Abstract
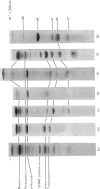
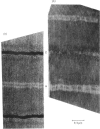
Z discs were isolated from Lethocerus flight muscle by removing the contractile proteins from myofibrils with a solution of high ionic strength. The protein composition of the Z discs was analysed by sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis; the major proteins were alpha-actinin, actin and tropomyosin. Z lines were selectively removed from intact myofibrils by digestion with crude lipase and chymotrypsin, but not by purified lipase.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashhurst D. E. Z-line of the flight muscle of belostomatid water bugs. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 28;27(2):385–389. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullard B., Dabrowska R., Winkelman L. The contractile and regulatory proteins of insect flight muscle. Biochem J. 1973 Oct;135(2):277–286. doi: 10.1042/bj1350277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORSI A., PERRY S. V. Some observations on the localization of myosin, actin and tropomyosin in the rabbit myofibril. Biochem J. 1958 Jan;68(1):12–17. doi: 10.1042/bj0680012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARAMVOLGYI N., METZGER-TOROK G., TIGYI-SEBES A. The Z- and M-formations of straited muscle. Acta Physiol Acad Sci Hung. 1962;22:223–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOA J. A micro biuret method for protein determination; determination of total protein in cerebrospinal fluid. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1953;5(3):218–222. doi: 10.3109/00365515309094189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garamvölgyi N. The arrangement of the myofilaments in the insect flight muscle. II. J Ultrastruct Res. 1965 Dec;13(5):425–434. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(65)90005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goli D. E., Suzuki A., Temple J., Holmes G. R. Studies on purified -actinin. I. Effect of temperature and tropomyosin on the -actinin-F-actin interaction. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):469–488. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90464-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goll D. E., Mommaerts W. F., Reedy M. K., Seraydarian K. Studies on alpha-actinin-like proteins liberated during trypsin digestion of alpha-actinin and of myofibrils. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Feb 4;175(1):174–194. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90156-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond K. S., Goll D. E. Purification of insect myosin and alpha-actinin. Biochem J. 1975 Oct;151(1):189–192. doi: 10.1042/bj1510189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harsányi V., Garamvölgyi N. On the Z-substance of striated muscle. Acta Biochim Biophys Acad Sci Hung. 1969;4(3):259–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masaki T., Endo M., Ebashi S. Localization of 6S component of a alpha-actinin at Z-band. J Biochem. 1967 Nov;62(5):630–632. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D. The role of actin in the temperature-dependent gelation and contraction of extracts of Acanthamoeba. J Cell Biol. 1976 Mar;68(3):579–601. doi: 10.1083/jcb.68.3.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. W. The contractile mechanism of insect fibrillar muscle. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1967;17:1–60. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(67)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rash J. E., Shay J. W., Biesele J. J. Urea extraction of Z bands, intercalated disks, and desmosomes. J Ultrastruct Res. 1968 Aug;24(3):181–189. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(68)90057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saide J. D., Ullrick W. C. Fine structure of the honeybee Z-disc. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):329–337. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saide J. D., Ullrick W. C. Purification and properties of the isolated honeybee Z-disc. J Mol Biol. 1974 Aug 25;87(4):671–683. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90077-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P., Hartwig J. H. Interactions between actin, myosin, and an actin-binding protein from rabbit alveolar macrophages. Alveolar macrophage myosin Mg-2+-adenosine triphosphatase requires a cofactor for activation by actin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 25;250(14):5706–5712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stromer M. H., Hartshorne D. J., Mueller H., Rice R. V. The effect of various protein fractions on Z- and M-line reconstitution. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jan;40(1):167–178. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]