Abstract
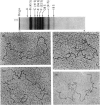
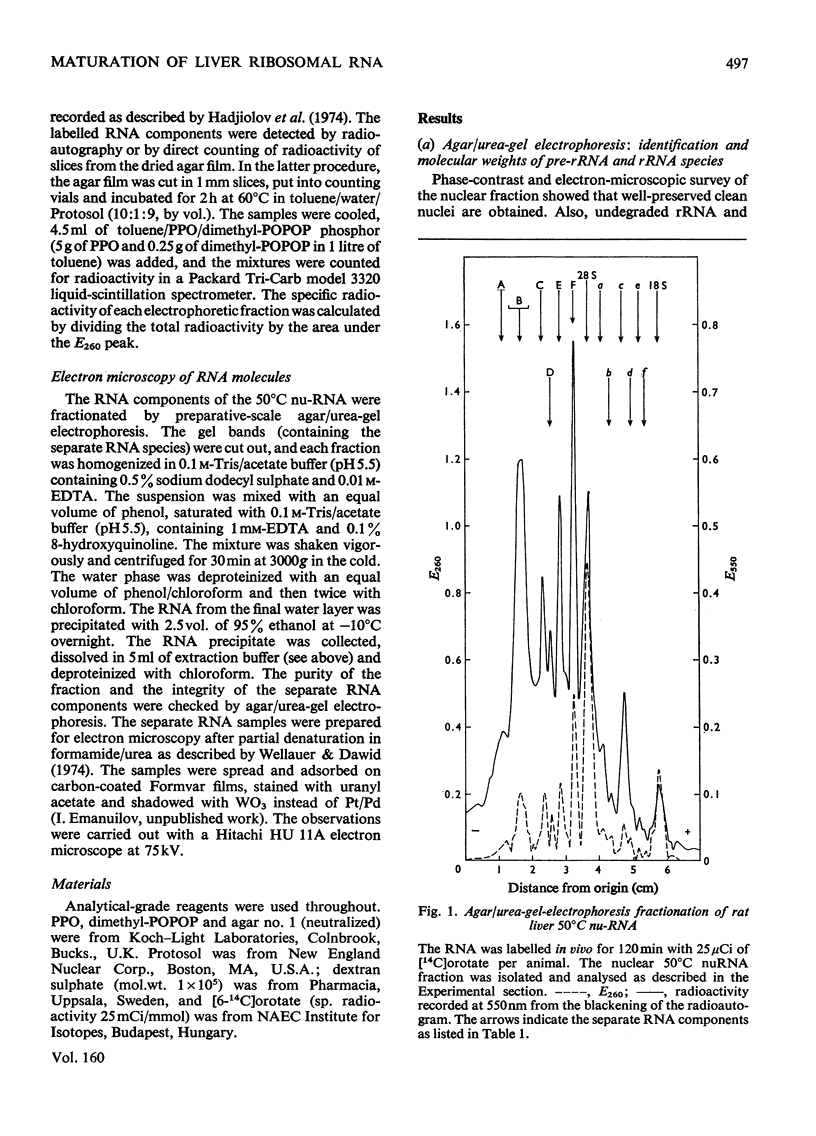
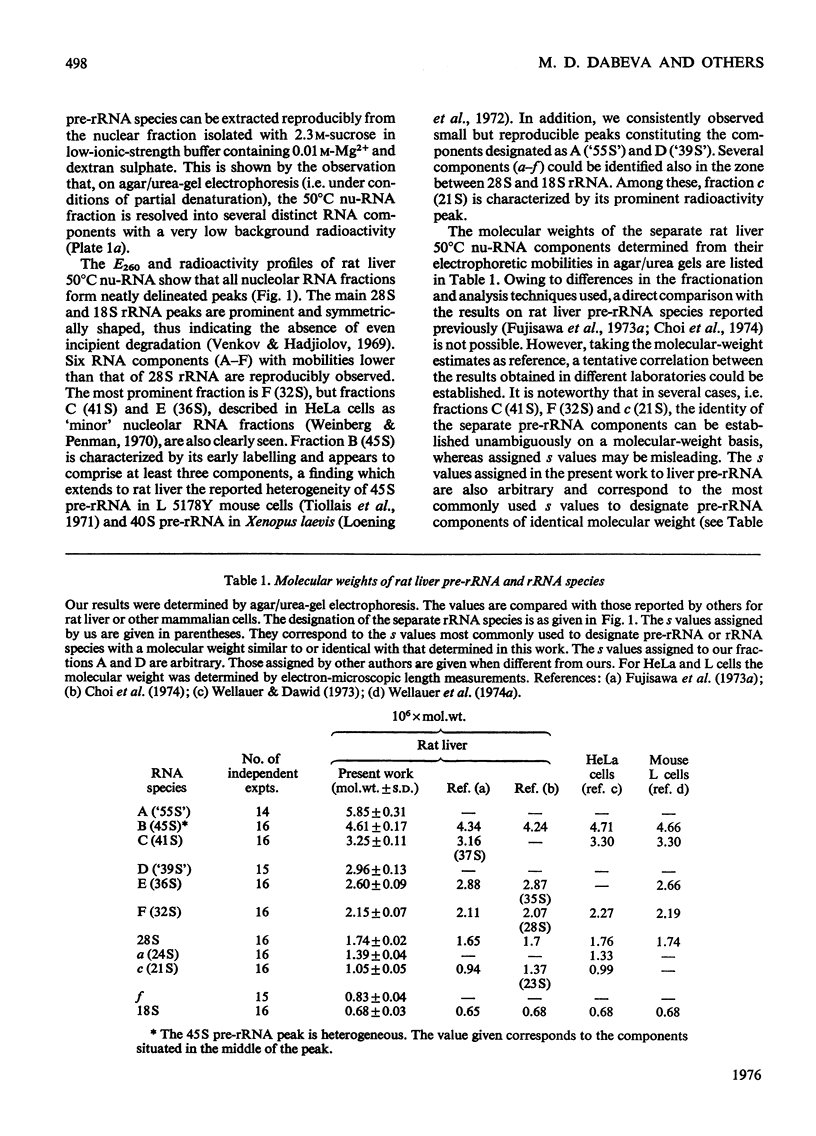
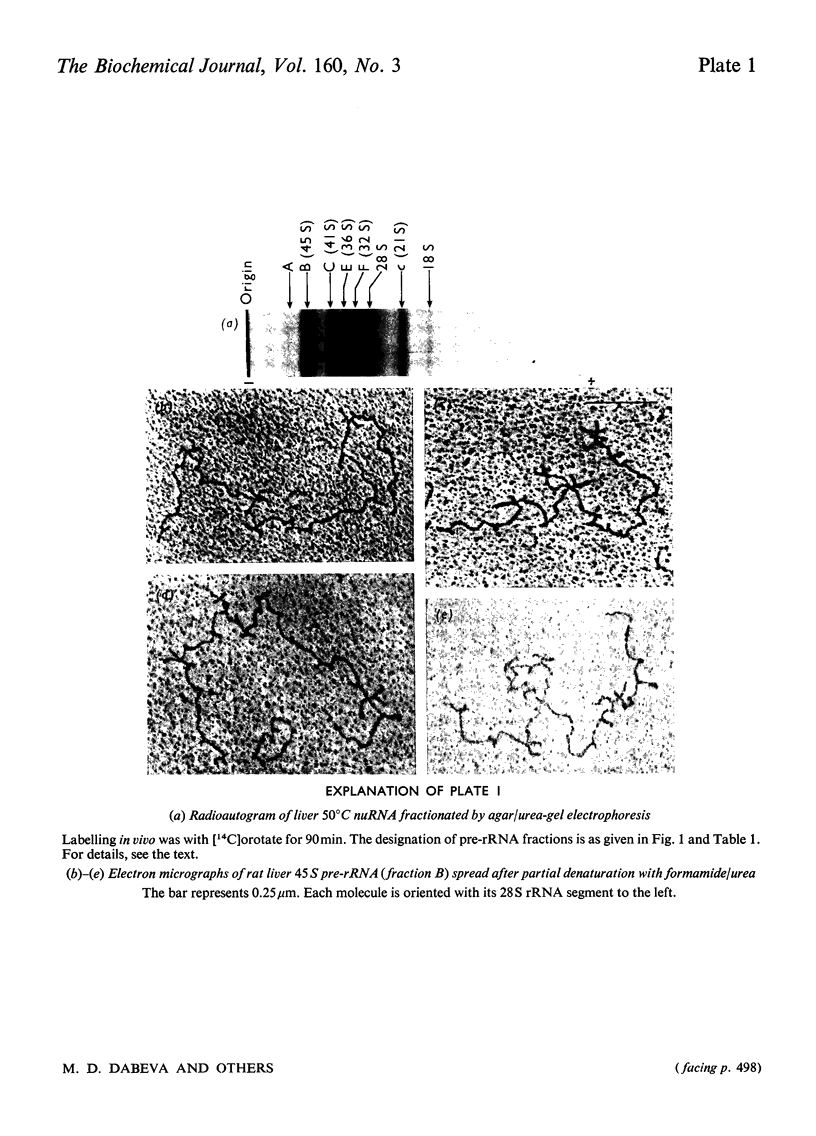
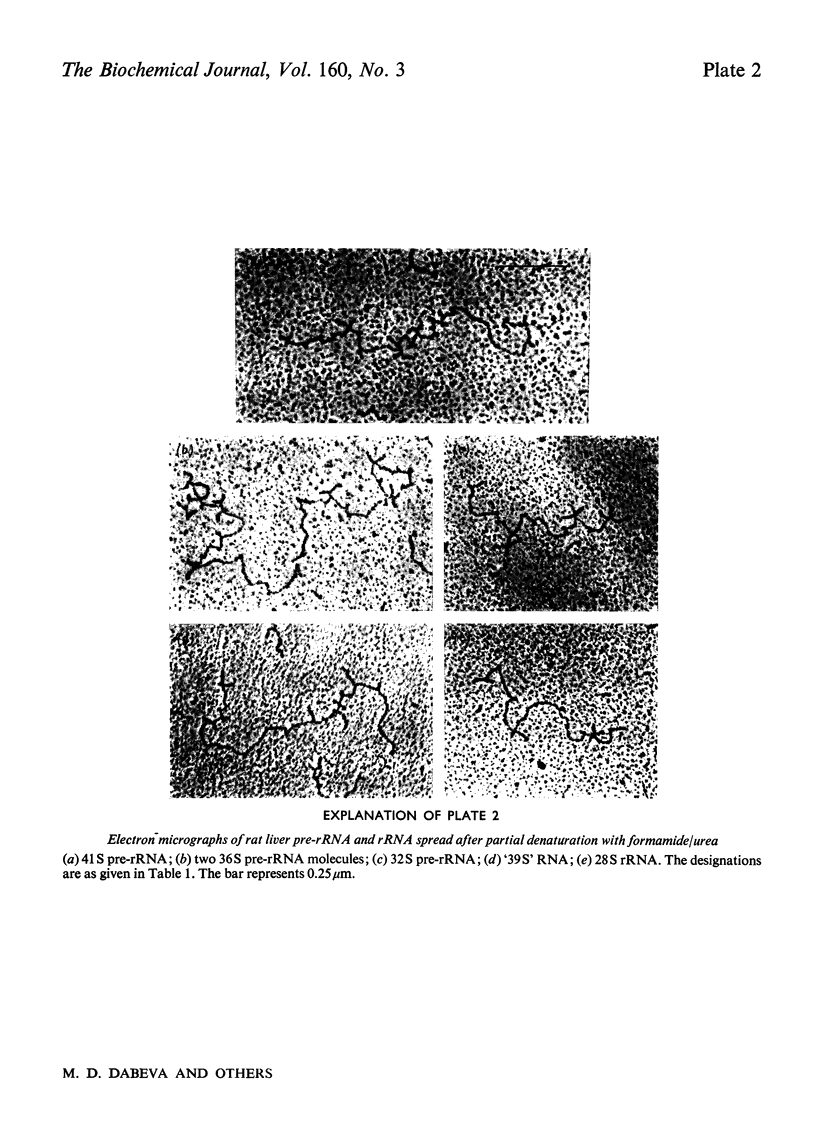
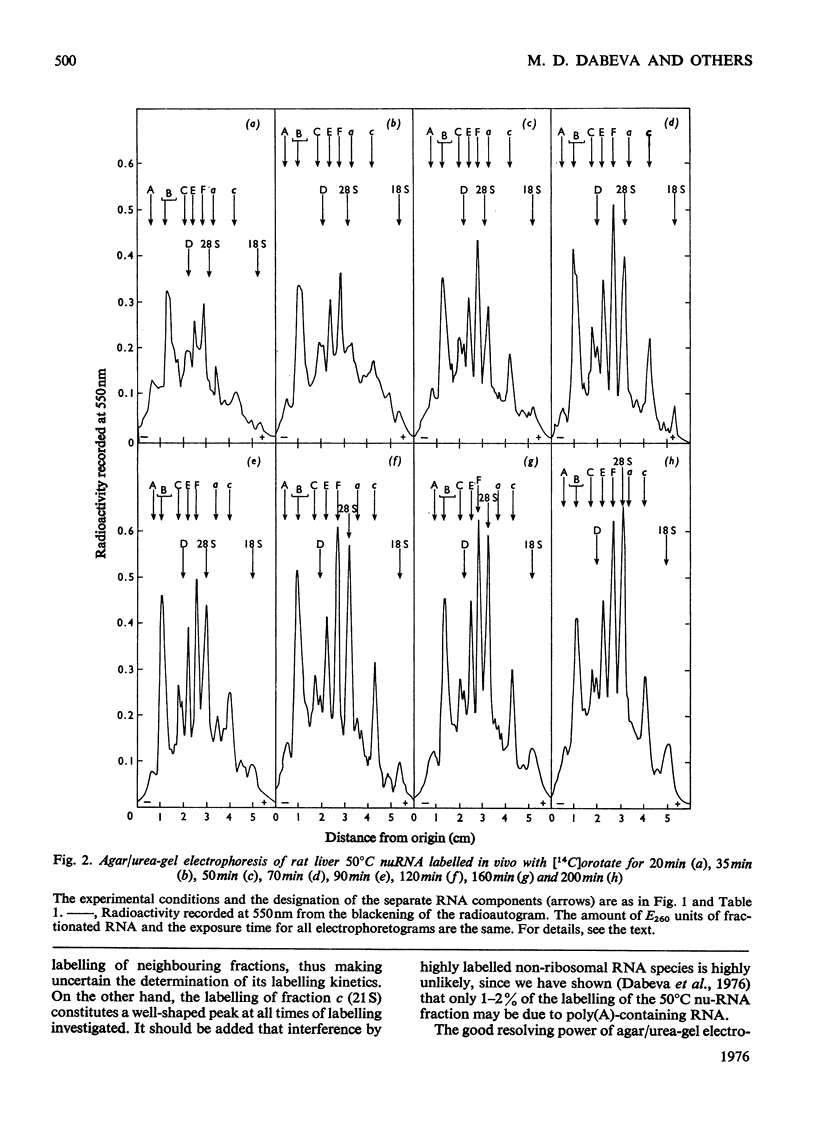
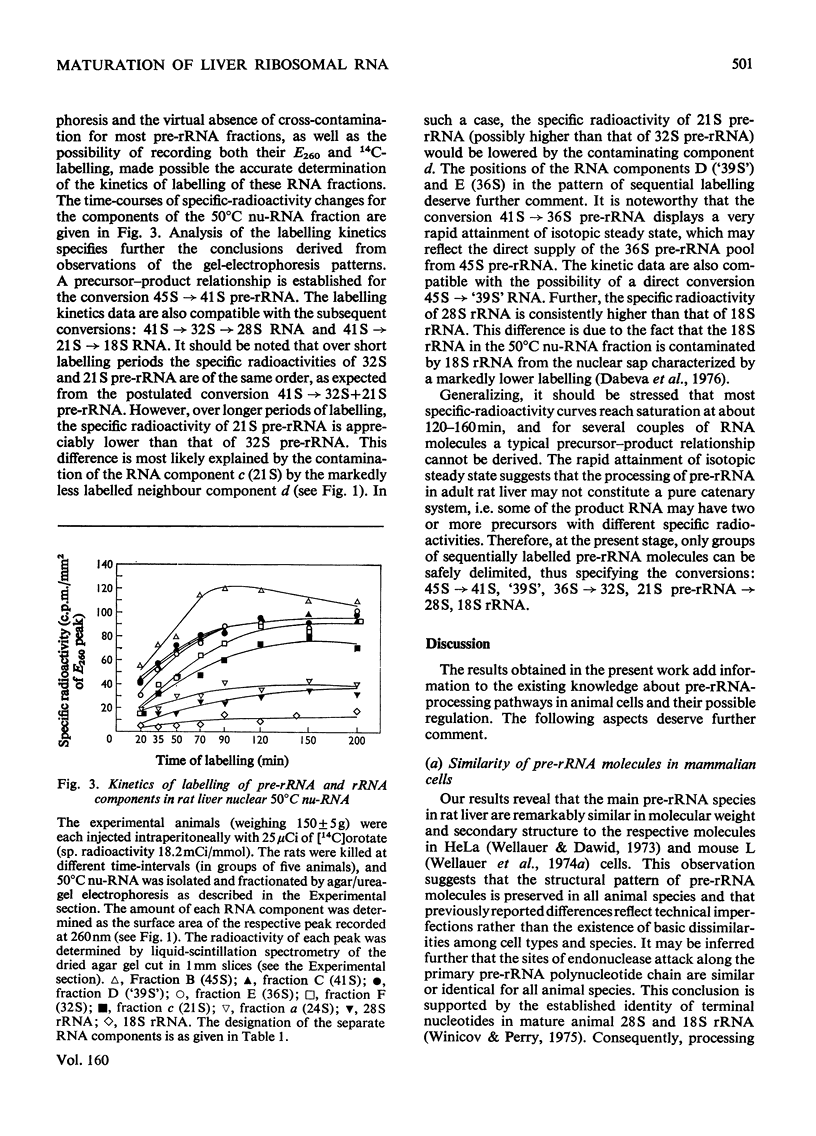
The maturation of pre-rRNA (precursor to rRNA)in liver nuclei is studied by agar/ureagel electrophoresis, kinetics of labelling in vivo with [14C] orotate and electron-microscopic observation of secondary structure of RNA molecules. (1) Processing starts from primary pre-rRNA molecules with average mol. wt. 4.6X10(6)(45S) containing the segments of both 28S and 18S rRNA. These molecules form a heterogeneous peak on electrophoresis. The 28S rRNA segment is homogeneous in its secondary structure. However, the large transcribed spacer segment (presumably at the 5'-end) is heterogeneous in size and secondary structure. A minor early labelled RNA component with mol.wt. about 5.8X10(6) is reproducibly found, but its role as a pre-rRNA species remains to be determined. (2) The following intermediate pre-rRNA species are identified: 3.25X10(6) mol.wt.(41S), a precursor common to both mature rRNA species ; 2.60X10(6)(36S) and 2.15X10(6)(32S) precursors to 28S rRNA; 1.05X10(6) (21S) precursor to 18S rRNA. The pre-rRNA molecules in rat liver are identical in size and secondary structure with those observed in other mammalian cells. These results suggest that the endonuclease-cleavage sites along the pre-rRNA chain are identical in all mammalian cells. (3) Labelling kinetics and the simultaneous existence of both 36S and 21S pre-rRNA reveal that processing of primary pre-rRNA in adult rat liver occurs simultaneously by at least two major pathways: (i) 45S leads to 41S leads to 32S+21S leads to 28S+18S rRNA and (ii) 45S leads to 41S leads to 36S+18S leads to 32S leads to 28S rRNA. The two pathways differ by the temporal sequence of endonuclease attack along the 41 S pre-rRNA chain. A minor fraction (mol.wt.2.9X10(6), 39S) is identified as most likely originating by a direct split of 28S rRNA from 45S pre-rRNA. These results show that in liver considerable flexibility exists in the order of cleavage of pre-rRNA molecules during processing.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHAUVEAU J., MOULE Y., ROUILLER C. Isolation of pure and unaltered liver nuclei morphology and biochemical composition. Exp Cell Res. 1956 Aug;11(2):317–321. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(56)90107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabeva M. D., Todorov B. N., Khadzhiolova A. A. Vnutriiadernoe raspredelenie ribosomnykh RNK iz pecheni krysy. Biokhimiia. 1976 Mar;41(3):458–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egawa K., Choi Y. C., Busch H. Studies on the role of 23 s nucleolar RNA as an intermediate in the synthesis of 18 s ribosomal RNA. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 28;56(3):565–577. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90402-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa T., Abe S., Kawada T., Satake M., Ogata K. Studies on the processing of 45-S RNA in rat liver nucleolus with specific reference to 29.5-S RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 12;324(2):226–240. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90140-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa T., Abe S., Satake M., Ogata K. Conversion of rat liver nucleolar 29.5-S RNA to 28-S RNA in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 12;324(2):241–253. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90141-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galibert F., Tiollais P., Eladari M. E. Fingerprinting studies of the maturation of ribosomal RNA in mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun 16;55(1):239–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02156.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadjiolov A. A., Cox R. A., Huvos P. The presence of a high-molecular-weight (guanine-plus-cytosine)-rich segment at the 3' end of rabbit 28S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1975 Jun;147(3):625–628. doi: 10.1042/bj1470625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadjiolov A. A., Dabeva M. D., Mackedonski V. V. The action of alpha-amanitin in vivo on the synthesis and maturation of mouse liver ribonucleic acids. Biochem J. 1974 Mar;138(3):321–334. doi: 10.1042/bj1380321a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maden B. E., Salim M., Summers D. F. Maturation pathway for ribosomal RNA in the Hela cell nucleolus. Nat New Biol. 1972 May 3;237(70):5–9. doi: 10.1038/newbio237005a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu M., Fujisawa T. Methylation of ribosomal RNA precursor and tRNA in rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 May 21;157(3):476–492. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90147-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P. Processing of RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:605–629. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purtell M. J., Anthony D. D. Changes in ribosomal RNA processing paths in resting and phytohemagglutinin-stimulated guinea pig lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3315–3319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quagliarotti G., Hidvegi E., Wikman J., Busch H. Structural analysis of nucleolar precursors of ribosomal ribonucleic acid. Comparative hybridizations of nucleolar and ribosomal ribonucleic acid with nucleolar deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1970 Apr 25;245(8):1962–1969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheer U., Trendelenburg M. F., Franke W. W. Transcription of ribosomal RNA cistrons. Correlation of morphological and biochemical data. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Jul;80(1):175–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90289-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J. M., Loening U. E. 5'-Ends of ribosomal and ribosomal precursor RNAs form Xenopus laevis. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Mar 15;43(1):59–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiollais P., Galibert F., Boiron M. Evidence for the existence of several molecular species in the "45S fraction" of mammalian ribosomal precursor RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1117–1120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toniolo D., Basilico C. Processing of ribosomal RNA in a temperature sensitive mutant of BHK cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 2;425(4):409–418. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toniolo D., Meiss H. K., Basilico C. A temperature-sensitive mutation affecting 28S ribosomal RNA production in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1273–1277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkov P. V., Hadjiolov A. A. Differential stability of 28s and 18s rat liver ribosomal ribonucleic acids. Biochem J. 1969 Oct;115(1):91–94. doi: 10.1042/bj1150091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A., Penman S. Processing of 45 s nucleolar RNA. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jan 28;47(2):169–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90337-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B., Kelley D. E., Perry R. P. Secondary structure maps of ribosomal RNA. II. Processing of mouse L-cell ribosomal RNA and variations in the processing pathway. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 25;89(2):397–407. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90527-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B. Secondary structure maps of RNA: processing of HeLa ribosomal RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2827–2831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B. Secondary structure maps of ribosomal RNA and DNA. I. Processing of Xenopus laevis ribosomal RNA and structure of single-stranded ribosomal DNA. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 25;89(2):379–395. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90526-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B. Structure and processing of ribosomal RNA: a comparative electron microscopic study in three animals. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1975 Jul;(26):214–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Reeder R. H., Carroll D., Brown D. D., Deutch A., Higashinakagawa T., Dawid I. B. Amplified ribosomal DNA from Xenopus laevis has heterogeneous spacer lengths. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2823–2827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winicov I. Alternate temporal order in ribosomal RNA maturation. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jan 15;100(2):141–155. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winicov I., Perry R. P. Enzymological aspects of processing of mammalian rRNA. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1975 Jul;(26):201–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]