Abstract
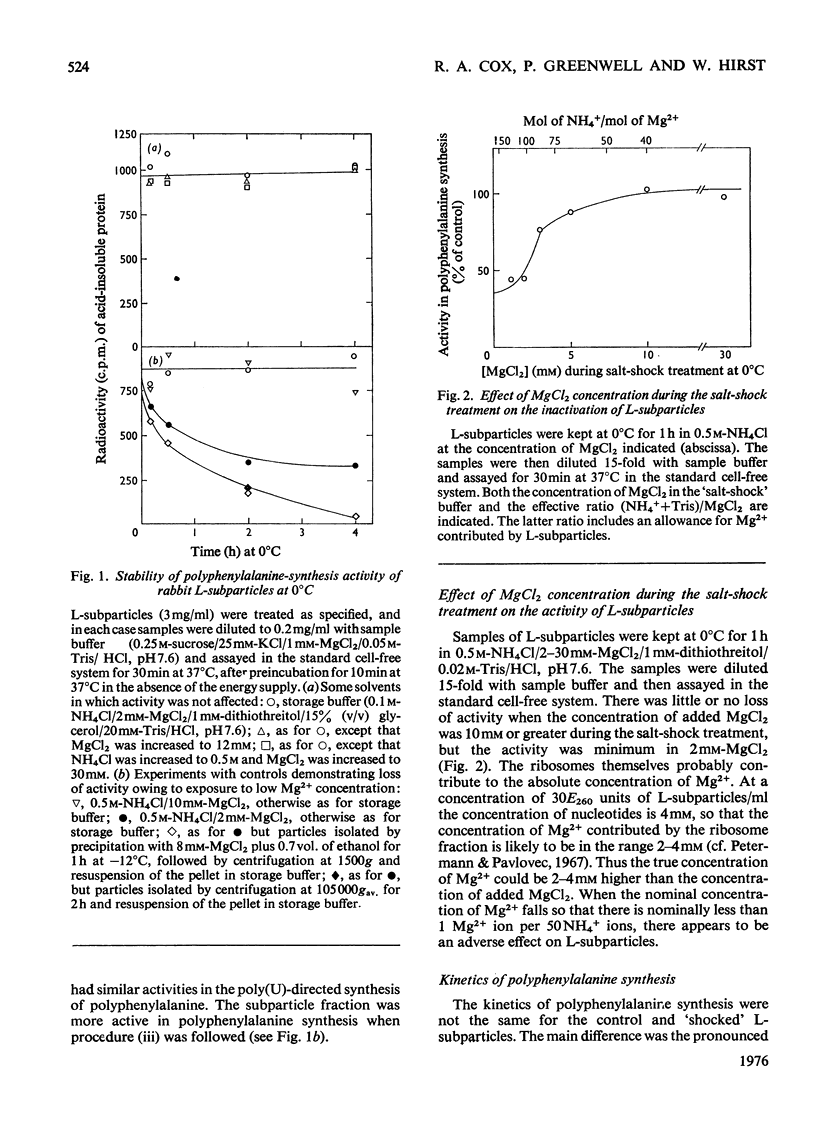
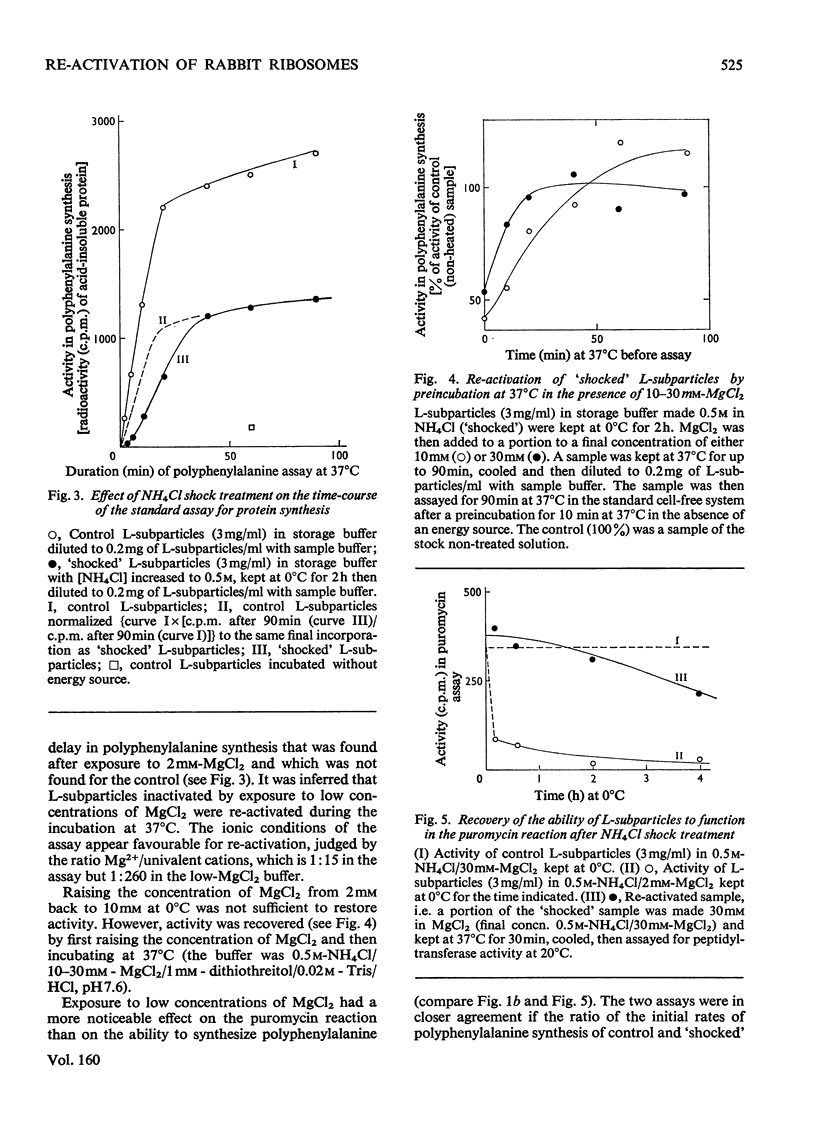
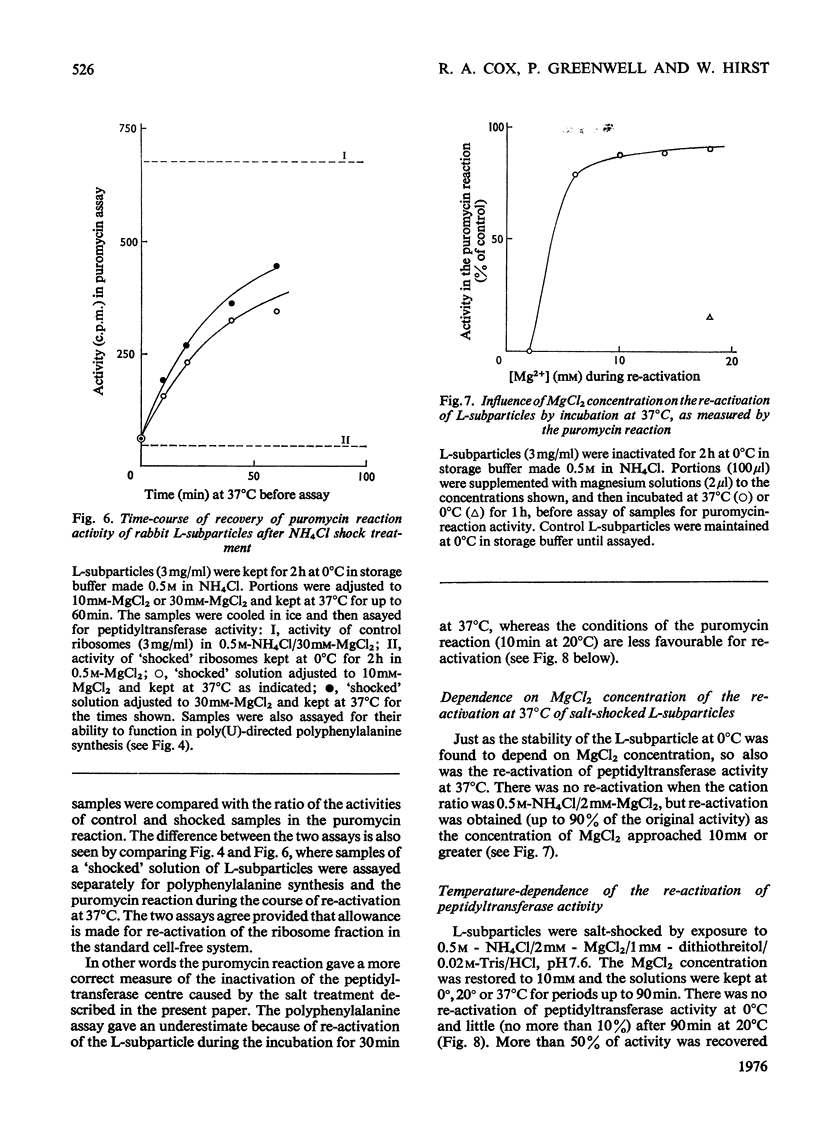
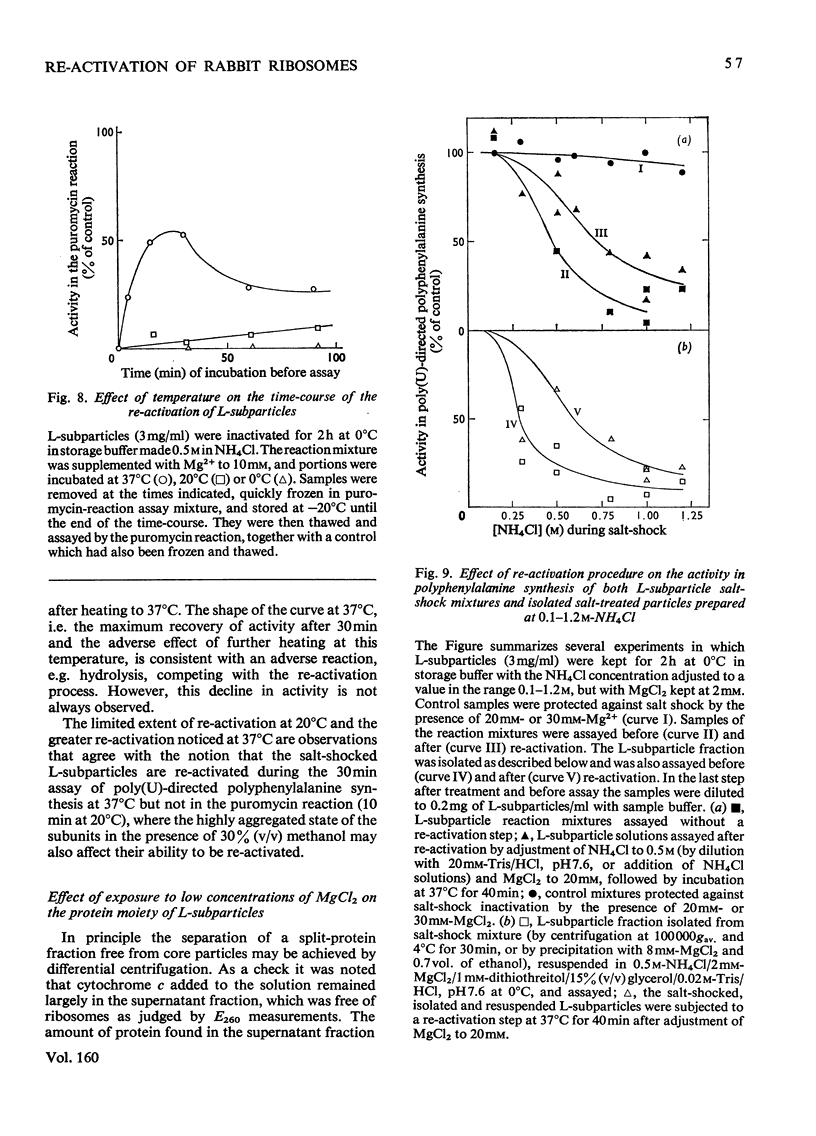
1. The larger subrivosomal particles of rabbit reticulocytes retained full activity in the puromycin reaction and in poly(U)-directed polyphenylalanine synthesis after 4h at 0 degrees C when buffered 0.5M-NH4Cl/10-30mM-MgCl2 was the solvent. 2. Activity in the puromycin reaction was diminished to approx 10% after 15-30 min at 0 degrees C when the concentration of MgCl2 was lowered to 2mM. 3. Activity was not restored when the concentration of MgCl2 was raised from 2mM to 10-30 mM at 0 degrees C. However, activity was recovered as measured by both assay systems when the ribosome fraction was heated to 37 degrees C at the higher concentrations of MgCl2. 4. Recovery of activity was noted during the course of the polyphenylalanine synthesis in 50 mM-KCl/5mM-MgCl2/25mM-Tris/HCl, pH 7.6, at 37 degrees C. Re-activation was slow at 20 degrees C and below. 5. No more than about 5% of the protein moiety of the subparticle was lost in 0.5M-NH4Cl on decreasing MgCl2 concentration from 10mM to 2mM. No proteins were detected in the supernatant fractions by gel electrophoresis after ribosomes were separated by differential centrifugation. The supernatant fraction was not essential for the recovery of activity. However, at higher (e.g. 1M) concentrations of NH4Cl, proteins were split from the subparticle. 6. The loss and regain of activity found on lowering and restoring the concentration of MgCl2 at 0.5M-NH4Cl appears to arise from a conformational change that does not seem to be associated with a loss and regain of particular proteins. 7. A 2% decrease in E260 was noticed when the concentration of Mg2+ was restored, and the change in the spectrum indicated a net increase of approx. 100A-U base-pairs per subribosomal particle. 8. When the concentration of Mg2+ was restored, S20,W of the subparticle remained at 52+/- 1S until the sample was incubated at 37 degrees C when S20,W increased to 56 +/- 1S compared with the value of 58 +/- 1S for the subparticle as originally isolated.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnstein H. R., Cox R. A., Hunt J. A. The function of high-molecular-weight ribonucleic acid from rabbit reticulocytes in haemoglobin biosynthesis. Biochem J. 1964 Sep;92(3):648–661. doi: 10.1042/bj0920648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitmeyer J. B., Noller H. F. Affinity labeling of specific regions of 23 S RNA by reaction of N-bromoacetyl-phenylalanyl-transfer RNA with Escherichia coli ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 5;101(3):297–306. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90149-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. C., Arnstein H. R. The controlled dissociation of proteins from rat liver ribosomes by potassium chloride. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Mar 1;13(1):149–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00911.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A. A spectrophotometric study of the secondary structure of ribonucleic acid isolated from the smaller and larger ribosomal subparticles of rabbit reticulocytes. Biochem J. 1970 Mar;117(1):101–118. doi: 10.1042/bj1170101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A. Conformation of nucleic acids and the analysis of the hypochromic effect. Biochem J. 1970 Dec;120(3):539–547. doi: 10.1042/bj1200539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Godwin E., Hastings J. R. Spectroscopic evidence for the uneven distribution of adenine and uracil residues in ribosomal ribonucleic acid of Drosophila melanogaster and of Plasmodium knowlesi and its possible evolutionary significance. Biochem J. 1976 Jun 1;155(3):465–475. doi: 10.1042/bj1550465a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Greenwell P. Reassembly of the peptidyltransferase centre of larger subparticles of rabbit reticulocyte ribosomes from a core-particle and split-protein fraction. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 15;160(3):533–546. doi: 10.1042/bj1600533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Hirst W. A study of the influence of magnesium ions on the conformation of ribosomal ribonucleic acid and on the stability of the larger subribosomal particle of rabbit reticulocytes. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 15;160(3):505–519. doi: 10.1042/bj1600505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Hirst W., Godwin E., Kaiser I. The circular dichroism of ribosomal ribonucleic acids. Biochem J. 1976 May 1;155(2):279–291. doi: 10.1042/bj1550279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A., Pratt H., Huvos P., Higginson B., Hirst W. A study of the thermal stability of ribosomes and biologically active subribosomal particles. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;134(3):775–793. doi: 10.1042/bj1340775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. A. The secondary structure of ribosomal ribonucleic acid in solution. Biochem J. 1966 Mar;98(3):841–857. doi: 10.1042/bj0980841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann V. A., Sprinzl M., Pongs O. The involvement of 5S RNA in the binding of tRNA to ribosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Oct 1;54(3):942–948. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90785-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falvey A. K., Staehelin T. Structure and function of mammalian ribosomes. II. Exchange of ribosomal subunits at various stages of in vitro polypeptide synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):21–34. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godwin E., Cox R. A., Huvos P. Studies of the RNA and protein moieties of the larger subribosomal particle of rabbit reticulocytes. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1974;33(5-6):733–752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwell P., Harris R. J., Symons R. H. Affinity labelling of 23-S ribosomal RNA in the active centre of Escherichia coli peptidyl transferase. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Dec 2;49(3):539–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03858.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard G. A., Traut R. R. Separation and radioautography of microgram quantities of ribosomal proteins by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jan 15;29(2):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80555-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltschmidt E., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. VII. Two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for fingerprinting of ribosomal proteins. Anal Biochem. 1970 Aug;36(2):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90376-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. Molecular weights of ribosomal RNA in relation to evolution. J Mol Biol. 1968 Dec;38(3):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90391-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martini O. H., Gould H. J. Enumeration of rabbit reticulocyte ribosomal proteins. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 14;62(2):403–405. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90435-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miskin R., Zamir A., Elson D. Inactivation and reactivation of ribosomal subunits: the peptidyl transferase activity of the 50 s subunit of Escherihia coli. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 14;54(2):355–378. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90435-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao T., Nakao M., Nagai F. Microdetermination of protein not affected by the presence of various buffers, sucrose, ATP, and eluates from polysaccharide derivatives. Anal Biochem. 1973 Oct;55(2):358–367. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90124-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M. Assembly of bacterial ribosomes. Science. 1973 Mar 2;179(4076):864–873. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4076.864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petermann M. L., Pavlovec A. The effect of temperature on the magnesium binding and ultracentrifugal properties of rat liver ribosomes. Biochemistry. 1967 Sep;6(9):2950–2958. doi: 10.1021/bi00861a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reboud A. M., Buisson M., Amoros M. J., Reboud J. P. Partial in vitro reconstitution of active 40S ribosomal subunits from rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Mar 24;46(6):2012–2018. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90752-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A., Jakes K. How ribosomes select initiator regions in mRNA: base pair formation between the 3' terminus of 16S rRNA and the mRNA during initiation of protein synthesis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4734–4738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TS'O P. O., VINOGRAD J. Studies on ribosomes from reticulocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Apr 29;49:113–129. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90875-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson H. A., Moldave K. Characterization of the peptidyltransferase reaction catalyzed by rat liver 60S ribosomal subunits. Biochemistry. 1974 Mar 26;13(7):1348–1353. doi: 10.1021/bi00704a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. L., Kimes B. W., Morris D. R. Cations and ribosome structure. 3. Effects on the 30S and 50S subunits of replacing bound Mg 2+ by inorganic cations. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 30;12(3):450–456. doi: 10.1021/bi00727a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamir A., Miskin R., Elson D. Inactivation and reactivation of ribosomal subunits: amino acyl-transfer RNA binding activity of the 30 s subunit of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1971 Sep 14;60(2):347–364. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90299-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


