Abstract
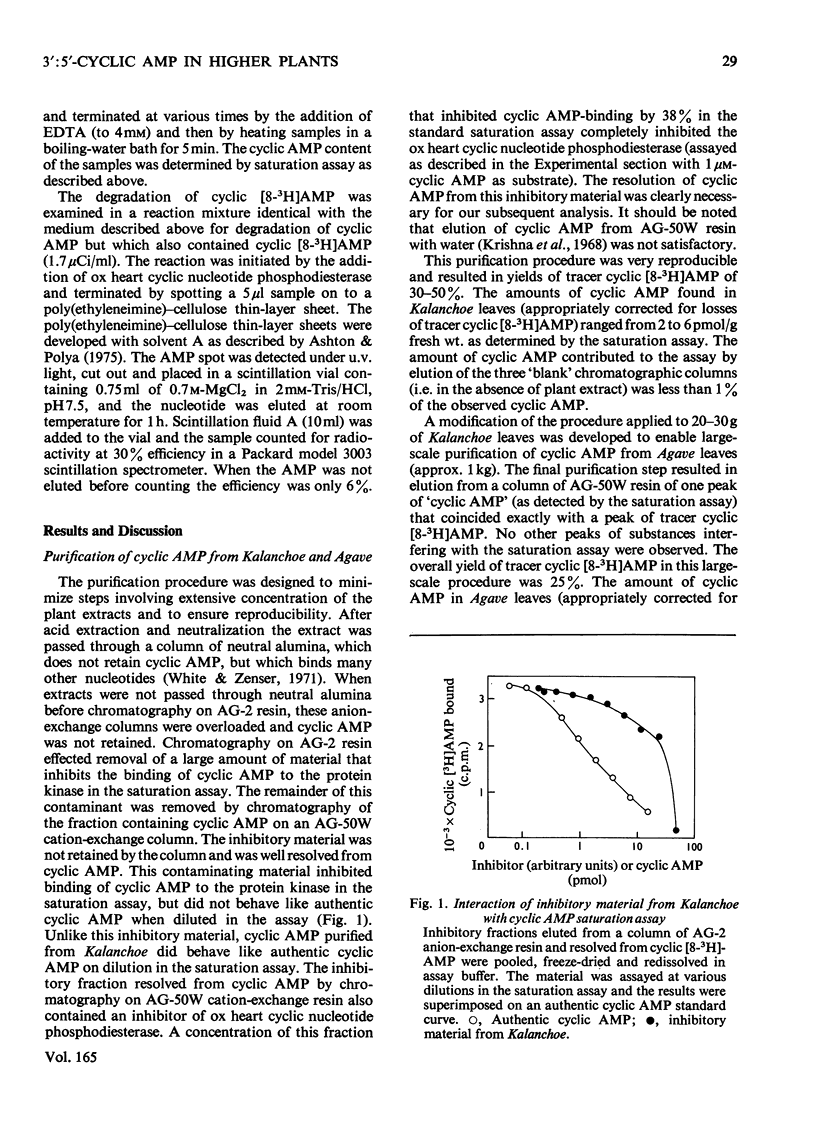
1.3':5'-Cyclic AMP was extensively purified from Kalanchoe daigremontiana and Agave americana by neutral alumina and anion- and cation-exchange column chromatography. Inclusion of 3':5'-cyclic [8-3H]AMP from the point of tissue extraction permitted calculation of yields. The purification procedure removed contaminating material that was shown to interfere with the 3':5'-cyclic AMP estimation and characterization procedures. 2. The partially purified 3':5'-cyclic AMP was quantified by means of a radiochemical saturation assay using an ox heart 3':5'-cyclic AMP-binding protein and by an assay involving activation of a mammalian protein kinase. 3. The plant 3':5'-cyclic AMP co-migrated with 3':5'-cyclic [8-3H]AMP on cellulose chromatography, poly(ethyleneimine)-cellulose chromatography and silica-gel t.l.c. developed with several solvent systems. 4. The plant 3':5'-cyclic AMP was degraded by ox heart 3':5'-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase at the same rates as authentic 3':5'-cyclic AMP. 1-Methyl-3-isobutylxanthine (1 mM), a specific inhibitor of the 3':5'-cyclic nucleotide phosphodieterase, completely inhibited such degradation. 5. The concentrations of 3':5'-cyclic AMP satisfying the above criteria in Kalanchoe and Agave were 2-6 and 1 pmol/g fresh wt. respectively. Possible bacterial contribution to these analyses was estimated to be less than 0.002pmol/g fresh wt. Evidence for the occurrence of 3':5'-cyclic AMP in plants is discussed.
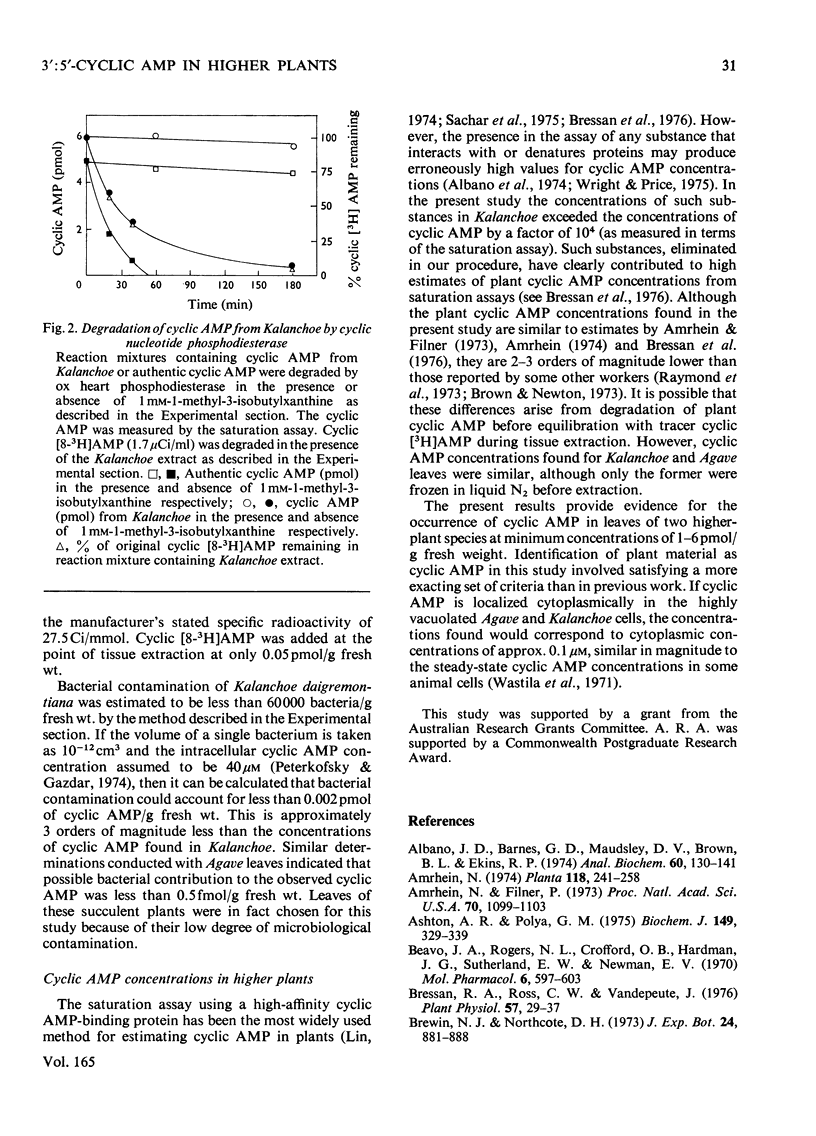
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albano J. D., Barnes G. D., Maudsley D. V., Brown B. L., Etkins R. P. Factors affecting the saturation assay of cyclic AMP in biological systems. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):130–141. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90137-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amrhein N., Filner P. Adenosine 3':5'-Cyclic Monophosphate in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: Isolation and Characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1099–1103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton A. R., Polya G. M. Higher-plant cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Resolution, partial purification and properties of three phosphodiesterases from potato tuber. Biochem J. 1975 Aug;149(2):329–339. doi: 10.1042/bj1490329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavo J. A., Rogers N. L., Crofford O. B., Hardman J. G., Sutherland E. W., Newman E. V. Effects of xanthine derivatives on lipolysis and on adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase activity. Mol Pharmacol. 1970 Nov;6(6):597–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bressan R. A., Ross C. W. Attempts to detect cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate in higher plants by three assay methods. Plant Physiol. 1976 Jan;57(1):29–37. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott D. C., Murray A. W. Evidence against an involvement of cyclic nucleotides in the induction of betacyanin synthesis by cytokinins. Biochem J. 1975 Feb;146(2):333–337. doi: 10.1042/bj1460333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg N. D., Larner J., Sasko H., O'Toole A. G. Enzymic analysis of cyclic 3', 5'-AMP in mammalian tissues and urine. Anal Biochem. 1969 Apr 4;28(1):523–544. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90208-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg N. D., O'Toole A. G. Analysis of cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate and cyclic 3',5'-guanosine monophosphate. Methods Biochem Anal. 1971;20:1–39. doi: 10.1002/9780470110393.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardman J. G., Davis J. W., Sutherland E. W. Effects of some hormonal and other factors on the excretion of guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate and adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in rat urine. J Biol Chem. 1969 Dec 10;244(23):6354–6362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler B., Levinstein R. Adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate in higher plants: assay, distribution and age-dependency. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 20;343(1):156–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(74)90247-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna G., Weiss B., Brodie B. B. A simple, sensitive method for the assay of adenyl cyclase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Oct;163(2):379–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Greengard P. An assay method for cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP based upon their abilities to activate cyclic AMP-dependent and cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinases. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1972;2:41–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin P. P. Cyclic nucleotides in higher plants? Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1974;4(0):439–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer S. E., Stull J. T., Wastila W. B., Thompson B. Assay of cyclic AMP by protein kinase activation. Methods Enzymol. 1974;38:66–73. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)38012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niles R. M., Mount M. S. Failure to Detect Cyclic 3', 5'-Adenosine Monophosphate in Healthy and Crown Gall Tumorous Tissues of Vicia faba. Plant Physiol. 1974 Sep;54(3):372–373. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.3.372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otten J., Johnson G. S., Pastan I. Regulation of cell growth by cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. Effect of cell density and agents which alter cell growth on cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate levels in fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):7082–7087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky A., Gazdar C. Glucose inhibition of adenylate cyclase in intact cells of Escherichia coli B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2324–2328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANDERATH K., RANDERATH E. ION-EXCHANGE CHROMATOGRAPHY OF NUCLEOTIDES ON POLY-(ETHYLENEIMINE)-CELLULOSE THIN LAYERS. J Chromatogr. 1964 Oct;16:111–125. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)82445-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond P., Narayanan A., Pradet A. Evidence for the presence of 3', 5'-cyclic AMP in plant tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Aug 21;53(4):1115–1121. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90580-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimann E. M., Walsh D. A., Krebs E. G. Purification and properties of rabbit skeletal muscle adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):1986–1995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovey K. C., Oldham K. G., Whelan J. A. A simple direct assay for cyclic AMP in plasma and other biological samples using an improved competitive protein binding technique. Clin Chim Acta. 1974 Nov 8;56(3):221–234. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(74)90133-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wastila W. B., Stull J. T., Mayer S. E., Walsh D. A. Measurement of cyclic 3',5'-denosine monophosphate by the activation of skeletal muscle protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):1996–2003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White A. A., Zenser T. V. Separation of cyclic 3',5'-nucleoside monophosphates from other nucleotides on aluminum oxide columns. Application to the assay of adenyl cyclase and guanyl cyclase. Anal Biochem. 1971 Jun;41(2):372–396. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90156-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. T., Price R. Protein-binding assay for cyclic AMP: possible interference by traces of trichloroacetate. Anal Biochem. 1975 Jul;67(1):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90304-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


