Abstract
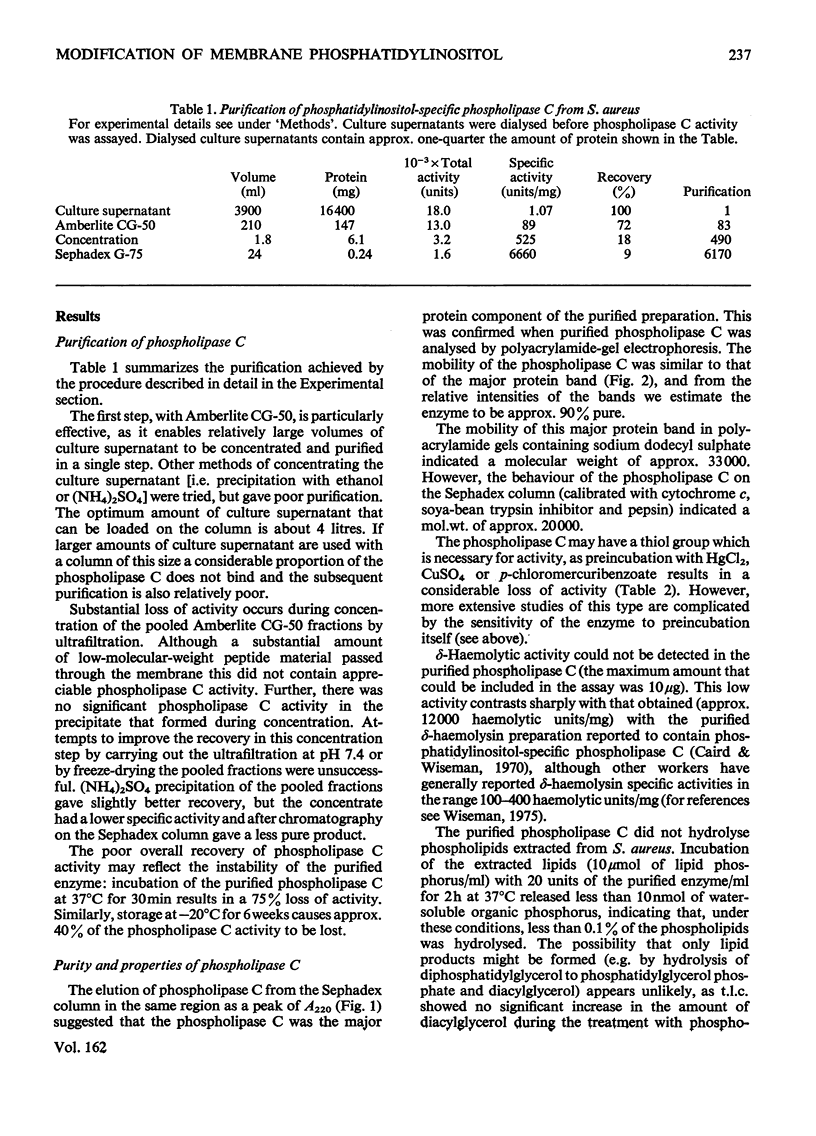
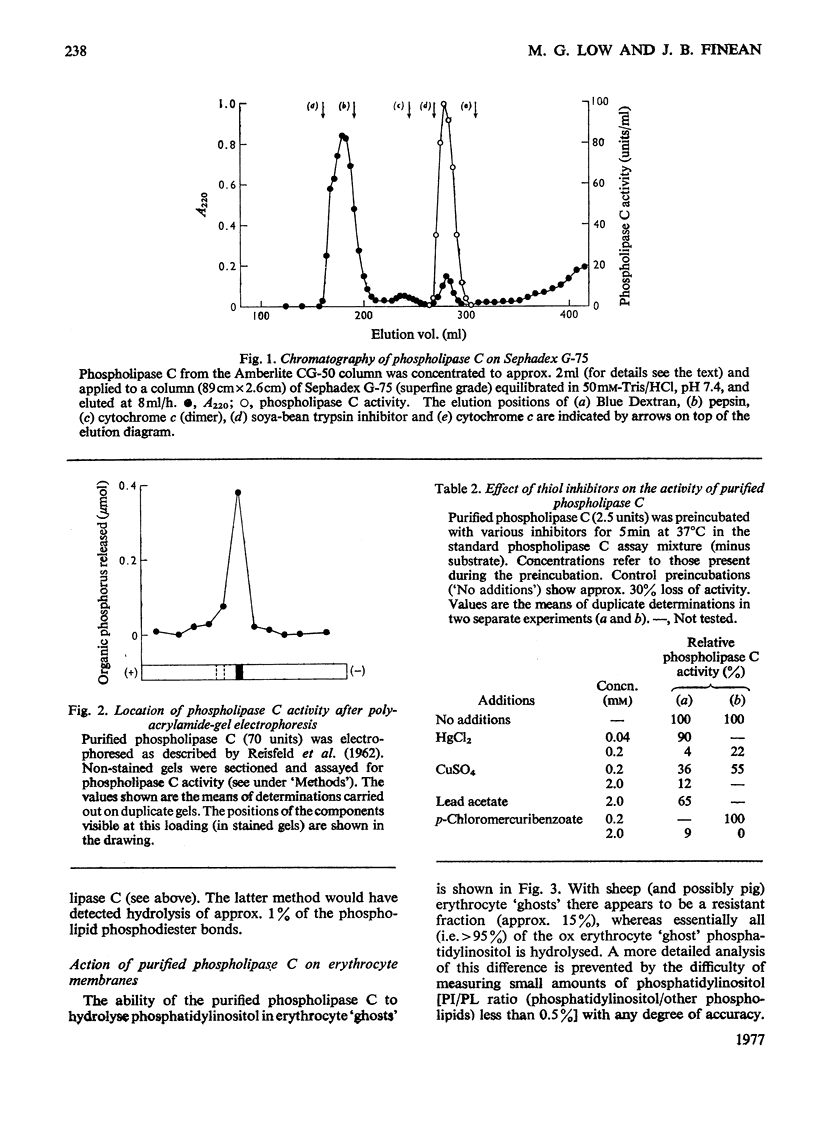
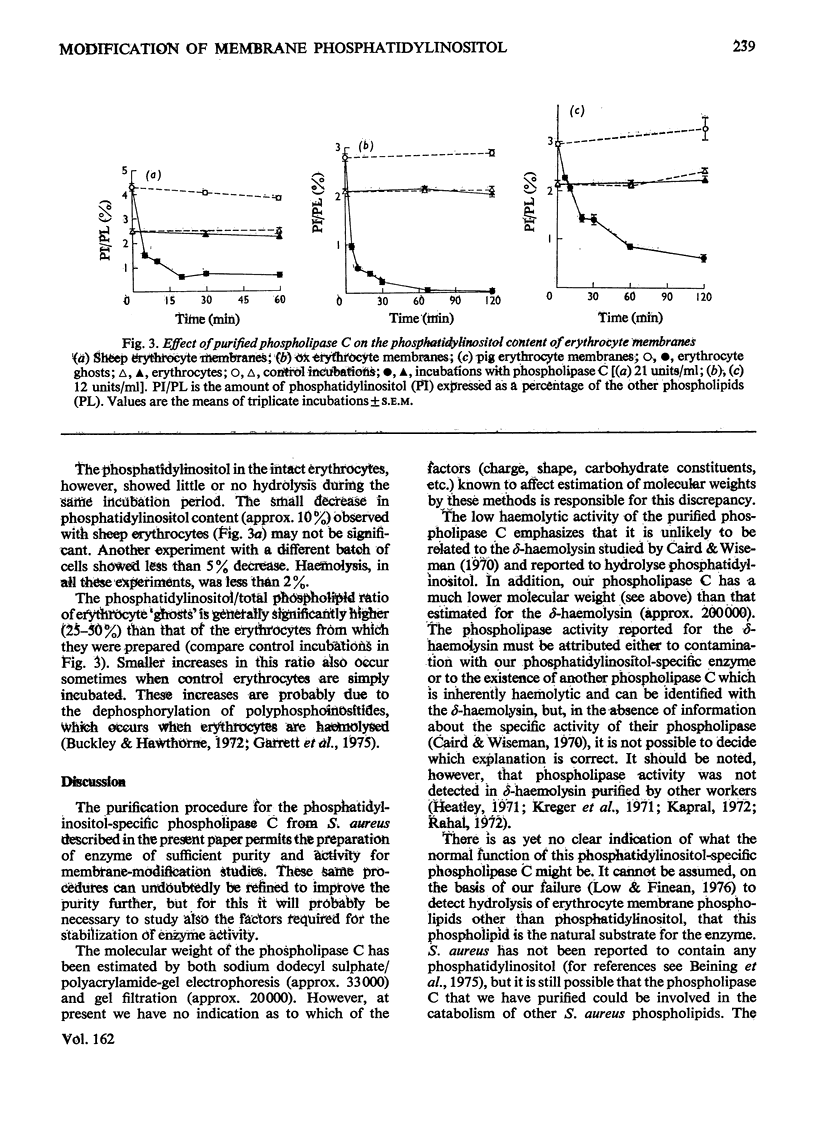
A phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C from Staphylococcus aureus was purified by a three-step procedure. The specific activity of the purified enzyme was approx. 6000 times that of the culture supernatant, with an overall recovery of approx. 10%. Estimation of the molecular weight by sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis and by gel filtration gave values of 33000 and 20000 respectively. A thiol group appears to be necessary for the activity of the enzyme. The purified enzyme had no detectable delta-haemolytic activity and was unable to hydrolyse S. aureus phospholipids. Phosphatidyl-inositol in erythrocyte 'ghosts' was readily hydrolysed by the purified phospholipase C. However, in contrast with our previous preliminary observations, phosphatidylinositol in intact erythrocytes was not significantly hydrolysed. These results suggest that at least 75-80% of the phosphatidylinositol is located at the inner leaflet of the membrane.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beining P. R., Huff E., Prescott B., Theodore T. S. Characterization of the lipids of mesosomal vesicles and plasma membranes from Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):137–143. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.137-143.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley J. T., Hawthorne J. N. Erythrocyte membrane polyphosphoinositide metabolism and the regulation of calcium binding. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7218–7223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burriss Garrett R. J., Redman C. M. Localization of enzymes involved in polyphosphoinositids metabolism on the cytoplasmic surface of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 28;382(1):58–64. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90372-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caird J. D., Wiseman G. M. Purification of the delta toxin os Staphylococcus aureus. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Aug;16(8):703–708. doi: 10.1139/m70-120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doery H. M., Magnusson B. J., Gulasekharam J., Pearson J. E. The properties of phospholipase enzymes in staphylococcal toxins. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Aug;40(2):283–296. doi: 10.1099/00221287-40-2-283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heatley N. G. A new method for the preparation and some properties of staphylococcal delta-haemolysin. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Dec;69(2):269–278. doi: 10.1099/00221287-69-2-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A. Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus delta hemolysin by phospholipids. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Nov;141(2):519–521. doi: 10.3181/00379727-141-36812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger A. S., Kim K. S., Zaboretzky F., Bernheimer A. W. Purification and properties of staphylococcal delta hemolysin. Infect Immun. 1971 Mar;3(3):449–465. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.3.449-465.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusaka I. Degradation of phospholipid and release of diglyceride-rich membrane vesicles during protoplast formation in certain gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):1173–1179. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.1173-1179.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Finean J. B. The action of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipases C on membranes. Biochem J. 1976 Jan 15;154(1):203–208. doi: 10.1042/bj1540203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISFELD R. A., LEWIS U. J., WILLIAMS D. E. Disk electrophoresis of basic proteins and peptides on polyacrylamide gels. Nature. 1962 Jul 21;195:281–283. doi: 10.1038/195281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahal J. J., Jr Comparative effects of purified staphylococcal alpha and delta toxins on mitochondrial metabolism. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jul;126(1):96–103. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.1.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. P., Kirscher L. B. Di- and triphosphoinositide metabolism in swine erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 10;202(2):283–294. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90190-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman G. M. The hemolysins of Staphylococcus aureus. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Dec;39(4):317–344. doi: 10.1128/br.39.4.317-344.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaal R. F., Roelofsen B., Colley C. M. Localization of red cell membrane constituents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 10;300(2):159–182. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(73)90003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


