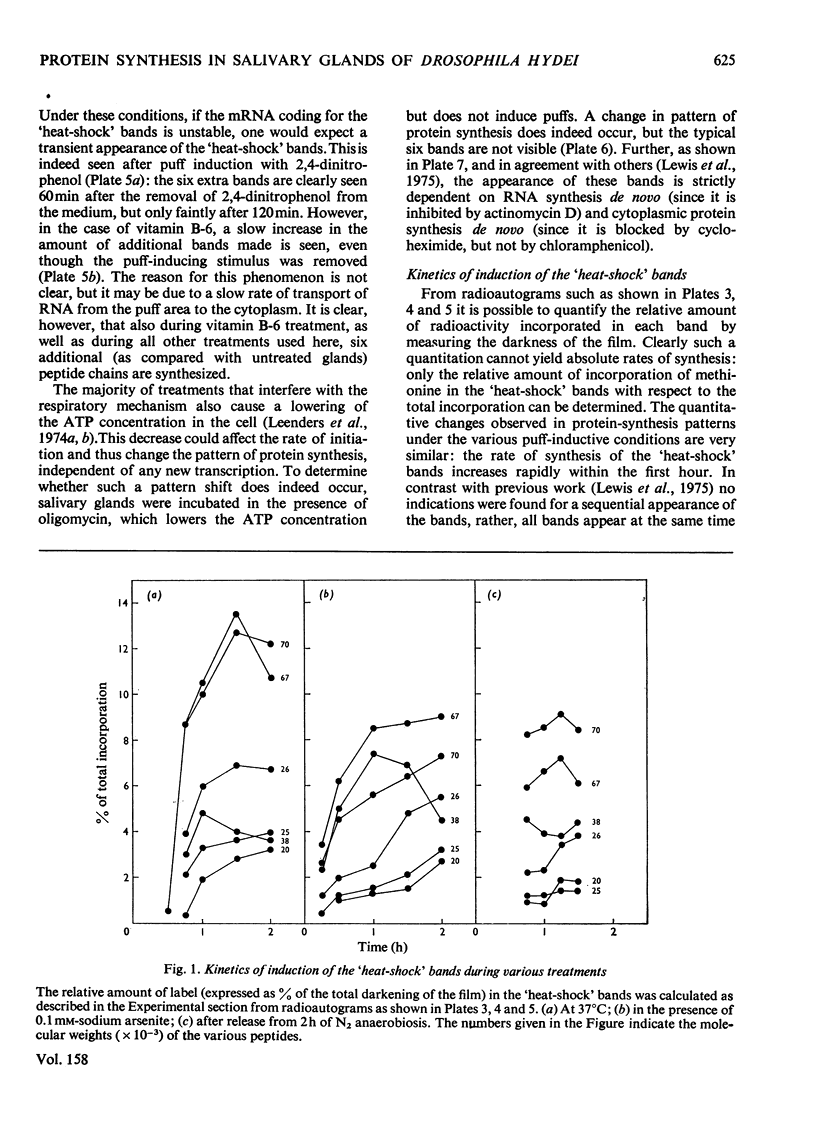
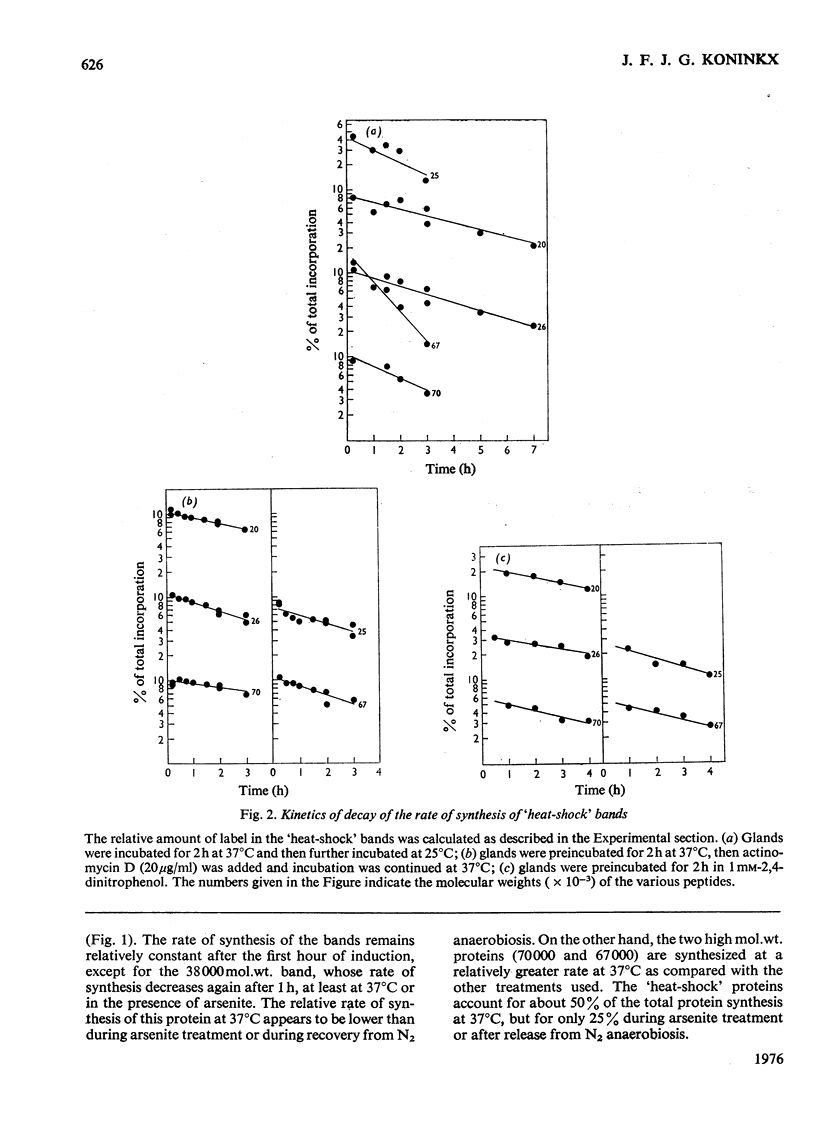
Several treatments, namely incubation at 37 degrees C, in the presence of arsenite, 2,4-dinitrophenol or vitamin B-6, or release from anaerobiosis induce the same set of puffs in the polythene chromosomes of salivary glands of Drosophila hydei. Analysis of changes in protein-synthetic patterns (as determined by radioautography of sodium dodecyl sulphate-gel electrophoretograms of extracts from [35S]methionine-labelled salivary glands) showed that concomitant with puff induction by these various treatments the same six strongly labelled polypeptide bands appeared. The amount of radioactive label in these peptides accounted for 25% of the total incorporation of [35S]methionine, except during incubation at 37 degrees C when it accounted for about 50%. The rate of synthesis of these peptides was maximal 1 h after the start of the puff-inducing treatment. The rate of decay of the rate of synthesis showed first-order kinetics both after removal of the puff-inducing stimulus or in the presence of actinomycin, with a half-life of approx. 4h.
Full text
PDF

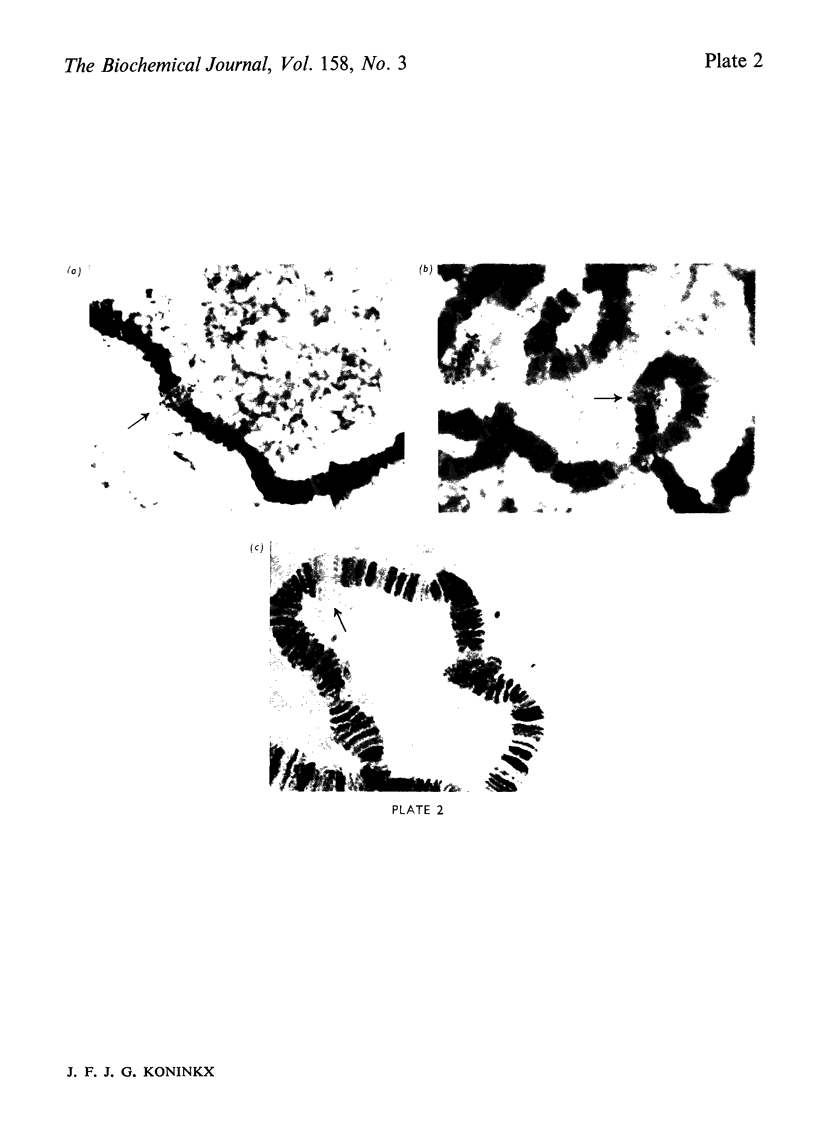




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashburner M. Patterns of puffing activity in the salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophila. V. Responses to environmental treatments. Chromosoma. 1970;31(3):356–376. doi: 10.1007/BF00321231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayuso-Parrilla M. S., Parrilla R. Control of hepatic protein synthesis. Differential effects of ATP levels on the initiation and elongation steps. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jul 15;55(3):593–599. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02196.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd J. B., Berendes H. D., Boyd H. Mass preparation of nuclei from the larval salivary glands of Drosophila hydei. J Cell Biol. 1968 Aug;38(2):369–376. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koninkx J. F. Induced transcription-dependent synthesis of mitochondrial reduced nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide dehydrogenase in Drosophila. Biochem J. 1975 Oct;152(1):17–22. doi: 10.1042/bj1520017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koninkx J. F., Leenders H. J., Birt L. M. A correlation between newly induced gene activity and an enhancement of mitochondrial enzyme activity in the salivary glands of Drosophila. Exp Cell Res. 1975 May;92(2):275–282. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90381-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leenders H. J., Beckers P. J. The effect of changes in the respiratory metabolism upon genome activity. A correlation between induced gene activity and an increase in activity of a respiratory enzyme. J Cell Biol. 1972 Nov;55(2):257–265. doi: 10.1083/jcb.55.2.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leenders H. J., Berendes H. D. The effect of changes in the respiratory metabolism upon genome activity in Drosophila. I. The induction of gene activity. Chromosoma. 1972;37(4):433–444. doi: 10.1007/BF00284892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leenders H. J., Kemp A., Koninkx J. F., Rosing J. Changes in cellular ATP, ADP and AMP levels following treatments affecting cellular respiration and the activity of certain nuclear genes in Drosophila salivary glands. Exp Cell Res. 1974 May;86(1):25–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90642-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M., Helmsing P. J., Ashburner M. Parallel changes in puffing activity and patterns of protein synthesis in salivary glands of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3604–3608. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F. Model for the regulation of mRNA translation applied to haemoglobin synthesis. Nature. 1974 Oct 4;251(5474):385–388. doi: 10.1038/251385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie S. L., Henikoff S., Meselson M. Localization of RNA from heat-induced polysomes at puff sites in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1117–1121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poels C. L. Mucopolysaccharide secretion from Drosophila salivary gland cells as a consequence of hormone induced gene activity. Cell Differ. 1972 Jun;1(2):63–78. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(72)90030-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RITOSSA F. M. EXPERIMENTAL ACTIVATION OF SPECIFIC LOCI IN POLYTENE CHROMOSOMES OF DROSOPHILA. Exp Cell Res. 1964 Sep;35:601–607. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(64)90147-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A., Hui H., Penman S. Two very different components of messenger RNA in an insect cell line. Cell. 1975 Feb;4(2):131–137. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90119-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A., Penman S., Pardue M. L. Analysis of drosophila mRNA by in situ hybridization: sequences transcribed in normal and heat shocked cultured cells. Cell. 1975 Apr;4(4):395–404. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90160-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tissières A., Mitchell H. K., Tracy U. M. Protein synthesis in salivary glands of Drosophila melanogaster: relation to chromosome puffs. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 15;84(3):389–398. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90447-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]