Abstract
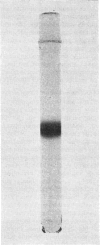
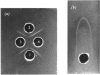
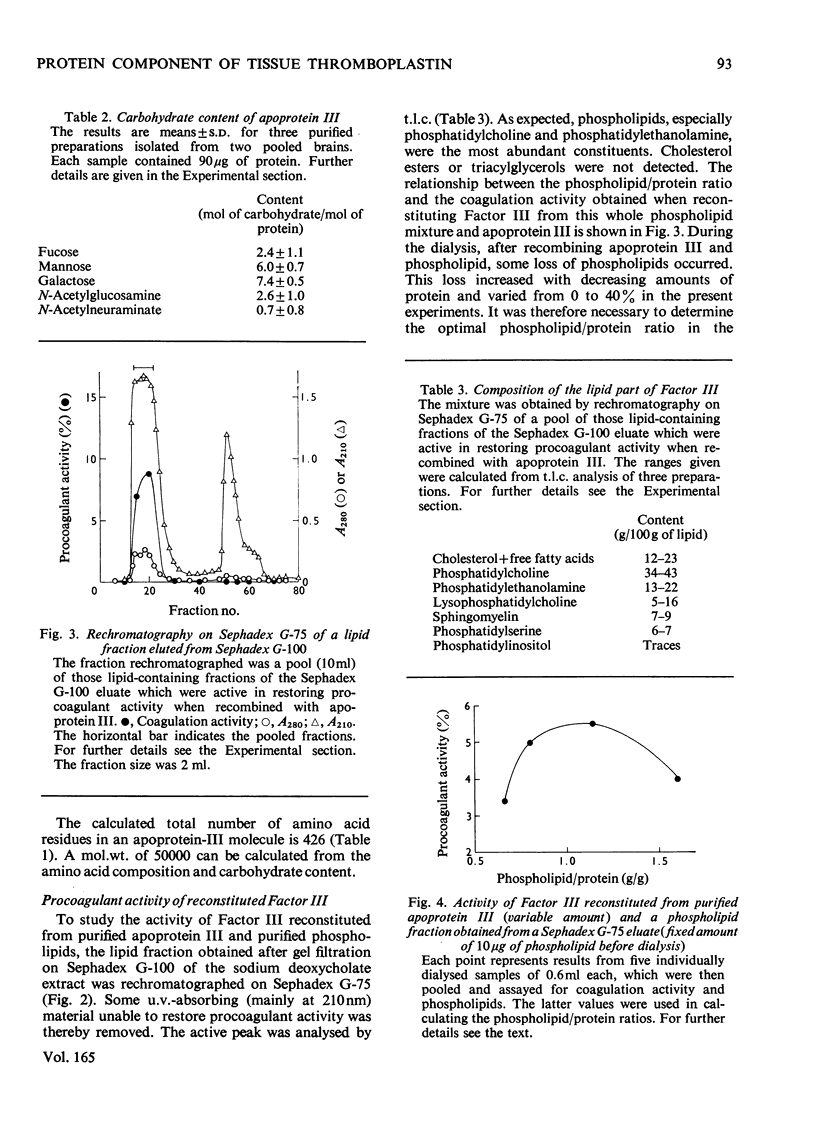
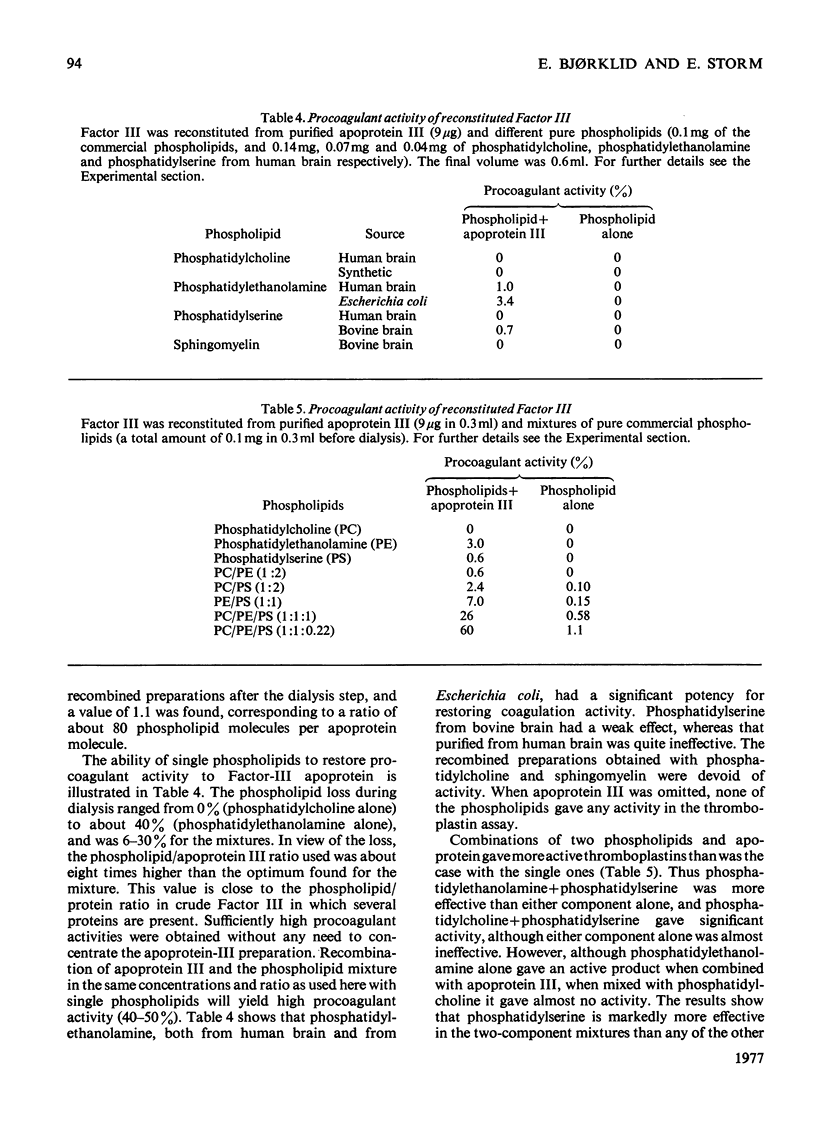
The protein component of tissue thromboplastib (Factor III) from human brain was purified by extraction of a microsomal fraction with sodium deoxycholate, gel filtration of the extract on Sephadex G-100 and preparative polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulphate. The product, apoprotein III, was homogeneous by anayltical polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis, and it induced monospecific antibodies in rabbits and goat as shown by immunodiffusion and immunoelectrophoresis. Amino acid- and carbohydrate-analysis data for apoprotein III are presented. The carbohydrate moiety of the protein consists of fucose, mannose, galactose, N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylneuraminate, amounting to a total content of 6.3g/100g. The apoprotein alone had no procoagulant activity. When Factor III was reconstituted by combining the pure apoprotein with a purified lipid fraction from the deoxycholate extract of crude Factor III, a high and optimal procoagulant activity was obtained at a phospholipid/protein ratio of 1.1g/g. Phosphatidylethanolamine alone had a weak but significant ability to restore activity, whereas phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylserine separately had almost none. Two-component mixtures were on average more effective, and three-component mixtures far more effective, than the single phospholipids. The inclusion of a small amount of phosphatidylserine was very important for high activity.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayer P. M., Deutsch E. Solubilisation von Gewebethromboplastin. Effekt verschiedener Detergentien. Acta Haematol. 1975;54(3):165–171. doi: 10.1159/000208068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerrum O. J., Bhakdi S., Bog-Hansen T. C., Knüfermann H., Wallach D. F. Quantitative immunoelectrophoresis of proteins in human erythrocyte membranes. Analysis of protein bands obtained by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Nov 3;406(4):489–504. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90027-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerrum O. J., Lundahl P. Crossed immunoelectrophoresis of human erythrocyte membrane proteins. Immunoprecipitation patterns for fresh and stored samples of membranes extensively solubilized with non-ionic detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 14;342(1):69–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorklid E., Otnaess A. B., Storm E., Prydz H., Johansen B. V., Froholm L. O. Treatment of tissue thromboplastin membranes with phospholipase C. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1973 Dec 31;30(3):509–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorklid E., Storm E., Osterud B., Prydz H. The interaction of the protein and phospholipid components of tissue thromboplastin (factor III) with the factors VII and X. Scand J Haematol. 1975 Mar;14(1):65–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1975.tb00294.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorklid E., Storm E., Prydz H. The protein component of human brain thromboplastin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 10;55(3):969–976. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91237-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull R. K., Jevons S., Barton P. G. Complexes of prothrombin with calcium ions and phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2747–2754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clamp J. R., Bhatti T., Chambers R. E. The determination of carbohydrate in biological materials by gas-liquid chromatography. Methods Biochem Anal. 1971;19:229–344. doi: 10.1002/9780470110386.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEUTSCH E., IRSIGLER K., LOMOSCHITZ H. STUDIEN UEBER GEWEBETHROMBOPLASTIN. 1. REINIGUNG, CHEMISCHE CHARAKTERISIERUNG UND TRENNUNG IN EINEN EISWISS-UND LIPOIDANTEIL. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1964 Oct 15;12:12–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H. Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1948–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonmori H., Takeda Y. Properties of canine tissue thromboplastins from brain, lung, arteries, and veins. Am J Physiol. 1975 Sep;229(3):618–626. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.3.618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRS C. H. The oxidation of ribonuclease with performic acid. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):611–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hvatum M., Prydz H. Studies on tissue thromboplastin--its splitting into two separable parts. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1969 Apr 30;21(2):217–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. R. Improved method of hexosamine determination. Anal Biochem. 1971 Dec;44(2):628–635. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90252-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B. ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY CROSSED ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1965 Feb;10:358–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu D. T., McCoy L. E. Phospholipid requirements of tissue thromboplastin in blood coagulation. Thromb Res. 1975 Jul;7(1):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(75)90137-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu D. T., McCoy L. E. Tissue extract thromboplastin: quantitation, fractionation and characterization of protein components. Thromb Res. 1975 Jul;7(1):199–199. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(75)90136-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara H., Sasaki R. M. High recovery of tryptophan from acid hydrolysates of proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Apr 29;35(2):175–181. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90263-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y. Characteristics and lipid requirements of coagulant proteins extracted from lung and brain: the specifity of protein component of tissue factor. J Clin Invest. 1969 Feb;48(2):322–331. doi: 10.1172/JCI105988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y., Esnouf M. P. Activation of a proteolytic system by a membrane lipoprotein: mechanism of action of tissue factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):310–314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y., Pitlick F. A. Purification and characterization of the protein component of tissue factor. Biochemistry. 1970 Dec 22;9(26):5100–5105. doi: 10.1021/bi00828a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y., Pitlick F. A. The tissue factor pathway of blood coagulation. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1972;1:1–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Molecular weight determination of protein-dodecyl sulfate complexes by gel electrophoresis in a discontinuous buffer system. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6328–6334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki Y., Tanford C. The solubility of amino acids and two glycine peptides in aqueous ethanol and dioxane solutions. Establishment of a hydrophobicity scale. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):2211–2217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otnaess A. B., Holm T. The effect of phospholipase C on human blood platelets. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jun;57(6):1419–1425. doi: 10.1172/JCI108411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitlick F. A. Concanavalin A inhibits tissue factor coagulant activity. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jan;55(1):175–179. doi: 10.1172/JCI107908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitlick F. A., Nemerson Y. Binding of the protein component of tissue factor to phospholipids. Biochemistry. 1970 Dec 22;9(26):5105–5113. doi: 10.1021/bi00828a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitlick F. A., Nemerson Y., Gottlieb A. J., Gordon R. G., Williams W. J. Peptidase activity associated with the tissue factor of blood coagulation. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2650–2657. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacterle G. R., Pollack R. L. A simplified method for the quantitative assay of small amounts of protein in biologic material. Anal Biochem. 1973 Feb;51(2):654–655. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Weissmann C. A rapid, sensitive, and specific method for the determination of protein in dilute solution. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):502–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subbaiah P. V., Bajwa S. S., Smith C. M., Hanahan D. J. Interactions of the components of the prothrombinase complex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 24;444(1):131–146. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90230-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]