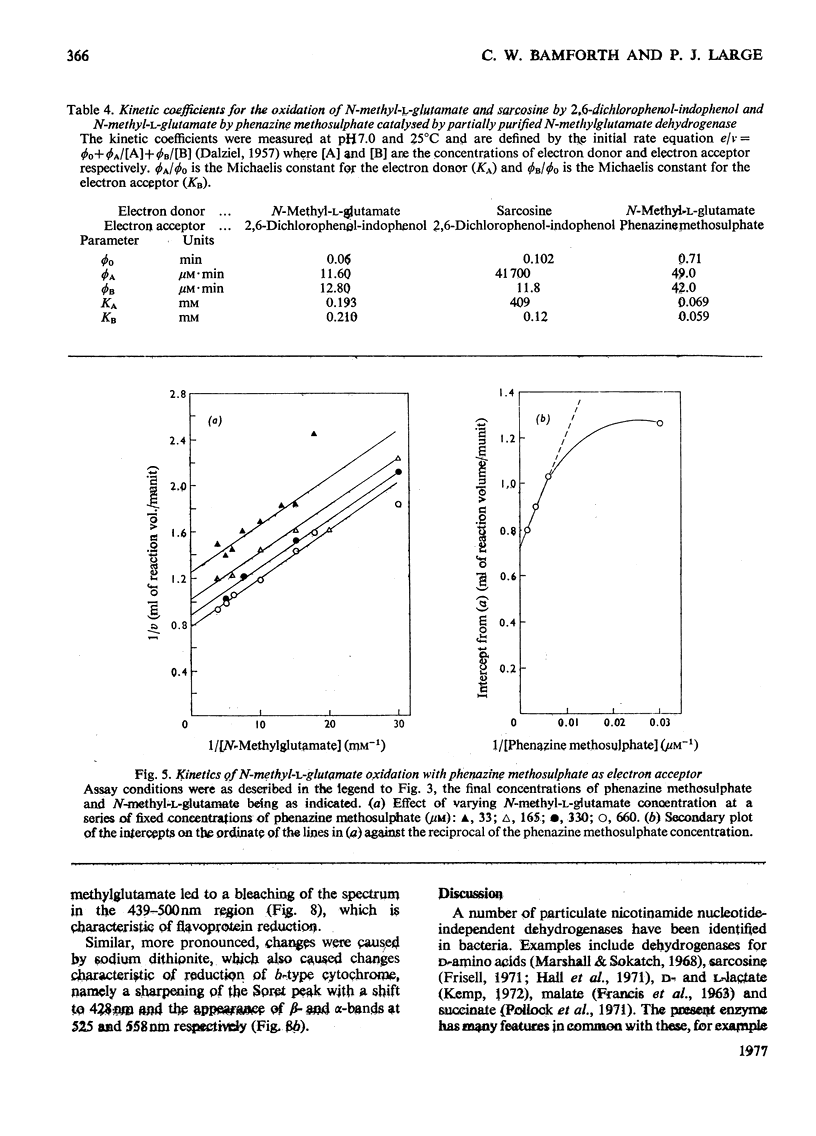
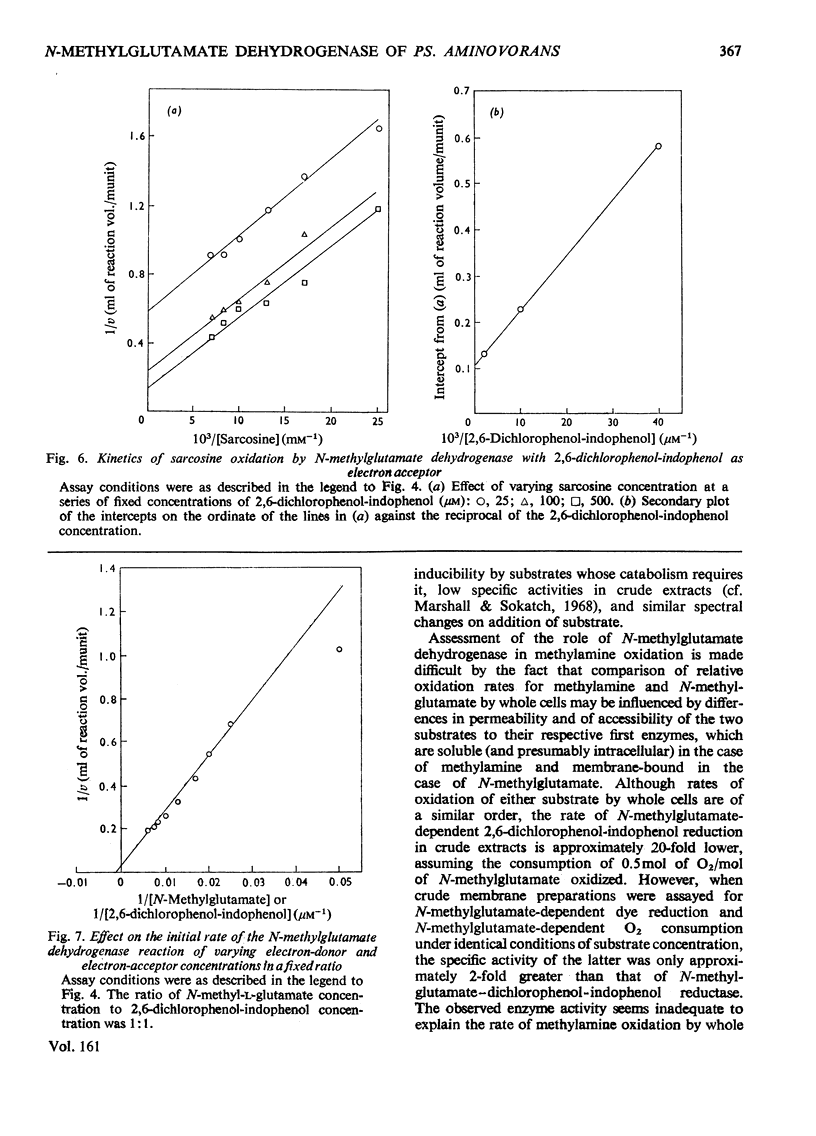
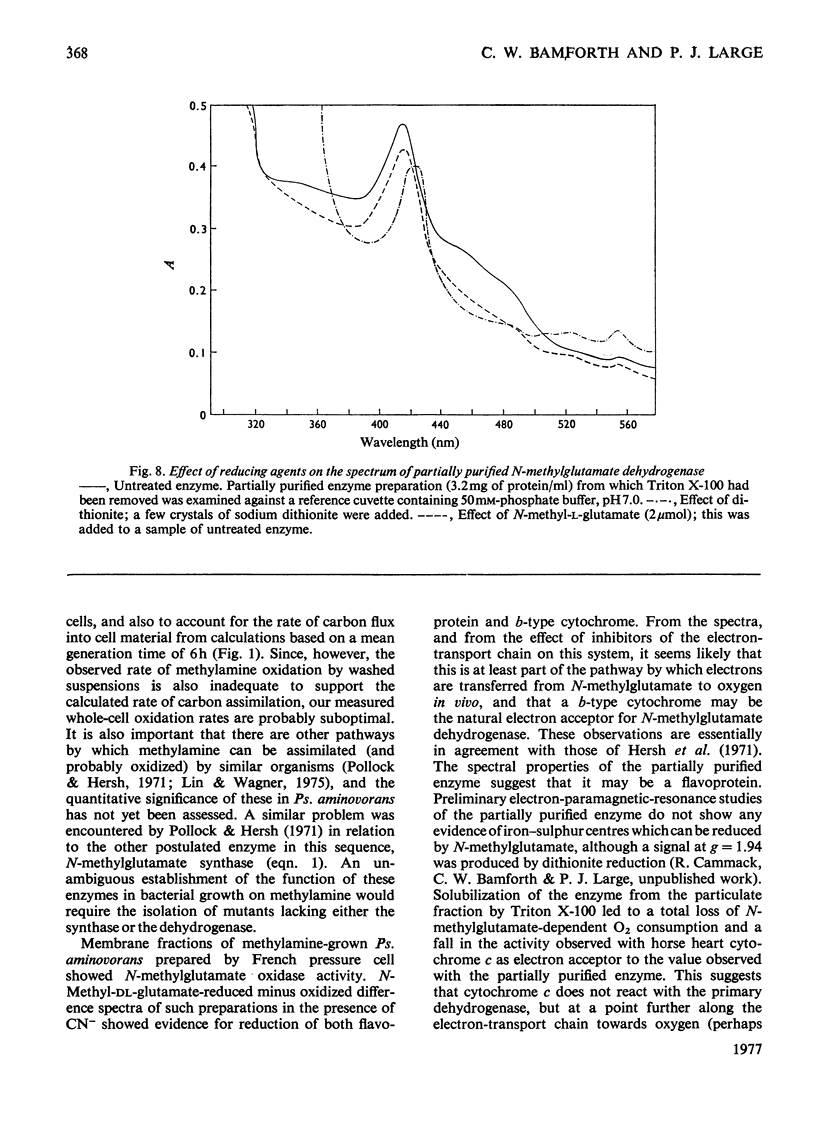
Abstract
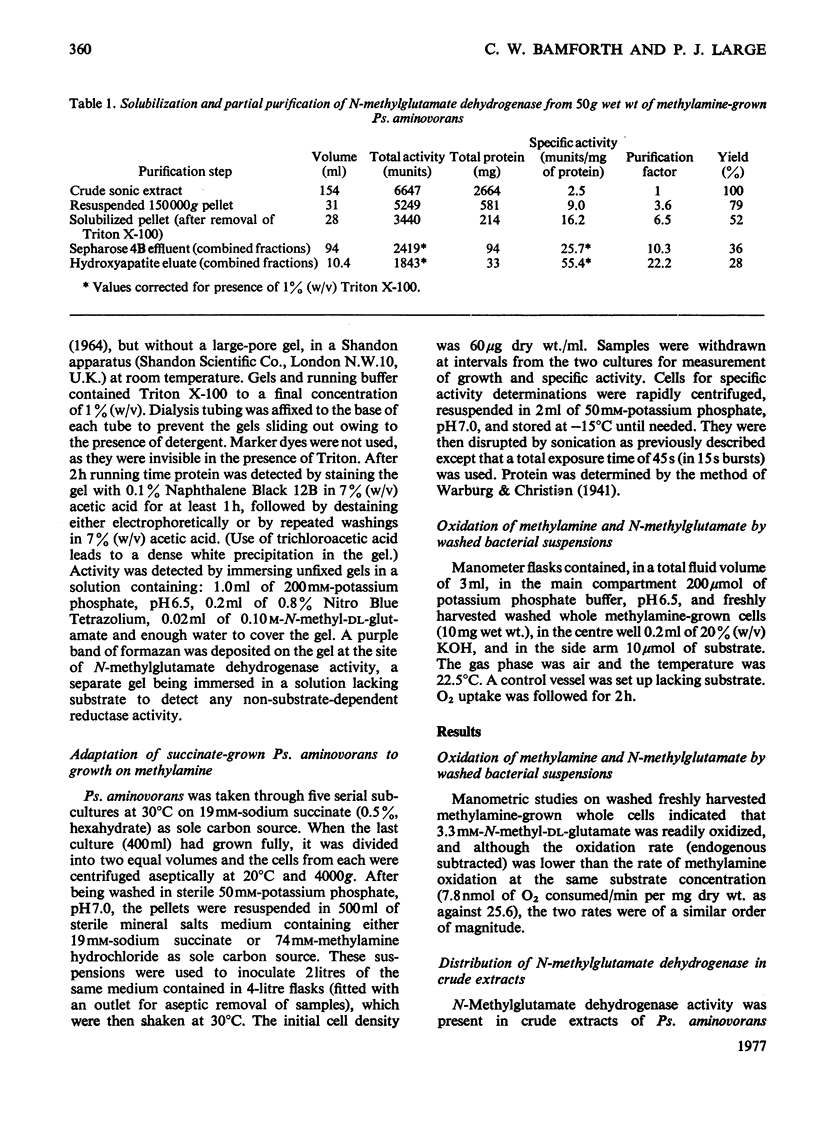
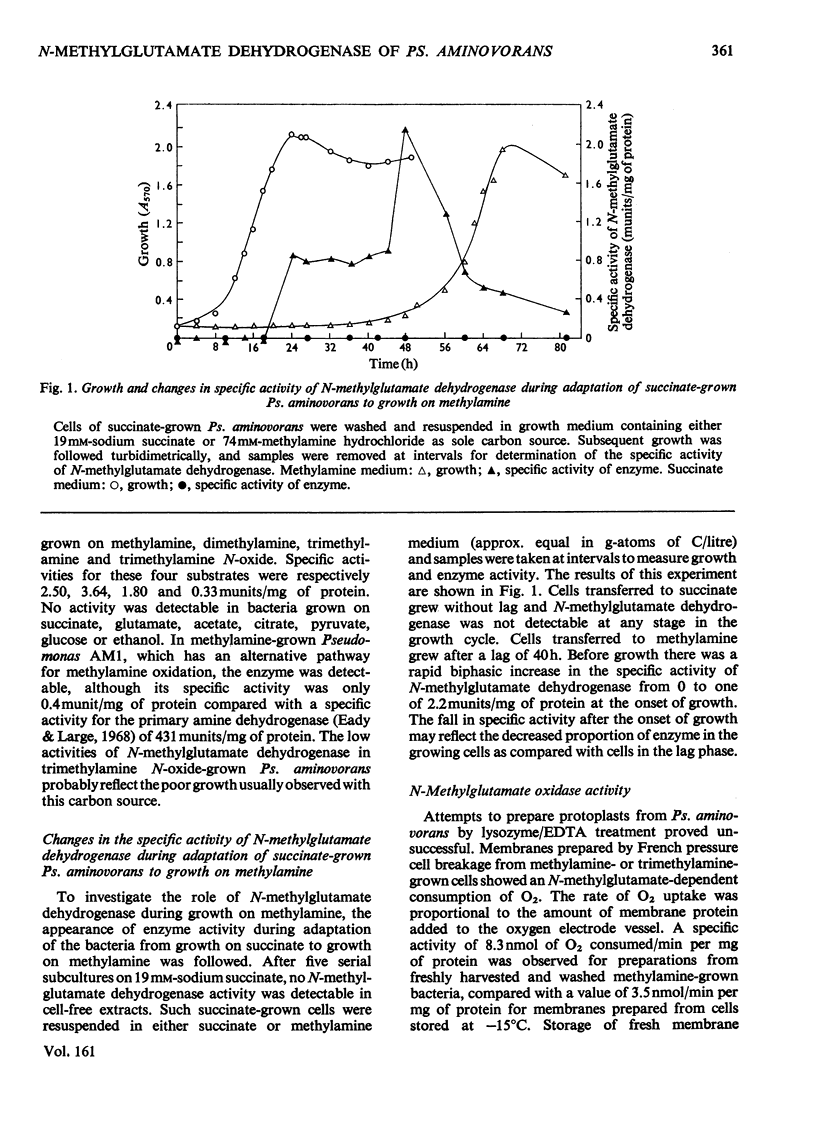
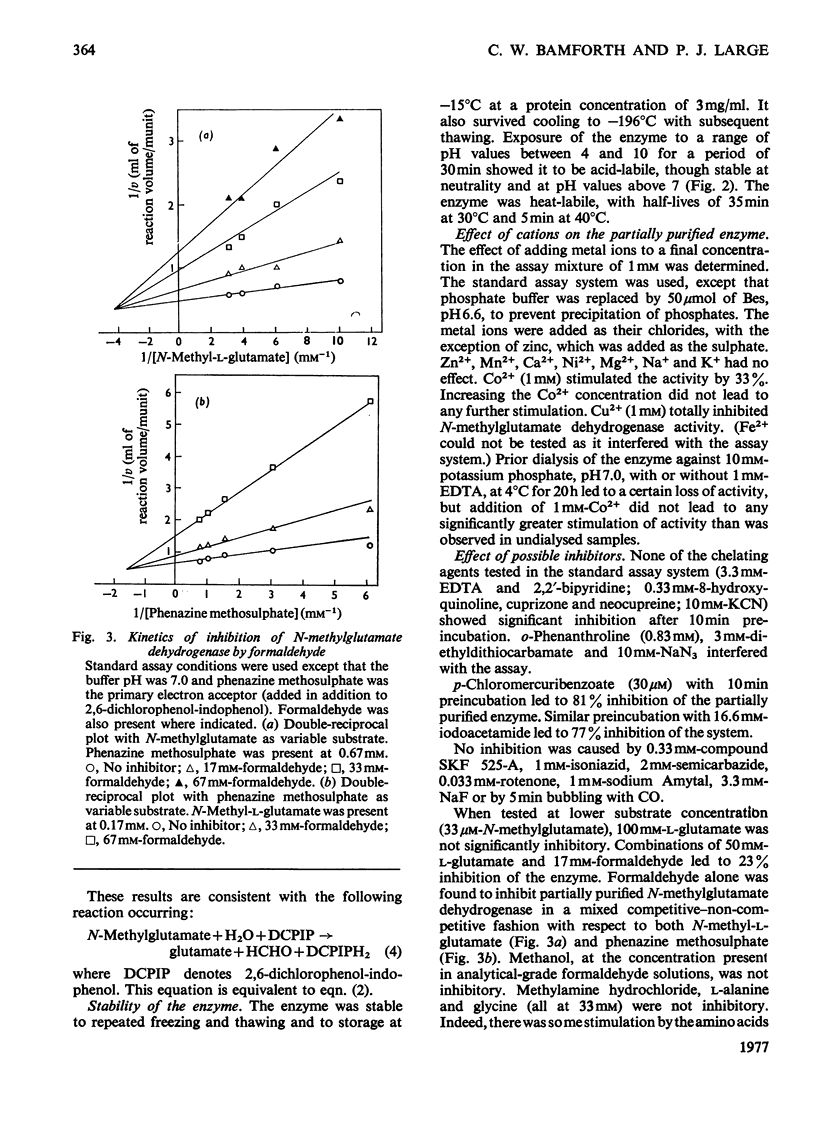
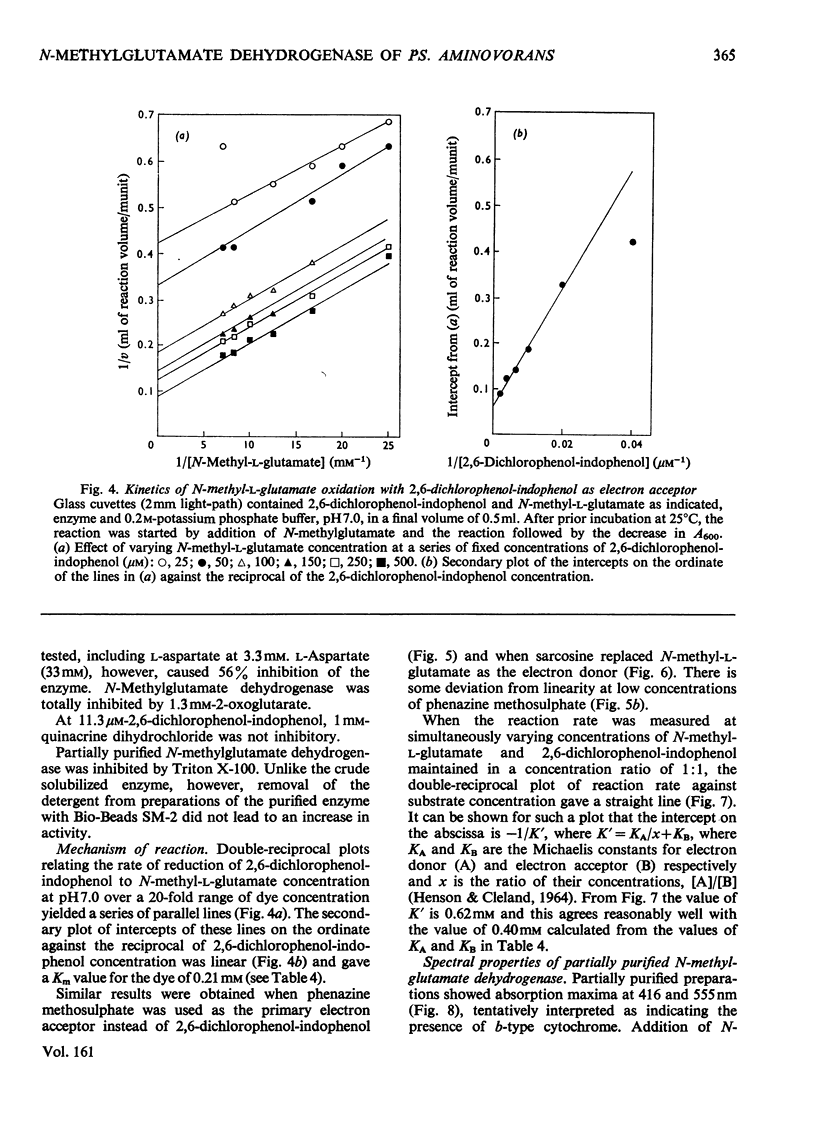
1. Extracts of amine-grown Pseudomonas aminovorans contained a particle-bound N-methylglutamate dehydrogenase (EC 1.5.99.5). The enzyme was not present in succinate-grown cells, and activity appeared before growth began in succinate-grown cells which had been transferred to methylamine growth medium. 2. Membrane-containing preparations from methylamine-grown cells catalysed an N-methylglutamate-dependent uptake of O2 or reduction of cytochrome c, which was sensitive to inhibitors of the electron-transport chain. 3. N-Methylglutamate dehydrogenase activity with phenazine methosulphate or 2,6-dichlorophenol-indophenol as electron acceptor could be solubilized with 1% (w/v) Triton X-100. The solubilized enzyme was much less active with cytochrome c as electron acceptor and did not sediment in 1 h at 150000g. Solubilization was accompanied by a change in the pH optimum for activity. 4. The solubilized enzyme was partially purified by Sepharose 4B and hydroxyapatite chromatograpy to yield a preparation 22-fold increased in specific activity over the crude extract. 5. The partially-purified enzyme was active with sarcosine, N-methylalanine and N-methylaspartate as well as with N-methylglutamate. Evidence suggesting activity with N-methyl D-amino acids as well as with the L-forms was obtained. 6. The enzyme was inhibited by p-chloromercuribenzoate, iodoacetamide and by both ionic and non-ionic detergents. 2-Oxoglutarate and formaldehyde were also inhibitors. 7. Kinetic analysis confirmed previous workers' observations of a group transfer (Ping Pong) mechanism. 8. Spectral observations suggested that the partially purified preparation contained flavoprotein and a b-type cytochrome. 9. The role of the enzyme in the oxidation of methylamine is discussed.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG J. M. THE MOLAR EXTINCTION COEFFICIENT OF 2,6-DICHLOROPHENOL INDOPHENOL. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Apr 4;86:194–197. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett M. C., Dawson A. P. The reaction of choline dehydrogenase with some electron acceptors. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;151(3):677–683. doi: 10.1042/bj1510677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton C. A., Crabbe M. J., Large P. J. Microbial oxidation of amines. Partial purification of a trimethylamine mono-oxygenase from Pseudomonas aminovorans and its role in growth on trimethylamine. Biochem J. 1974 May;140(2):253–263. doi: 10.1042/bj1400253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLELAND W. W. The kinetics of enzyme-catalyzed reactions with two or more substrates or products. III. Prediction of initial velocity and inhibition patterns by inspection. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Feb 12;67:188–196. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91816-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerniglia C. E., Perry J. J. Metabolism of n-propylamine, isopropylamine, and 1,3-propane diamine by Mycobacterium convolutum. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):285–289. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.285-289.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrastil J., Wilson J. T. A sensitive colorimeter method for formaldehyde. Anal Biochem. 1975 Jan;63(1):202–207. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90205-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby J., Zatman L. J. Enzymological aspects of the pathways for trimethylamine oxidation and C1 assimilation of obligate methylotrophs and restricted facultative methylotrophs. Biochem J. 1975 Jun;148(3):513–520. doi: 10.1042/bj1480513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby J., Zatman L. J. Trimethylamine metabolism in obligate and facultative methylotrophs. Biochem J. 1973 Jan;132(1):101–112. doi: 10.1042/bj1320101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl J. S., Mehta R. J., Hoare D. S. New obligate methylotroph. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):916–921. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.916-921.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eady R. R., Jarman T. R., Large P. J. Microbial oxidation of amines. Partial purification of a mixed-function secondary-amine oxidase system from Pseudomonas aminovorans that contains an enzymically active cytochrome-P-420-type haemoprotein. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(2):449–459. doi: 10.1042/bj1250449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eady R. R., Large P. J. Microbial oxidation of amines. Spectral and kinetic properties of the primary amine dehydrogenase of Pseudomonas AM1. Biochem J. 1971 Aug;123(5):757–771. doi: 10.1042/bj1230757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eady R. R., Large P. J. Purification and properties of an amine dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas AM1 and its role in growth on methylamine. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(1):245–255. doi: 10.1042/bj1060245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANCIS M. J., HUGHES D. E., KORNBERG H. L., PHIZACKERLEY P. J. THE OXIDATION OF L-MALATE BY PSEUDOMONAS SP. Biochem J. 1963 Dec;89:430–438. doi: 10.1042/bj0890430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisell W. R. One-carbon metabolism in microorganisms. I. Oxidative demethylation in a sarcosine-utilizing bacterium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Jan;142(1):213–222. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90277-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garewal H. S. A procedure for the estimation of microgram quantities of triton X-100. Anal Biochem. 1973 Aug;54(2):319–324. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90359-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENSON C. P., CLELAND W. W. KINETIC STUDIES OF GLUTAMIC OXALOACETIC TRANSAMINASE ISOZYMES. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:338–345. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersh L. B., Peterson J. A., Thompson A. A. An N-methyl glutamate dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas M.A. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Jul;145(1):115–120. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersh L. B., Stark M. J., Worthen S., Fiero M. K. N-methylglutamate dehydrogenase: kinetic studies on the solubilized enzyme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 May;150(1):219–226. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90029-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway P. W. A simple procedure for removal of Triton X-100 from protein samples. Anal Biochem. 1973 May;53(1):304–308. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90436-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarman T. R., Large P. J. Distribution of the enzymes oxidizing secondary and tertiary amines in Pseudomonas aminovorans grown on various substrates. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Nov;73(1):205–208. doi: 10.1099/00221287-73-1-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp M. B. D- and L-lactate dehydrogenases of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(1):307–309. doi: 10.1042/bj1300307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilmartin J. V., Rossi-Bernardi L. The binding of carbon dioxide by horse haemoglobin. Biochem J. 1971 Aug;124(1):31–45. doi: 10.1042/bj1240031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn L. D., Kaback H. R. Mechanisms of active transport in isolated bacterial membrane vesicles. XV. Purification and properties of the membrane-bound D-lactate dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7012–7017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M. C., Wagner C. Purification and characterization of N-methylalanine dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):3746–3751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loginova N. V., Trotsenko Iu A. Fermenty metabolizma metanola i metilamina u Pseudomonas methylica. Mikrobiologiia. 1974 Nov-Dec;43(6):979–985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall V. P., Sokatch J. R. Oxidation of D-amino acids by a particulate enzyme from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1419–1424. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1419-1424.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Netrusov A. I. NAD-zavisimaia N-metilglutamatdegidrigenaza--novyi ferment metabolizma metilamina u metilotrofov. Mikrobiologiia. 1975 May-Jun;44(3):552–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock J. J., Linder R., Salton M. R. Characterization of the membrane-bound succinic dehydrogenase of Micrococcus lysodeikticus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):230–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.230-238.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock R. J., Hersh L. B. N-methylglutamate synthetase. Purification and properties of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4737–4743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J., Cooper J. M. Method of determining oxygen concentrations in biological media, suitable for calibration of the oxygen electrode. Anal Biochem. 1970 Feb;33(2):390–399. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Herrera J., Ramiŕez A. M. Solubilization and properties of succinate dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli. Rev Latinoam Microbiol. 1973 Jul-Sep;15(3):133–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGER T. P., KEARNEY E. B. Determination of succinic dehydrogenase activity. Methods Biochem Anal. 1957;4:307–333. doi: 10.1002/9780470110201.ch9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw W. V., Tsai L., Stadtman E. R. The enzymatic synthesis of N-methylglutamic acid. J Biol Chem. 1966 Feb 25;241(4):935–945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J. The molecular organization of membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):805–833. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.004105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steenkamp D. J., Mallinson J. Trimethylamine dehydrogenase from a methylotrophic bacterium. I. Isolation and steady-state kinetics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 13;429(3):705–719. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90319-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


