Abstract
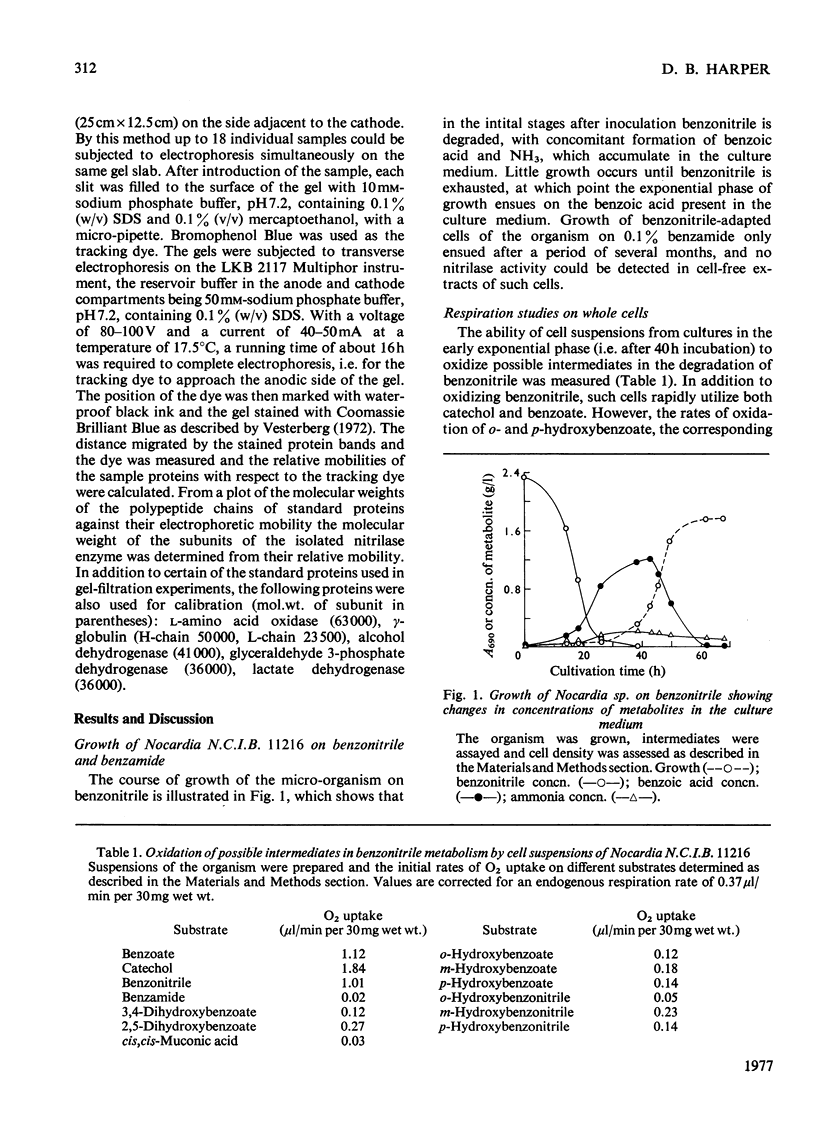
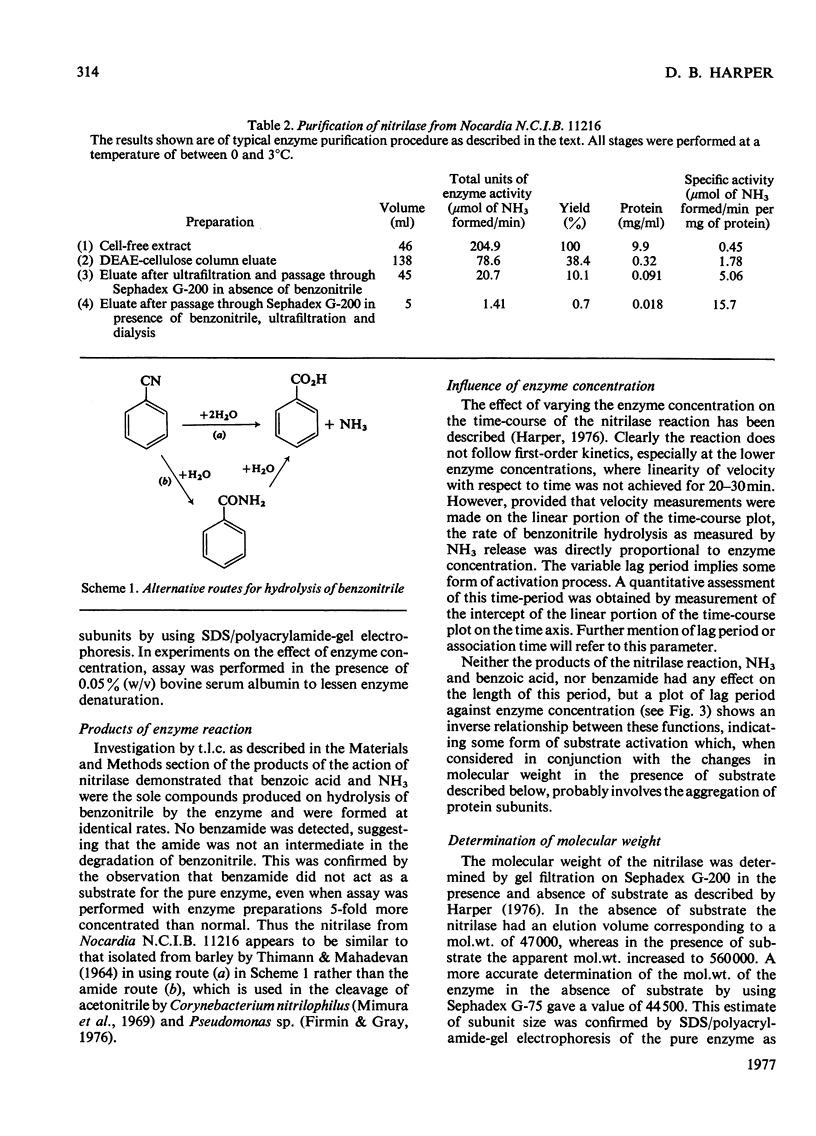
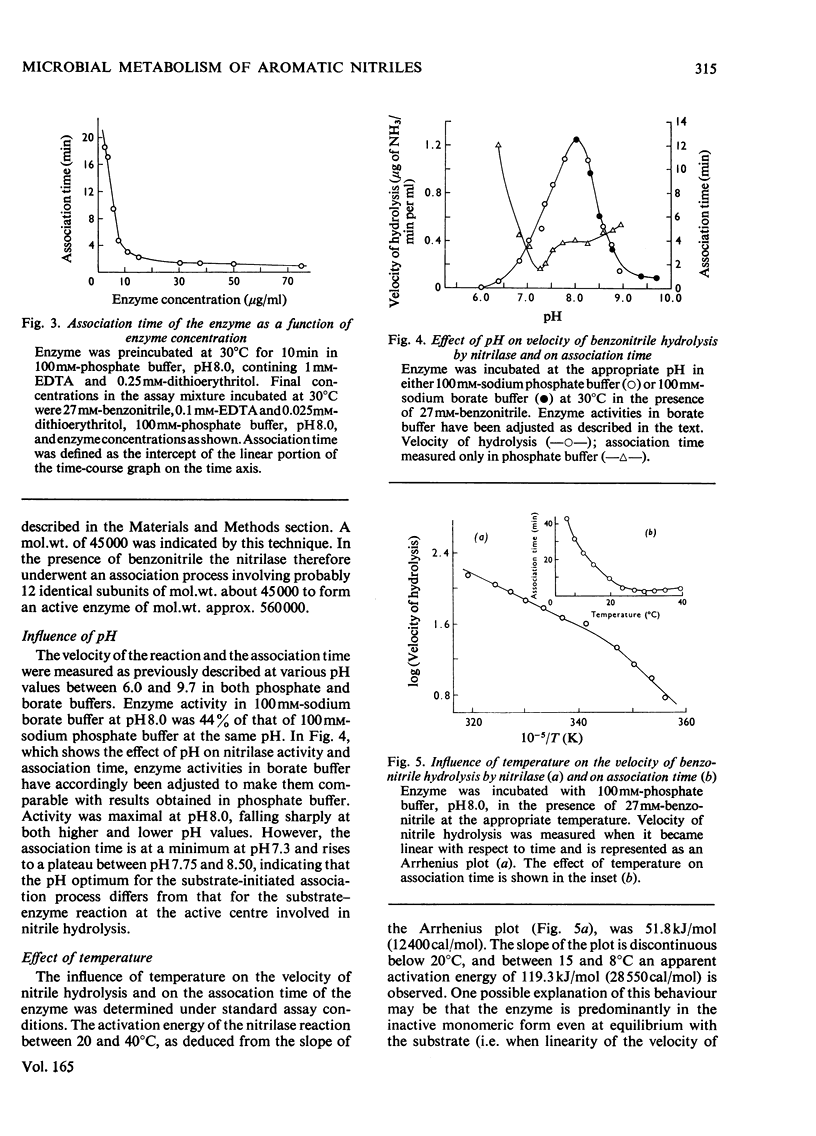
1. An organism utilizing benzonitrile as sole carbon and nitrogen source was isolated by the enrichment-culture technique and identified as a Nocardia sp. of the rhodochrous group. 2. Respiration studies indicate that nitrile degradation proceeds through benzoic acid and catechol. 3. Cell-free extracts of benzonitrile-grown cells contain an enzyme that catalyses the conversion of benzonitrile directly into benzoic acid without intermediate formation of benzamide. 4. This nitrilase enzyme was purified by DEAE-cellulose chromatography and gel filtration on Sephadex G-100 in the presence and absence of substrate. The purity of the enzyme was confirmed by sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis and isoelectric focusing on polyacrylamide gel. 5. The enzyme shows a time-dependent substrate-activation process in which the substrate catalyses the association of inactive subunits of mol.wt. 45000 to form the polymeric 12-unit active enzyme of mol.wt. 560000. The time required for complete association is highly dependent on the concentration of the enzyme, temperature and pH. 6. The associated enzyme has a pH optimum of 8.0 and Km with benzonitrile as substrate of 4mm. The activation energy of the reaction as deduced from the Arrhenius plot is 51.8kJ/mol. 7. Enzyme activity is inhibited by thiol-specific reagents and several metal ions. 8. Studies with different substrates indicate that the nitrilase is specific for nitrile groups directly attached to the benzene ring. Various substituents in the ring are compatible with activity, though ortho-substitution, except by fluorine, renders the nitrile invulnerable to attack. 9. The environmental implications of these findings and the possible significance of the enzyme in the regulation of metabolism are discussed.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FAWCETT J. K., SCOTT J. E. A rapid and precise method for the determination of urea. J Clin Pathol. 1960 Mar;13:156–159. doi: 10.1136/jcp.13.2.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firmin J. L., Gray D. O. The biochemical pathway for the breakdown of methyl cyanide (acetonitrile) in bacteria. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 15;158(2):223–229. doi: 10.1042/bj1580223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOOK R. H., ROBINSON W. G. RICININE NITRILASE. II. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Dec;239:4263–4267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper D. B. Purification and properties of an unusual nitrilase from Nocardia N.C.I.B. 11216. Biochem Soc Trans. 1976;4(3):502–504. doi: 10.1042/bst0040502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAHADEVAN S., THIMANN K. V. NITRILASE. II. SUBSTRATE SPECIFICITY AND POSSIBLE MODE OF ACTION. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jul;107:62–68. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90269-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON W. G., HOOK R. H. RICININE NITRILASE. I. REACTION PRODUCT AND SUBSTRATE SPECIFICITY. J Biol Chem. 1964 Dec;239:4257–4262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THIMANN K. V., MAHADEVAN S. NITRILASE. I. OCCURRENCE, PREPARATION, AND GENERAL PROPERTIES OF THE ENZYME. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Apr;105:133–141. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90244-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesterberg O. Isoelectric focusing of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 26;257(1):11–19. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90248-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Pringle J. R., Osborn M. Measurement of molecular weights by electrophoresis on SDS-acrylamide gel. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:3–27. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


