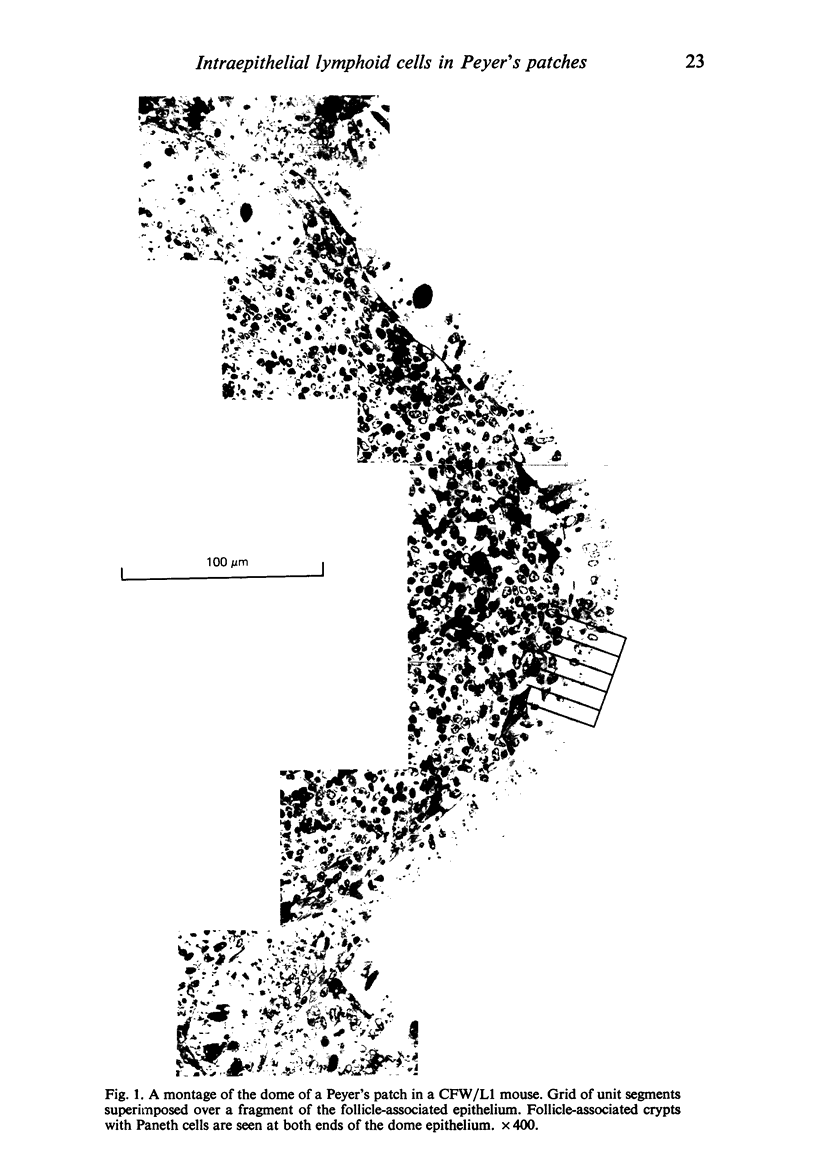
Abstract
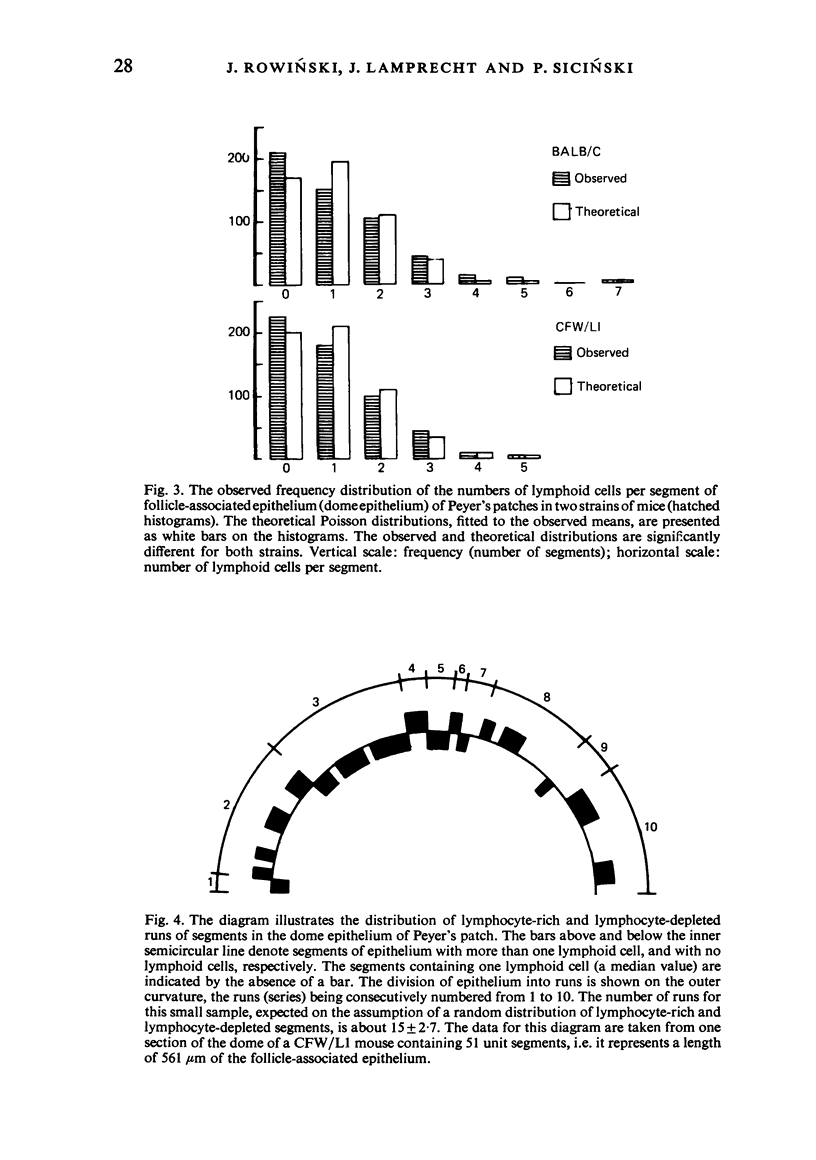
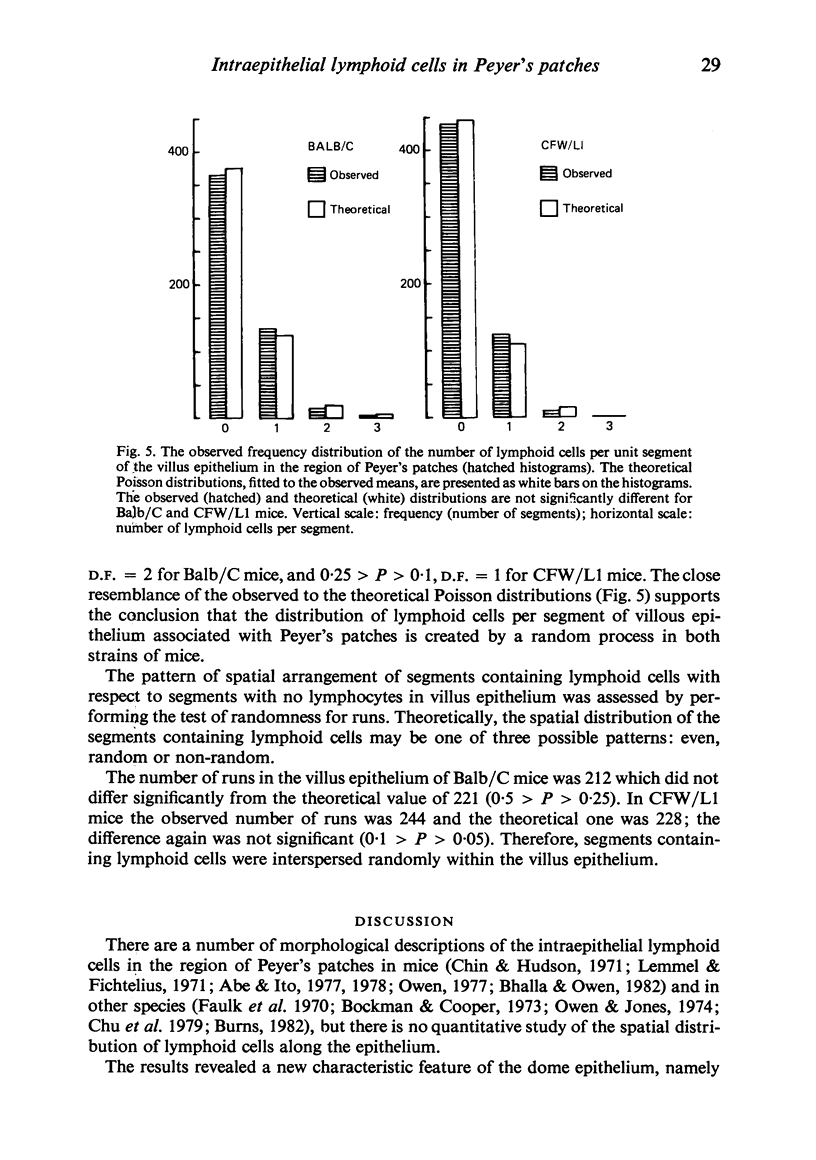
The spatial distribution of intraepithelial lymphoid cells in follicle-associated and villus epithelium within Peyer's patches was studied quantitatively in Balb/C and CFW/L1 mice. The results were essentially the same for both strains. The distribution of the number of lymphoid cells per segmental length (equal to an average width of an epithelial cell) of dome epithelium was found to be non-random, since it deviated significantly from the theoretical Poisson distribution. Some segments of the dome epithelium, therefore, are lymphocyte-rich and some are lymphocyte-depleted, i.e. they contain either more, or less lymphoid cells than expected from the random distribution. This was in contrast to the distribution in the epithelial layer of the villi, in which the distribution of the number of lymphoid cells per segment followed the Poisson distribution. It was also demonstrated that segments rich in lymphocytes in the dome epithelium occurred in series or clusters. Lymphoid cell clustering was not observed in the villus epithelium. Possible mechanisms responsible for the non-random spatial distribution of lymphoid cells within the dome epithelium of the mouse Peyer's patches are discussed.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe K., Ito T. Qualitative and quantitative morphologic study of Peyer's patches of the mouse after neonatal thymectomy and hydrocortisone injection. Am J Anat. 1978 Feb;151(2):227–237. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001510206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhalla D. K., Owen R. L. Cell renewal and migration in lymphoid follicles of Peyer's patches and cecum--an autoradiographic study in mice. Gastroenterology. 1982 Feb;82(2):232–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockman D. E., Cooper M. D. Pinocytosis by epithelium associated with lymphoid follicles in the bursa of Fabricius, appendix, and Peyer's patches. An electron microscopic study. Am J Anat. 1973 Apr;136(4):455–477. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001360406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns R. B. Histology and immunology of Peyer's patches in the domestic fowl (Gallus domesticus). Res Vet Sci. 1982 May;32(3):359–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin K. N., Hudson G. Ultrastructure of Peyer's patches in the normal mouse. Acta Anat (Basel) 1971;78(2):306–318. doi: 10.1159/000143594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu R. M., Glock R. D., Ross R. F. Gut-associated lymphoid tissues of young swine with emphasis on dome epithelium of aggregated lymph nodules (Peyer's patches) of the small intestine. Am J Vet Res. 1979 Dec;40(12):1720–1728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlington D., Rogers A. W. Epithelial lymphocytes in the small intestine of the mouse. J Anat. 1966 Oct;100(Pt 4):813–830. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulk W. P., McCormick J. N., Goodman J. R., Yoffey J. M., Fudenberg H. H. Peyer's patches: morphologic studies. Cell Immunol. 1970 Nov;1(5):500–520. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson A. Intraepithelial lymphocytes of the small intestine. Gut. 1977 Nov;18(11):921–937. doi: 10.1136/gut.18.11.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson A., Parrott D. M. The effect of antigen deprivation on thymus-dependent and thymus-independent lymphocytes in the small intestine of the mouse. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Dec;12(4):477–488. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemmel E. M., Fichtelius K. E. Life span of lymphocytes within intestinal epithelium, Peyer's patch epithelium, epidermis, and liver of mice. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1971;41(5):716–728. doi: 10.1159/000230563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. L., Jones A. L. Epithelial cell specialization within human Peyer's patches: an ultrastructural study of intestinal lymphoid follicles. Gastroenterology. 1974 Feb;66(2):189–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. L. Sequential uptake of horseradish peroxidase by lymphoid follicle epithelium of Peyer's patches in the normal unobstructed mouse intestine: an ultrastructural study. Gastroenterology. 1977 Mar;72(3):440–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. W., Jarvis L. G., King I. S. Cell proliferation in follicle-associated epithelium of mouse Peyer's patch. Am J Anat. 1980 Oct;159(2):157–166. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001590204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. W., Peacock M. A. "M" cell distribution in follicle-associated epithelium of mouse Peyer's patch. Am J Anat. 1980 Oct;159(2):167–175. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001590205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf J. L., Rubin D. H., Finberg R., Kauffman R. S., Sharpe A. H., Trier J. S., Fields B. N. Intestinal M cells: a pathway for entry of reovirus into the host. Science. 1981 Apr 24;212(4493):471–472. doi: 10.1126/science.6259737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]