Abstract
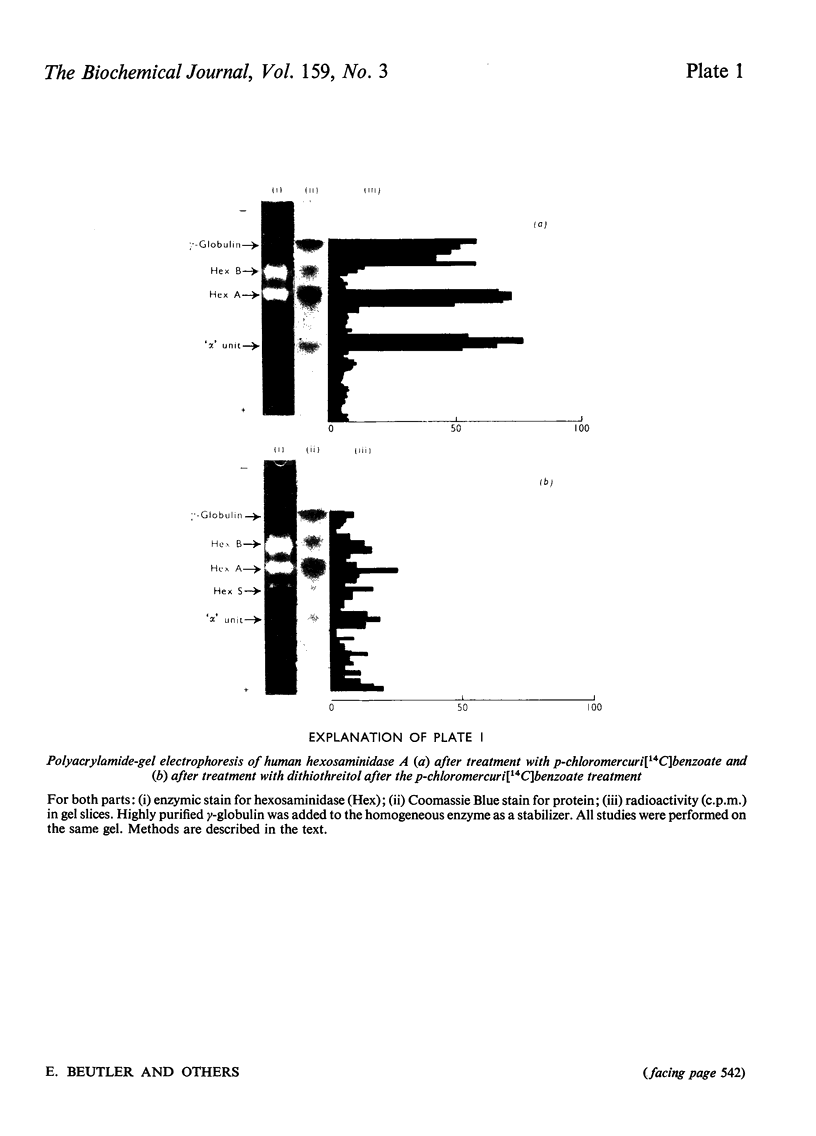
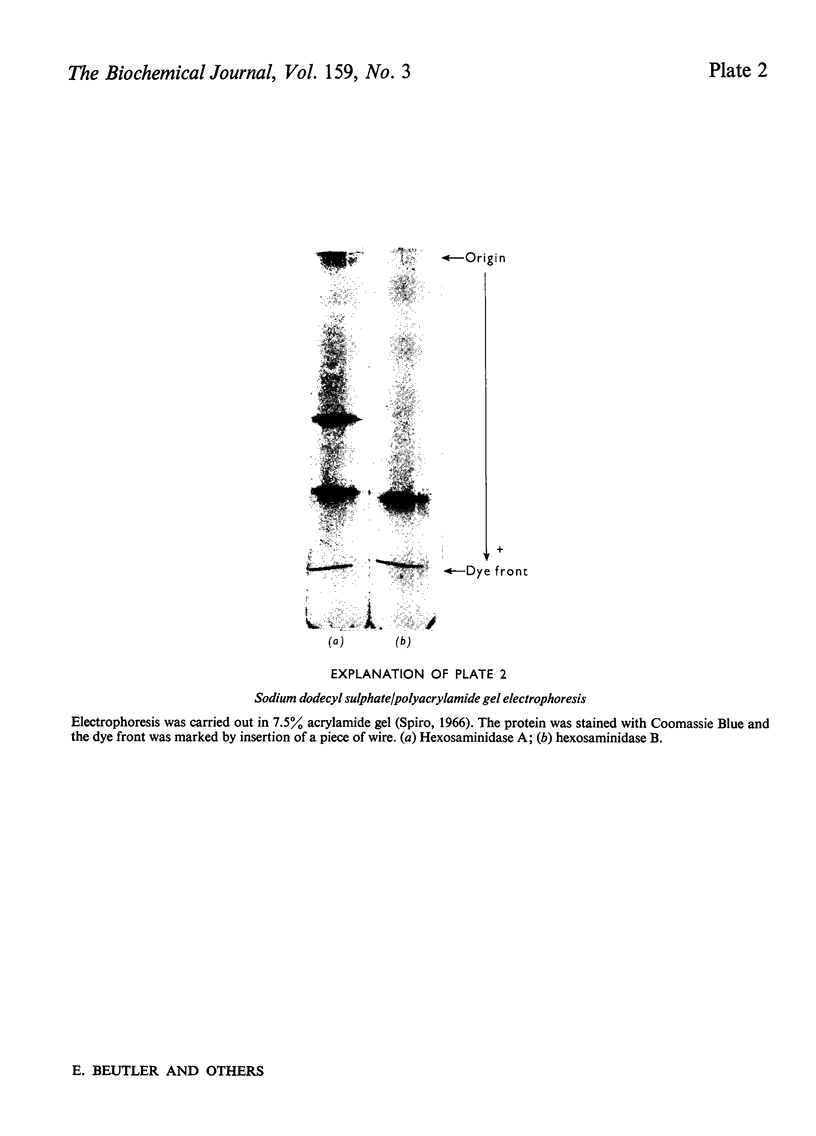
Previous studies of the subunit structure of hexosaminidase gave ambiguous results, but suggested that the enzyme was composed of six equally sized subunits. Dissociation of hexosaminidase A with p-chloromercuribenzoate produces an alkylated fragment with mol.wt. approx. 50000, which is converted into hexosaminidase S by treatment with dithiothreitol. Treatment of native hexosaminidase A with sodium dodecylsulphate results in the formation of a large and a small fragment. However, although the native enzyme has a sedimentation coefficient of 5.8S, dissociation by S-carboxymethylation and maleic anhydride treatment results in subunits exhibiting a single schlieren boundary on analytical ultracentrifugation with a sedimentation coefficient of 2.18S. These results indicate that the enzyme is composed of four subunits, each with molwt. approx. 25000-27000. The mol.wt. of the native enzymes is calculated to be approx. 110000. Our data are consistent with the subunit structures of hexosaminidases A, B and S as being alpha2beta2, beta4 and alpha4 respectively.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutler E., Kuhl W., Comings D. Hexosaminidase isozyme in type O Gm2 gangliosidosis (Sandhoff-Jatzkewitz disease). Am J Hum Genet. 1975 Sep;27(5):628–638. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler E., Kuhl W. Subunit structure of human hexosaminidase verified: interconvertibility of hexosaminidase isozymes. Nature. 1975 Nov 20;258(5532):262–264. doi: 10.1038/258262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler E., Villacorte D., Kuhl W., Guinto E., Srivastava S. Nonenzymatic conversion of human hexosaminidase A. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Aug;86(2):195–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Rosemeyer M. A. Subunit interactions of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from human erythrocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Mar;8(1):8–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00488.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASS L. F. ALDOLASE DISSOCIATION INTO SUBUNITS BY REACTION WITH SUCCINIC ANHYDRIDE. Biochemistry. 1964 Apr;3:535–541. doi: 10.1021/bi00892a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikonne J. U., Rattazzi M. C., Desnick R. J. Characterization of Hex S, the major residual beta hexosaminidase activity in type O Gm2 gangliosidosis (Sandhoff-Jatzkewitz disease). Am J Hum Genet. 1975 Sep;27(5):639–650. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. E., Yoshida A. Purification and chemical characterization of human hexosaminidases A and B. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 1;159(3):535–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1590535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D., Stirling J. L. N-Acetyl-beta-glucosaminidases in human spleen. Biochem J. 1968 Apr;107(3):321–327. doi: 10.1042/bj1070321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava S. K., Yoshida A., Awasthi Y. C., Beutler E. Studies on human beta-D-N-acetylhexosaminidases. II. Kinetic and structural properties. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2049–2053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANTIS D. A. EQUILIBRIUM ULTRACENTRIFUGATION OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:297–317. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]