Abstract
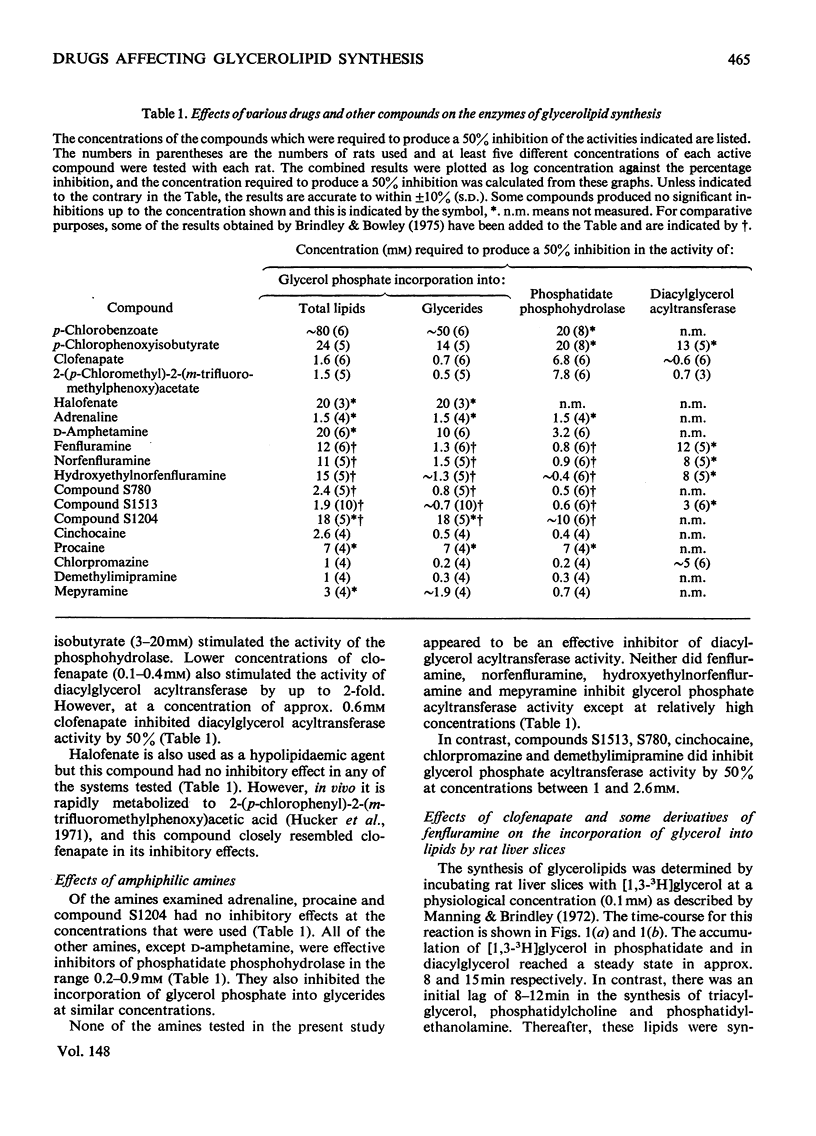
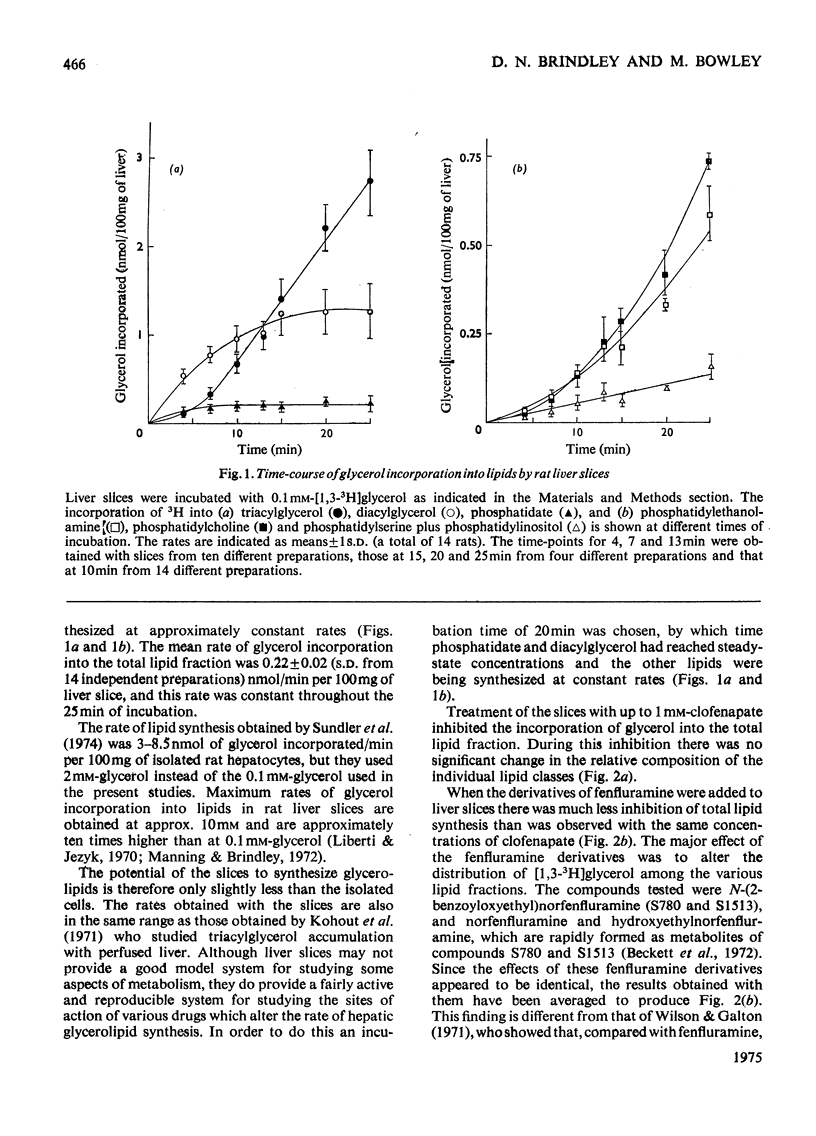
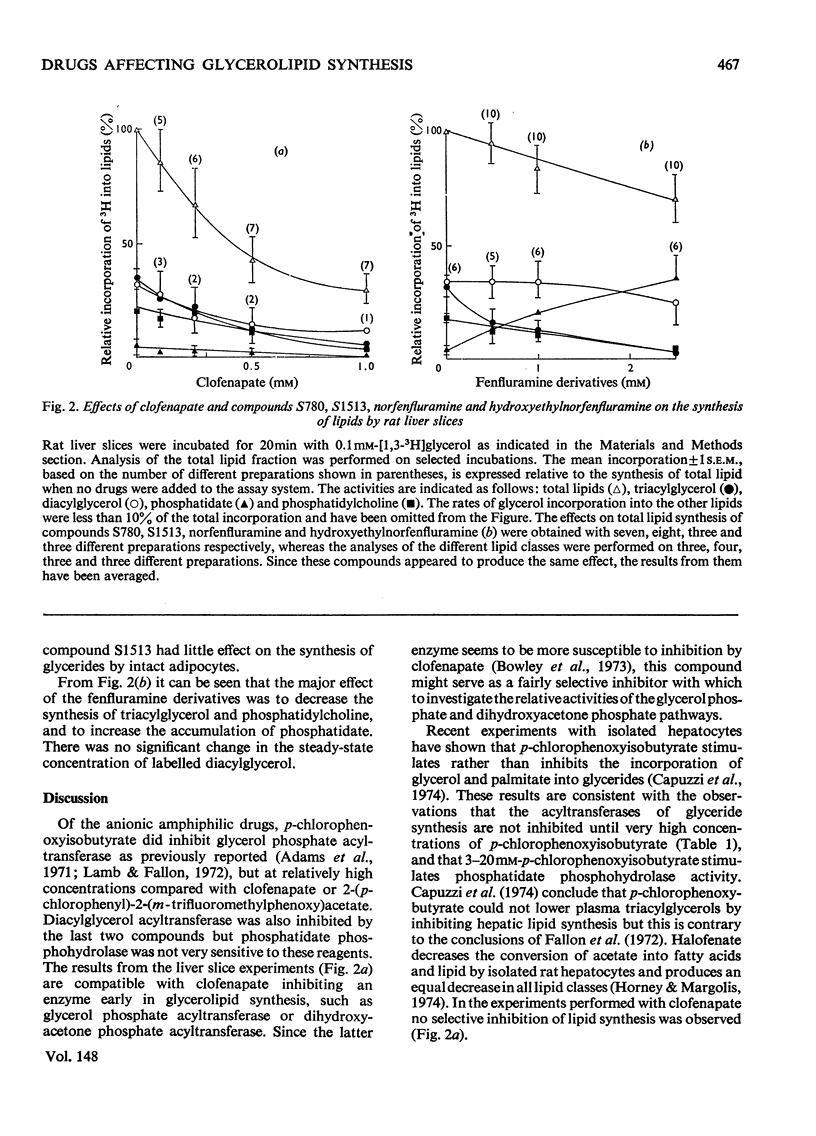
The effects on glycerolipid synthesis of a series of compounds including many drugs were investigated in cell-free preparations and slices of rat liver. p-Chlorobenzoate, p-chlorophenoxyisobutyrate, halofenate, D-amphetamine, adrenaline, procaine and N-[2-(4-chloro-3-sulphamoylbenzoyloxy)ethyl]norfenfluramine had little inhibitory effect on any of the systems investigated. Two amphiphilic anions, clofenapate and 2-(p-chlorophenyl)-2-(m-trifluoromethylphenoxy)acetate, both inhibited glycerol phosphate acyltransferase and diacylglycerol acyltransferase at approx. 1.6 and 0.7 mm respectively. Clofenapate (1 mm) also inhibited the incorporation of glycerol into lipids by rat liver slices without altering the relative proportions of the different lipids synthesized. The amphilic amines, mepyramine, fenfluramine, norfenfluramine, hydroxyethylnorfenfluramine, N-(2-benzoyloxyethyl)norfenfluramine, cinchocaine, chlorpromazine and demethylimipramine inhibited phosphatidate phosphohydrolase by 50% at concentrations between 0.2 and 0.9 mm. The last four compounds inhibited glycerol phosphate acyltransferase by 50% at concentrations between 1 and 2.6 mm. None of the amines examined appeared to be an effective inhibitor of diacylglycerol acyltransferase. Norfenfluramine, hydroxyethylnorfenfluramine and N-(2-benzoyloxyethyl)norfenfluramine produced less inhibition of glycerol incorporation into total lipids than was observed with equimolar clofenapate. The major effect of these amines in liver slices was to inhibit triacylglycerol and phosphatidylcholine synthesis and to produce a marked accumulation of phosphatidate. The results are discussed in terms of the control of glycerolipid synthesis. They partly explain the observed effects of the various drugs on lipid metabolism. The possible use of these compounds as biochemical tools with which to investigate the reactions of glycerolipid synthesis is considered.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams L. L., Webb W. W., Fallon H. J. Inhibition of hepatic triglyceride formation by clofibrate. J Clin Invest. 1971 Nov;50(11):2339–2346. doi: 10.1172/JCI106732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan D., Michell R. H. Enhanced synthesis de novo of phosphatidylinositol in lymphocytes treated with cationic amphiphilic drugs. Biochem J. 1975 Jun;148(3):471–478. doi: 10.1042/bj1480471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckett A. H., Shenoy E. V., Brookes L. G. The absorption, metabolism and elimination of (plus minus)-N-(2-benzoyloxyethyl)norfenfluramine (JP992) in man. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1972 Apr;24(4):281–288. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1972.tb08987.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowley M., Manning R., Brindlay D. N. The tritium isotope effect of sn-glycerol 3-phosphate oxidase and the effects of clofenapate and N-(2-benzoyloxyethyl)norfenfluramine on the esterification of glycerol phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate by rat liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1973 Oct;136(2):421–427. doi: 10.1042/bj1360421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brindley D. N., Hübscher G. The intracellular distribution of the enzymes catalysing the biosynthesis of glycerides in the intestinal mucosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Dec 2;106(3):495–509. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90066-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brindley D. N. The intracellular phase of fat absorption. Biomembranes. 1974;4B(0):621–671. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3336-4_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brindley D. N. The relationship between palmitoyl-coenzyme A synthetase activity and esterification of sn-glycerol 3-phosphate by the microsomal fraction of guinea-pig intestinal mucosa. Biochem J. 1973 Apr;132(4):707–715. doi: 10.1042/bj1320707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capuzzi D. M., Lackman R. D., Uberti M. O., Reed M. A. Stimulation of hepatic triglyceride synthesis and secretion by clofibrate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Oct 23;60(4):1499–1508. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90367-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig G. M. A comparison of clofibrate and its derivative methyl clofenapate. Atherosclerosis. 1972 Mar-Apr;15(2):265–271. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(72)90076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M. A hydrolytic procedure for the identification and estimation of individual phospholipids in biological samples. Biochem J. 1960 Apr;75:45–53. doi: 10.1042/bj0750045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daae L. N., Aas M. Fatty acid activation and acyl transfer in rat liver during clofibrate feeding. Atherosclerosis. 1973 May-Jun;17(3):389–400. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(73)90030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dannenburg W. N., Kardian B. C., Norrell L. Y. Fenfluramine and triglyceride synthesis by microsomes of the intestinal mucosa in the rat. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1973 Jan;201(1):115–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fallon H. J., Adams L. L., Lamb R. G. A review of studies on the mode of action of clofibrate and betabenzalbutyrate. Lipids. 1972 Feb;7(2):106–109. doi: 10.1007/BF02532596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajra A. K., Seguin E. B., Agranoff B. W. Rapid labeling of mitochondrial lipids by labeled orthophosphate and adenosine triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 10;243(7):1609–1616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitzemann R. J., Loh H. H. Effect of d-amphetamine on the turnover, synthesis and metabolism of brain phosphatidylcholine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Nov 1;22(21):2731–2741. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90133-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homcy C. J., Margolis S. Comparison of the effects of clofibrate and halofenate (MK-185) in isolated rat hepatocytes. Atherosclerosis. 1974 May-Jun;19(3):381–391. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9150(74)80003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hucker H. B., Grady L. T., Michniewicz B. M., Stauffer S. C., White S. E., Maha G. E., McMahon F. G. Metabolism of a new hypolipidemic agent, 2-acetamidoethyl(p-chlorophenyl) (m-trifluoromethylphenoxy)-acetate (halofenate) in the rat, dog, rhesus monkey and man. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Nov;179(2):359–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohout M., Kohoutova B., Heimberg M. The regulation of hepatic triglyceride metabolism by free fatty acids. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 25;246(16):5067–5074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. G., Fallon H. J. An enzymatic explanation for dietary induced alterations in hepatic glycerolipid metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 26;348(1):179–188. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(74)90104-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. G., Fallon H. J. Inhibition of monoacylglycerophosphate formation by chlorophenoxyisobutyrate and -benzalbutyrate. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1281–1287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawther P. J., Waller R. E. Physical hazards. Postgrad Med J. 1975;51 (Suppl 2):suppl 51–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard B. E., Neuhoff V. The effect of D-amphetamine on the concentration of phospholipids in the rat hippocampus. Z Naturforsch C. 1974 Mar-Apr;29(3):187–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberti J. P., Jezyk P. F. Lipid biosynthesis in rat-liver slices: effects of ions, ATP and substrate concentration on glycerol incorporation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jul 14;210(2):221–229. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangiapane E. H., Lloyd-Davies K. A., Brindley D. N. A study of some enzymes of glycerolipid biosynthesis in rat liver after subtotal hepatectomy. Biochem J. 1973 May;134(1):103–112. doi: 10.1042/bj1340103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning R., Brindley D. N. Tritium isotope effects in the measurement of the glycerol phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate pathways of glycerolipid biosynthesis in rat liver. Biochem J. 1972 Dec;130(4):1003–1012. doi: 10.1042/bj1301003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. B., Bizzi A. Effects of amphetamine and fenfluramine on the net release of triglycerides of very low density lipoproteins by slices of rat liver. Biochem Pharmacol. 1972 Apr 15;21(8):1143–1150. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(72)90108-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell M. P., Brindley D. N., Hübscher G. Properties of phosphatidate phosphohydrolase. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jan;18(2):214–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01233.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacht J., Agranoff B. W. Acetylcholine stimulates hydrolysis of 32 P-labeled phosphatidic acid in guinea pig synaptosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Feb 5;50(3):934–941. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91335-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacht J., Agranoff B. W. Stimulation of hydrolysis of phosphatidic acid by cholinergic agents in guinea pig synaptosomes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 10;249(5):1551–1557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P. J., Hurley P. J. Effect of clofibrate on low-density lipoprotein turnover in essential hypercholesterolaemia. J Atheroscler Res. 1969 Jan-Feb;9(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/s0368-1319(69)80063-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P. The membrane actions of anesthetics and tranquilizers. Pharmacol Rev. 1972 Dec;24(4):583–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. E., Sedgwick B., Brindley D. N., Hübscer G. The role of phosphatidate phosphohydrolase in glyceride biosynthesis. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Dec;3(1):70–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb19499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundler R., Akesson B., Nilsson A. Effect of different fatty acids on glycerolipid synthesis in isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5102–5107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez M., Nicholls D. G., Brindley D. N. [The relationship between palmitoyl-coenzyme A synthetase activity and esterification of sn-glycerol 3-phosphate in rat liver mitochondria]. Biochem J. 1973 Apr;132(4):697–706. doi: 10.1042/bj1320697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vavrecka M., Mitchell M. P., Hübscher G. The effect of starvation on the incorporation of palmitate into glycerides and phospholipids of rat liver homogenates. Biochem J. 1969 Nov;115(2):139–145. doi: 10.1042/bj1150139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. P., Galton D. J. The effect of drugs on lipogenesis from glucose and palmitate in human adipose tissue. Horm Metab Res. 1971 Jul;3(4):262–266. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1094145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagihara Y., Bleasdale J. E., Hawthorne J. N. Effects of acetylcholine on the incorporation of (32P)orthophosphate in vitro into the phospholipids of subsynaptosomal, membranes from guinea-pig brain. J Neurochem. 1973 Jul;21(1):173–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb04237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


