Abstract
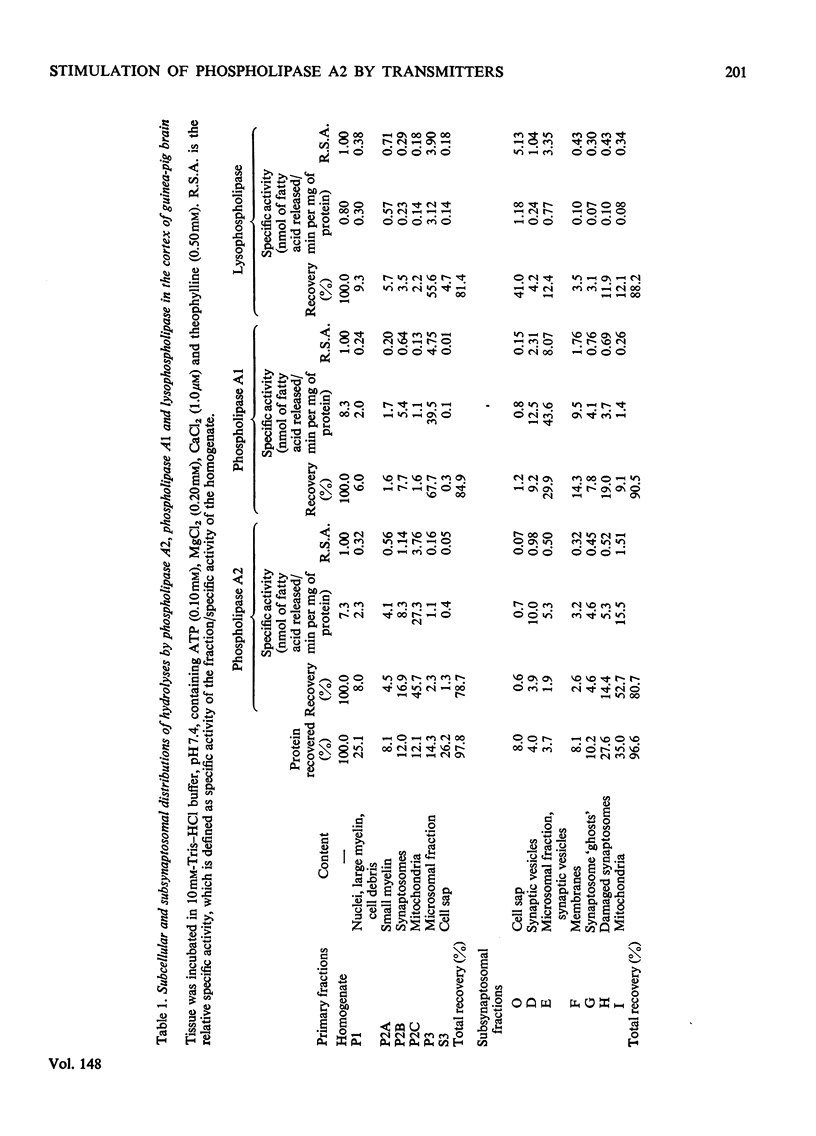
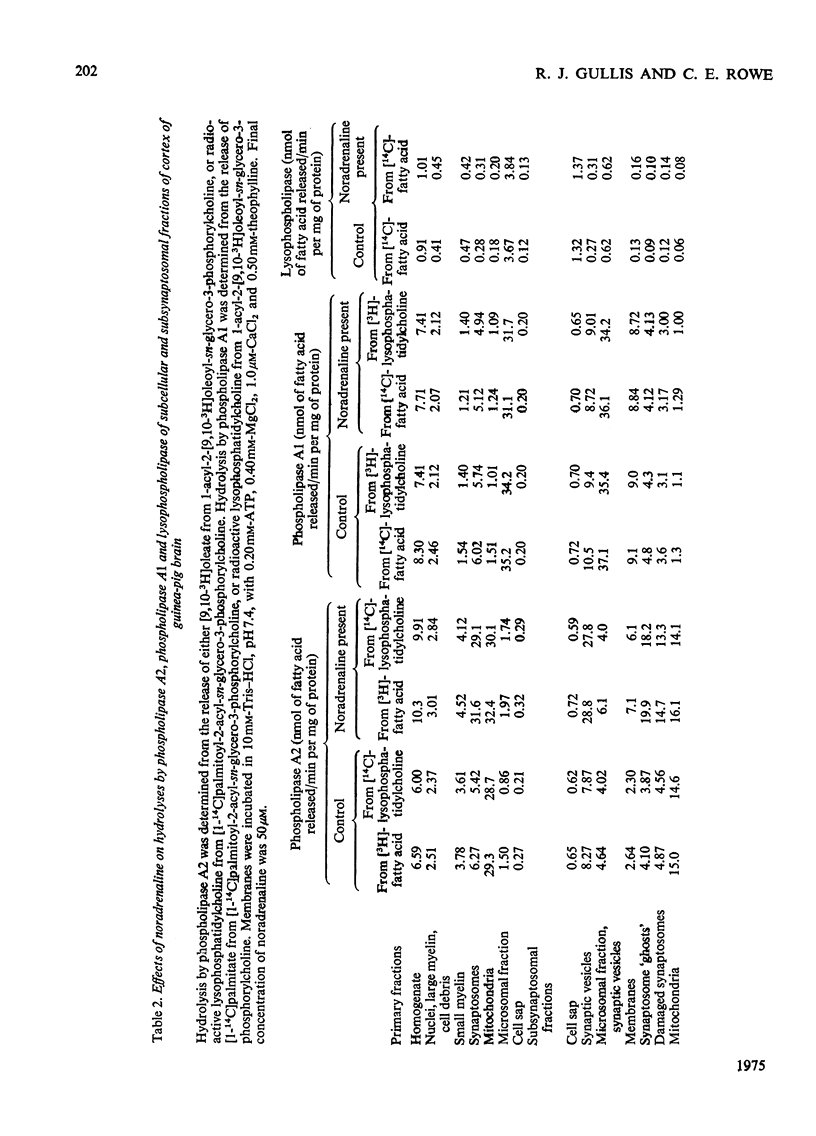
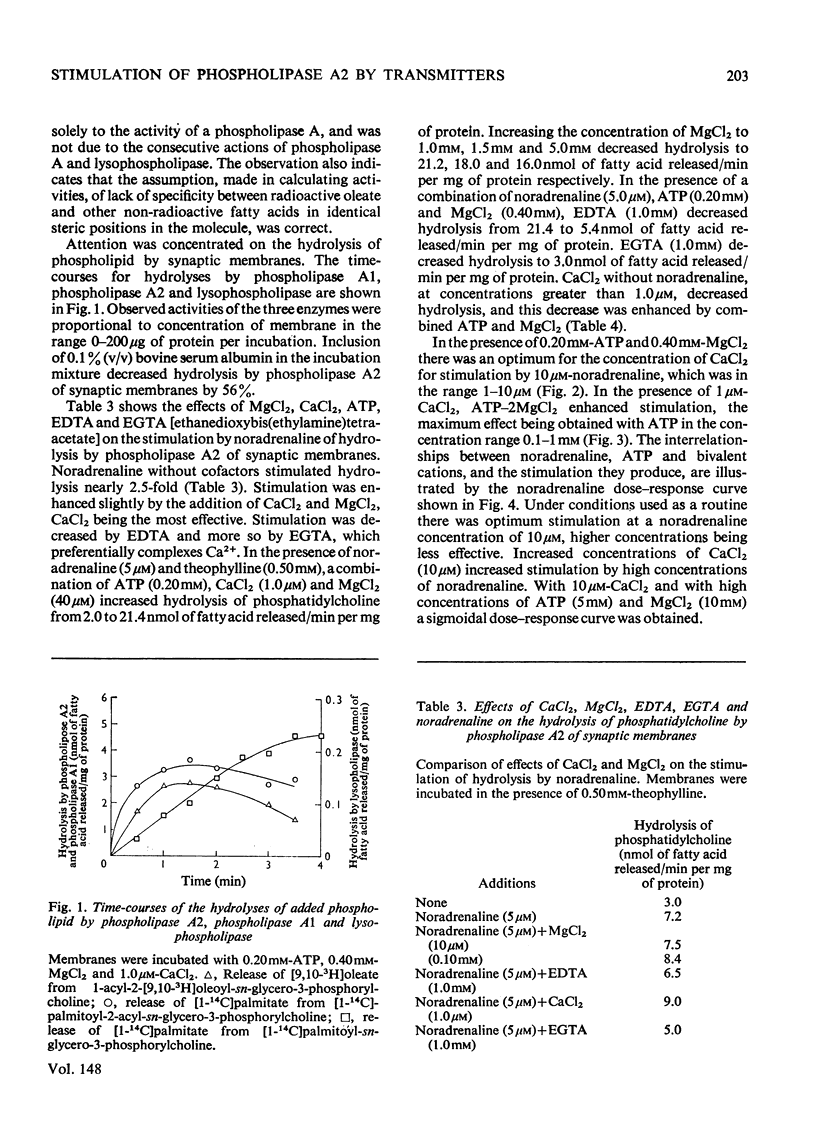
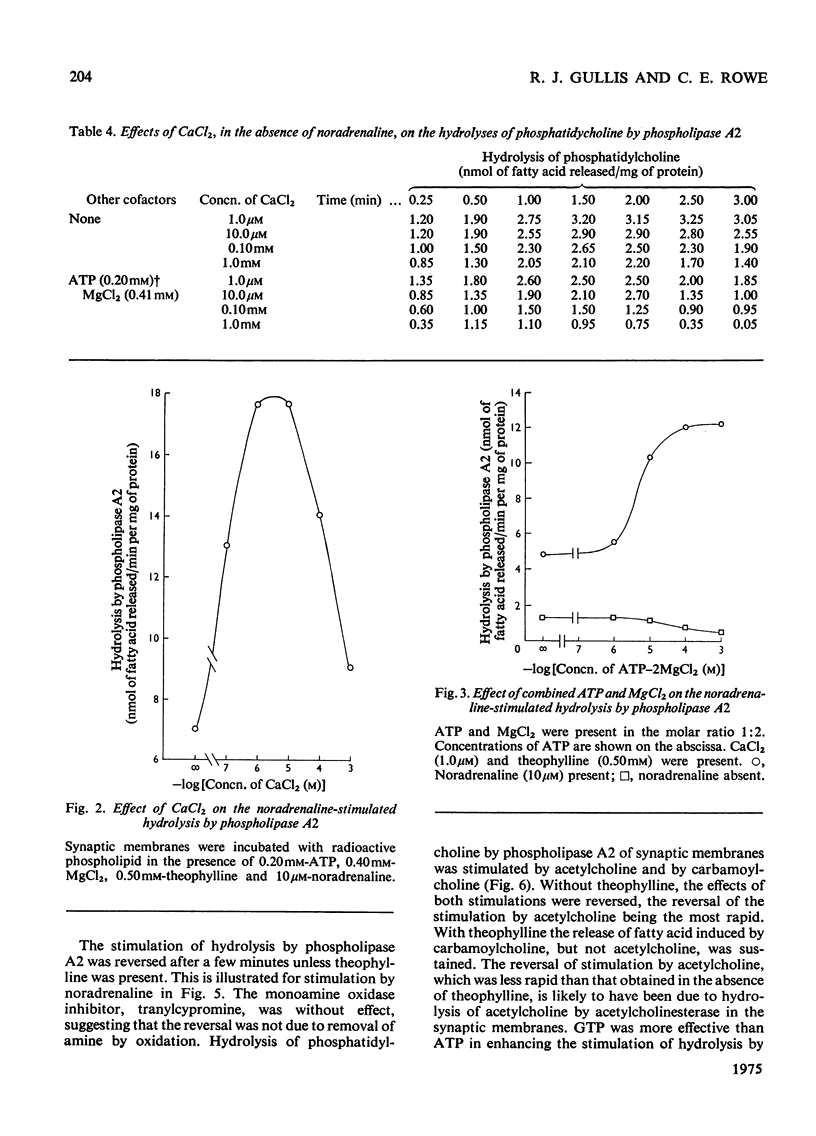
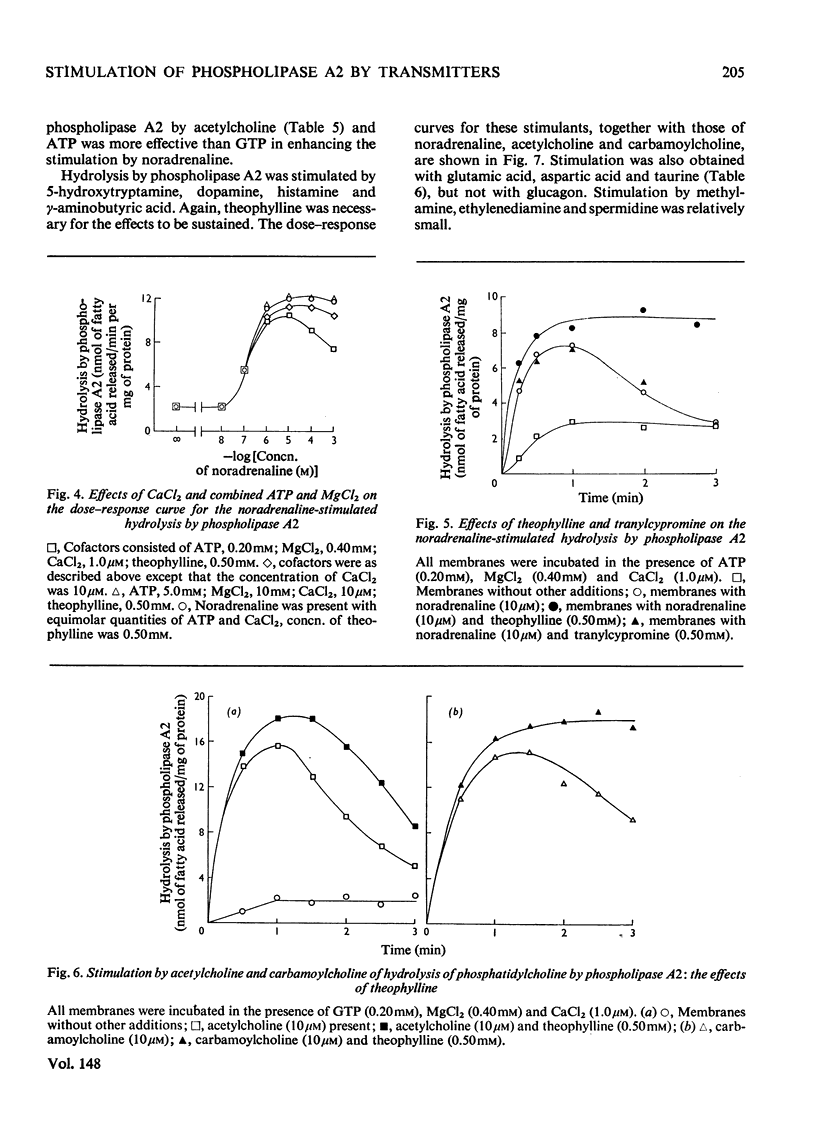
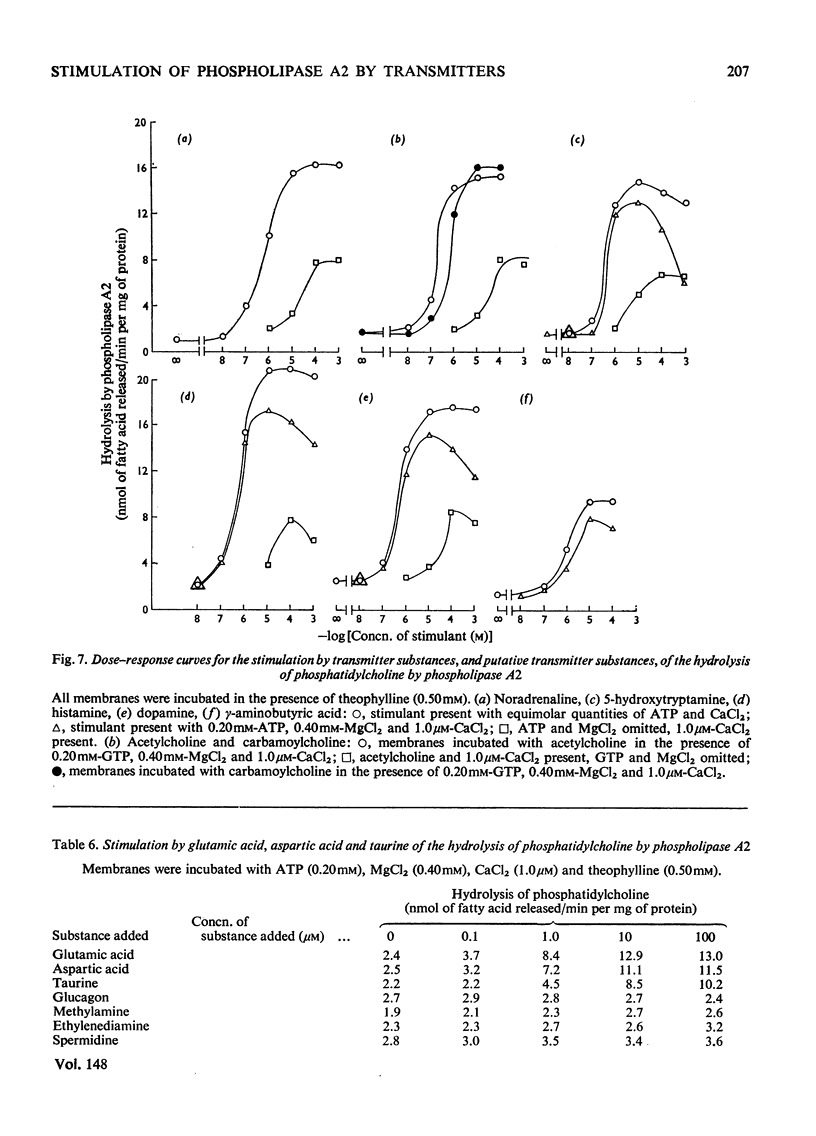
1. The distribution of the hydrolyses of phosphatidylcholine by phospholipase A2 and phospholipase A1, and the hydrolysis of lysophosphatidylcholine by lysophospholipase, in subcellular and subsynaptosomal fractions of cerebral cortices of guinea-pig brain, was determined. 2. Noradrenaline stimulated hydrolysis by phospholipase A2 in whole synaptosomes, synaptic membranes and fractions containing synaptic vesicles. 3. Stimulation of hydrolysis by phospholipase A2 in synaptic membranes by noradrenaline was enhanced by CaCl2, and by a mixture of ATP and MgCl2. The optimum concentration of CaCl2, in the presence of ATP and MgCl2, for stimulation by 10 muM-noradrenaline was in the range 1-10muM. The optimum concentration for ATP-2MgCl2 in the presence of 1 muM-CaCl2 was in the range 0.1-1mM. 4. Hydrolysis by phospholipase A2 of synaptic membranes was also stimulated by acetylcholine, carbamoylcholine, 5-hydroxytryptamine, dopamine (3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine), histamine, psi-aminobutyric acid, glutamic acid and aspartic acid. With appropriate concentrations of cofactors, sigmoidal dose-response curves were obtained, half-maximum stimulations being obtained with concentrations of stimulant in the range 0.1-1muM. 5. Taurine also stimulated hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine by phospholipase A2. There were only slight stimulations with methylamine, ethylenediamine or spermidine. No stimulation was obtained with glucagon.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bazán N. G., Jr Changes in free fatty acids of brain by drug-induced convulsions, electroshock and anaesthesia. J Neurochem. 1971 Aug;18(8):1379–1385. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb00002.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazán N. G., Jr Effects of ischemia and electroconvulsive shock on free fatty acid pool in the brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Oct 6;218(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90086-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazán N. G., Jr Phospholipases A 1 and A 2 in brain subcellular fractions. Acta Physiol Lat Am. 1971;21(2):101–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. F., Webster G. R. On the phospholipase A 2 activity of human cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1972 Feb;19(2):333–340. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. F., Webster G. R. The differentiation of phospholipase A1 and A2 in rat and human nervous tissues. J Neurochem. 1970 Nov;17(11):1543–1554. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb03724.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIDSON F. M., LONG C. The structure of the naturally occurring phosphoglycerides. 4. Action of cabbage-leaf phospholipase D on ovolecithin and related substances. Biochem J. 1958 Jul;69(3):458–466. doi: 10.1042/bj0690458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. N., Kaczmarek L. K. Taurine--a possible neurotransmitter? Nature. 1971 Nov 12;234(5324):107–108. doi: 10.1038/234107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichberg J., Whittaker V. P., Dawson R. M. Distribution of lipids in subcellular particles of guinea-pig brain. Biochem J. 1964 Jul;92(1):91–100. doi: 10.1042/bj0920091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTFRIED E. L., RAPPORT M. M. The biochemistry of plasmalogens. I. Isolation and characterization of phosphatidal choline, a pure native plasmalogen. J Biol Chem. 1962 Feb;237:329–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatt S., Barenholz Y., Roitman A. Isolation of rat brain lecithinase-A, specific for the alpha'-position of lecithin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jul 20;24(2):169–172. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90714-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatt S. Purification and properties of phospholipase A-1 from rat and calf brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jun 4;159(2):304–316. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(68)90079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullis R. J., Rowe C. E. Stimulation of phospholipase A2 of synaptosomes of guinea-pig brain by noradrenaline and other amines. Biochem Soc Trans. 1973 Jul;1(4):849–849. doi: 10.1042/bst0010849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King E. J. The colorimetric determination of phosphorus. Biochem J. 1932;26(2):292–297. doi: 10.1042/bj0260292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDS W. E. EFFECTS OF DOUBLE BOND CONFIGURATION ON LECITHIN SYNTHESIS. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1965 Jun;42:465–467. doi: 10.1007/BF02540085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDS W. E. Metabolism of glycerolipids. 2. The enzymatic acylation of lysolecithin. J Biol Chem. 1960 Aug;235:2233–2237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibovitz Z., Gatt S. Isolation of lysophospholipase, free of phospholipase activity, from rat brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 22;164(2):439–441. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90173-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long C., Staples D. A. Chromatographic separation of brain lipids. 2. Ethanolamine-containing phospholipids. Biochem J. 1961 Sep;80(3):557–562. doi: 10.1042/bj0800557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunt G. G., Rowe C. E. The effect of cholinergic substances on the production of unesterified fatty acids in brain. Brain Res. 1971 Dec 10;35(1):215–220. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90606-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORTON W. T. Potentiometric iodometric determination of plasmalogen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Feb 26;38:340–342. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91250-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachbaur J., Colbeau A., Vignais P. M. Distribution of membrane-confined phospholipases A in the rat hepatocyte. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 9;274(2):426–446. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90189-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C. J., Rowe C. E. Stimulation of the production of unesterified fatty acids in nerve endings of guinea-pig brain in vitro by noradrenaline and 5-hydroxytryptamine. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(3):575–585. doi: 10.1042/bj1260575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON A. F., LANDS W. E. Positional specificites in phospholipid hydrolyses. Biochemistry. 1962 Sep;1:804–810. doi: 10.1021/bi00911a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman Y. E., Verhagen J. Evidence of a membrane-bound phospholipase A in rat liver lysosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Feb 20;38(4):670–677. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90633-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajan K. S., Davis J. M., Colburn R. W., Jarke F. H. Metal chelates in the storage and transport of neurotransmitters: formation of mixed ligand chelates of Mg 2+ -ATP with biogenic amines. J Neurochem. 1972 Apr;19(4):1099–1116. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01430.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe C. E. The measurement of triglyceride in brain and the metabolism of brain triglyceride in vitro. J Neurochem. 1969 Feb;16(2):205–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb05938.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ A., BACHELARD H. S., McIL WAIN H. The sodium-stimulated adenosine-triphosphatase activity and other properties of cerebral microsomal fractions and subfractions. Biochem J. 1962 Sep;84:626–637. doi: 10.1042/bj0840626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNYDER F., STEPHENS N. A simplified spectrophotometric determination of ester groups in lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jul;34:244–245. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90255-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skipski V. P., Peterson R. F., Barclay M. Quantitative analysis of phospholipids by thin-layer chromatography. Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):374–378. doi: 10.1042/bj0900374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyvoda O. S., Rowe C. E. Glyceride lipases in nerve endings of guinea-pig brain and their stimulation by noradrenaline, 5-hydroxytryptamine and adrenaline. Biochem J. 1973 Feb;132(2):233–248. doi: 10.1042/bj1320233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker V. P., Michaelson I. A., Kirkland R. J. The separation of synaptic vesicles from nerve-ending particles ('synaptosomes'). Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):293–303. doi: 10.1042/bj0900293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woelk H., Porcellati G. Subcellular distribution and kinetic properties of rat brain phospholipases A1 and A2. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1973 Jan;354(1):90–100. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1973.354.1.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


