Abstract
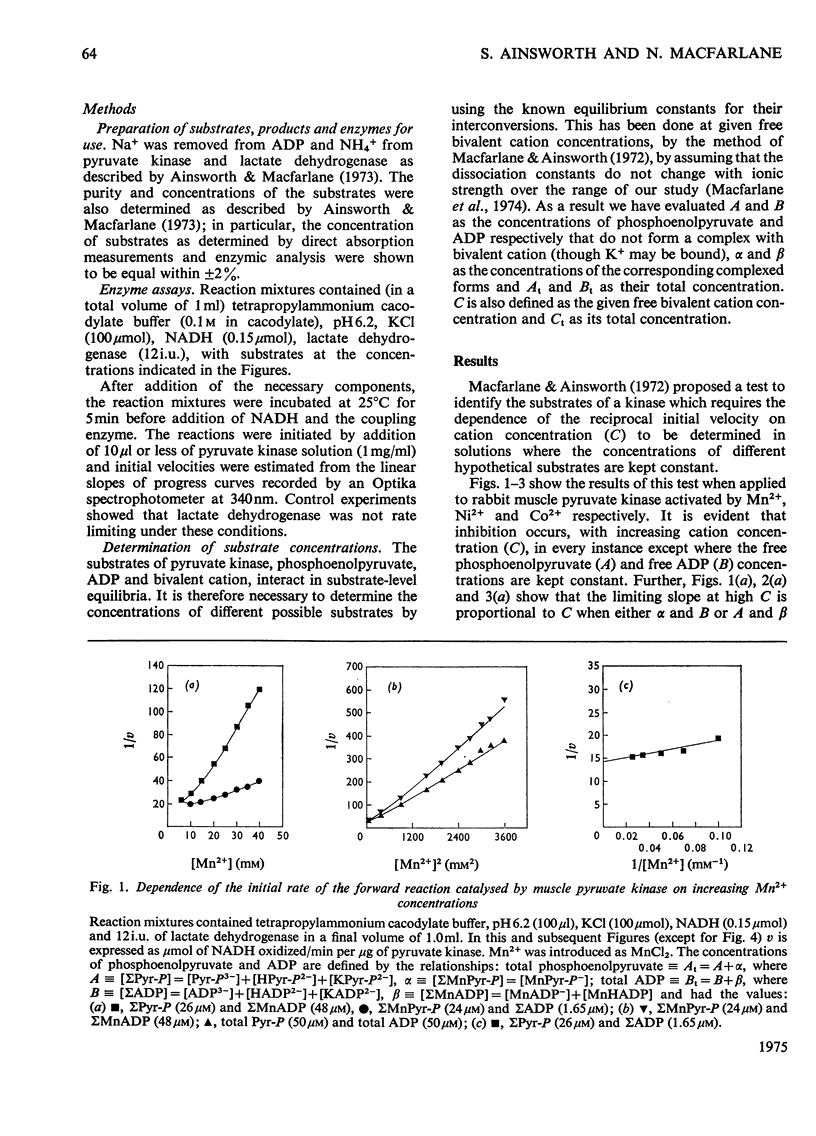
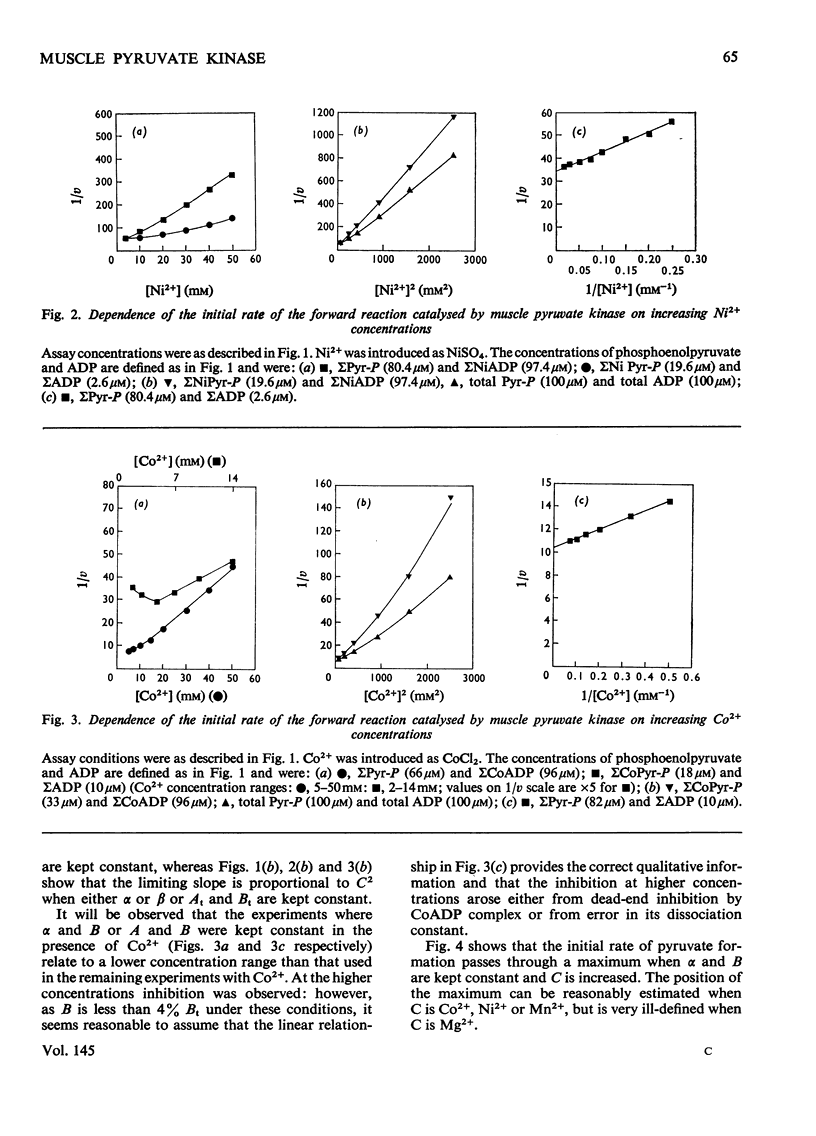
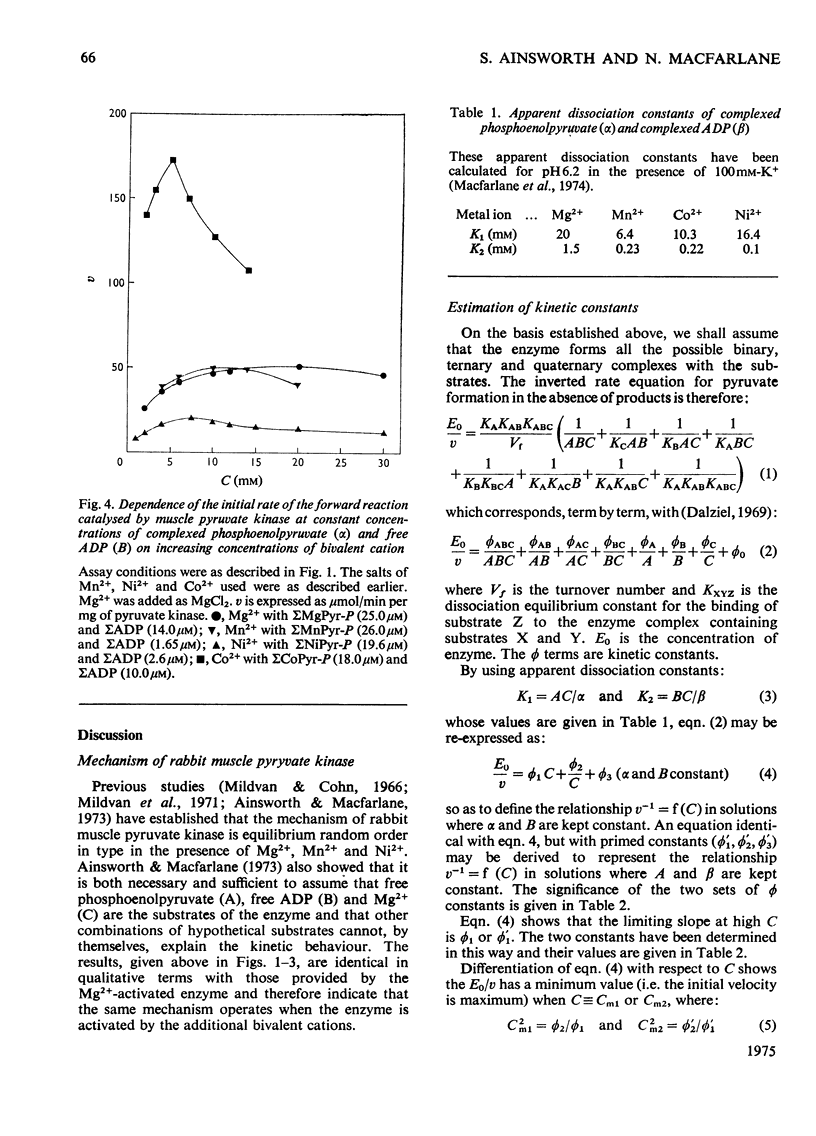
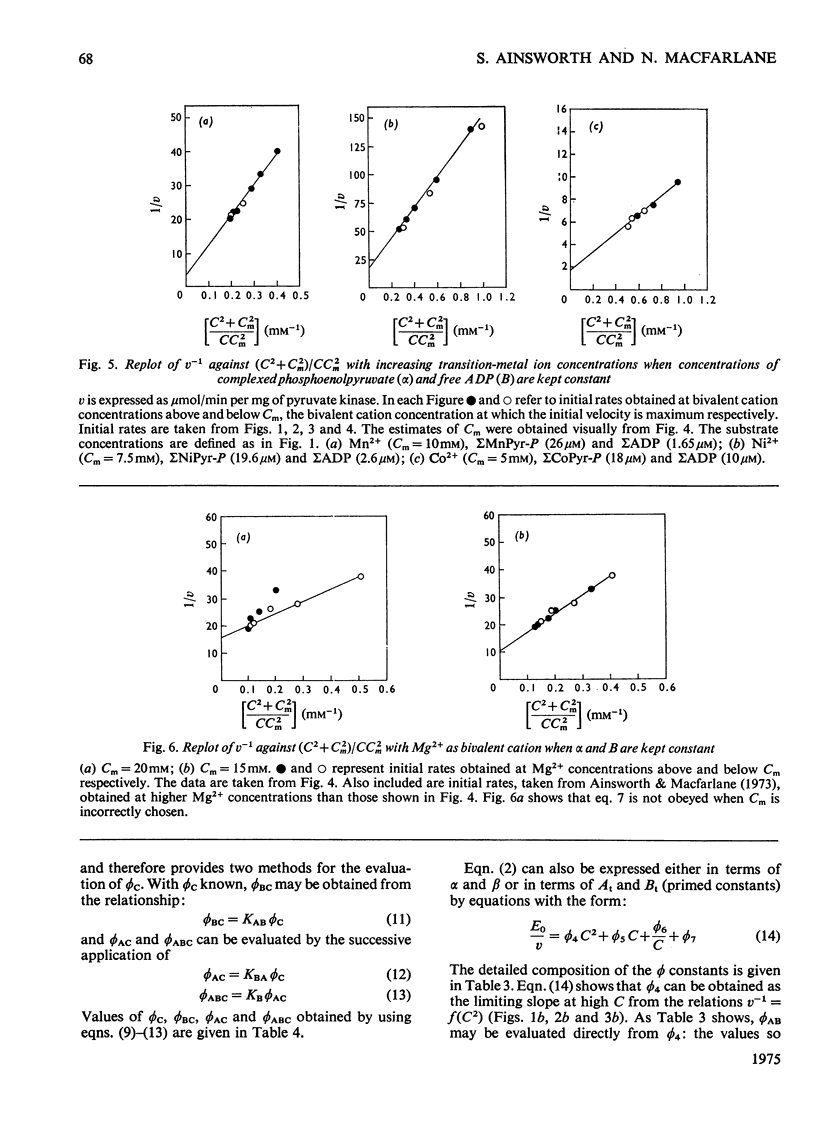
The paper reports a comparative study of the effects of Mn2+, Ni2+ and Co2+ on the reaction of ADP with phosphoenolypyruvate when catalysed by K+-activated rabbit muscle pyruvate kinase. The activation and subsequent inhibition that occurs as the bivalent ion concentration is increased is taken as evidence that the substrates of the enzyme are phosphoenolypyruvate, uncomplexed ADP and free bivalent cation. Kinetic constants for the binding of the bivalent cation to the enzyme are reported.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ainsworth S., MacFarlane N. A kinetic study of rabbit muscle pyruvate kinase. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;131(2):223–236. doi: 10.1042/bj1310223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bygrave F. L. Studies on the interaction of metal ions with pyruvate kinase from Ehrlich ascites-tumour cells and from rabbit muscle. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):488–494. doi: 10.1042/bj1010488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN M. MAGNETIC RESONANCE STUDIES OF METAL ACTIVATION OF ENZYMIC REACTIONS OF NUCLEOTIDES AND OTHER PHOSPHATE SUBSTRATES. Biochemistry. 1963 Jul-Aug;2:623–629. doi: 10.1021/bi00904a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalziel K. The interpretation of kinetic data for enzyme-catalysed reactions involving three substrates. Biochem J. 1969 Sep;114(3):547–556. doi: 10.1042/bj1140547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyde E., Morrison J. F. The interaction of Mg2+ and ATP4- with ATP: creatine phosphotransferase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Mar 18;178(1):47–60. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90130-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KACHMAR J. F., BOYER P. D. Kinetic analysis of enzyme reactions. II. The potassium activation and calcium inhibition of pyruvic phosphoferase. J Biol Chem. 1953 Feb;200(2):669–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAYNE F. J., SUELTER C. H. EFFECTS OF TEMPERATURE, SUBSTRATE, AND ACTIVATING CATIONS ON THE CONFORMATIONS OF PYRUVATE KINASE IN AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS. J Am Chem Soc. 1965 Feb 20;87:897–900. doi: 10.1021/ja01082a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayne F. J., Price N. C. Conformational changes in the allosteric inhibition of muscle pyruvate kinase by phenylalanine. Biochemistry. 1972 Nov 7;11(23):4415–4420. doi: 10.1021/bi00773a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson-Raźnikiewicz M. The phosphoglycerate kinase reaction and its metal ion specificity. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Nov;17(1):183–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01152.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILDVAN A. S., COHN M. KINETIC AND MAGNETIC RESONANCE STUDIES OF THE PYRUVATE KINASE REACTION. I. DIVALENT METAL COMPLEXES OF PYRUVATE KINASE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:238–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane N., Ainsworth S. A kinetic study of pig liver pyruvate kinase activated by fructose diphosphate. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):499–508. doi: 10.1042/bj1390499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlane N., Hoy T. G., Ainsworth S. The calculation of species arising from the interaction of univalent and bivalent cations with common metabolites incorporating phosphate groups. Int J Biomed Comput. 1974 Jul;5(3):165–173. doi: 10.1016/0020-7101(74)90027-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mildvan A. S., Cohn M. Kinetic and magnetic resonance studies of the pyruvate kinase reaction. II. Complexes of enzyme, metal, and substrates. J Biol Chem. 1966 Mar 10;241(5):1178–1193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed G. H., Cohn M. Electron paramagnetic resonance studies of manganese (II)-pyruvate kinase-substrate complexes. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6436–6442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARNER R. C. Physical properties of crystalline fluorokinase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Dec;78(2):494–496. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90373-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimhurst J. M., Manchester K. L. Comparison of ability of Mg and Mn to activate the key enzymes of glycolysis. FEBS Lett. 1972 Nov 1;27(2):321–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80650-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


