Abstract
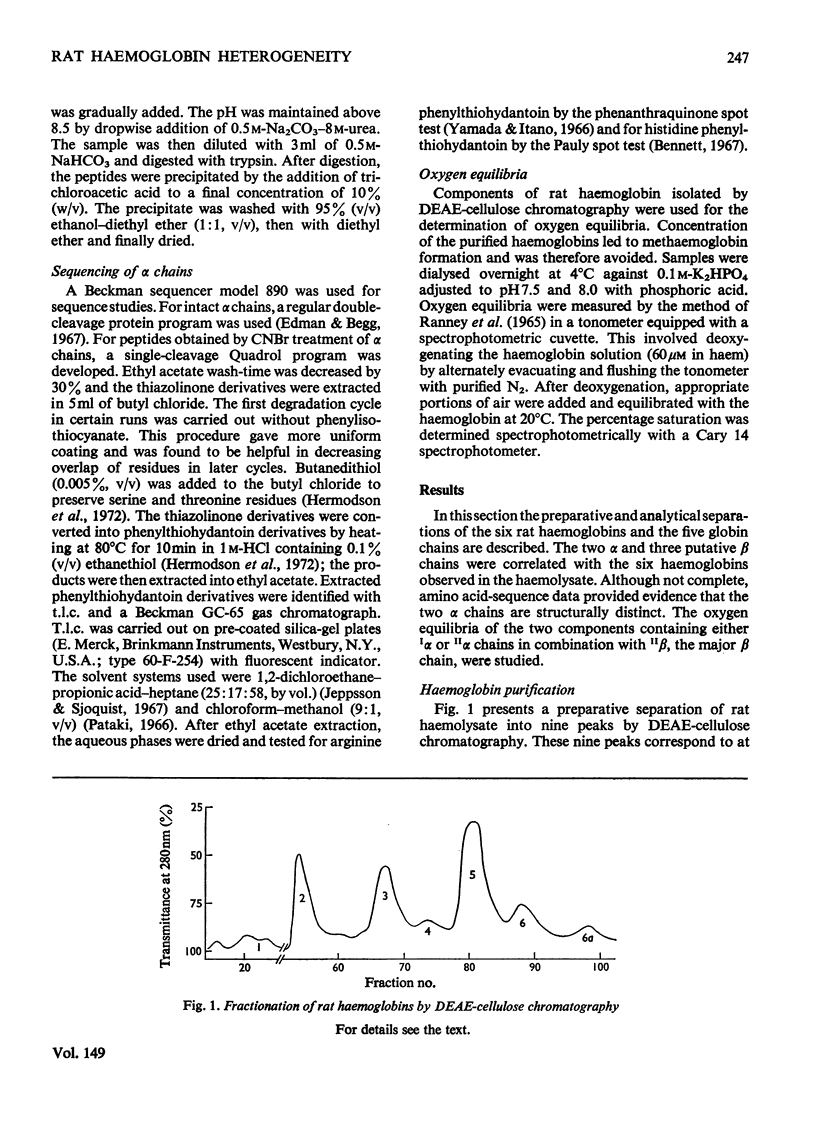
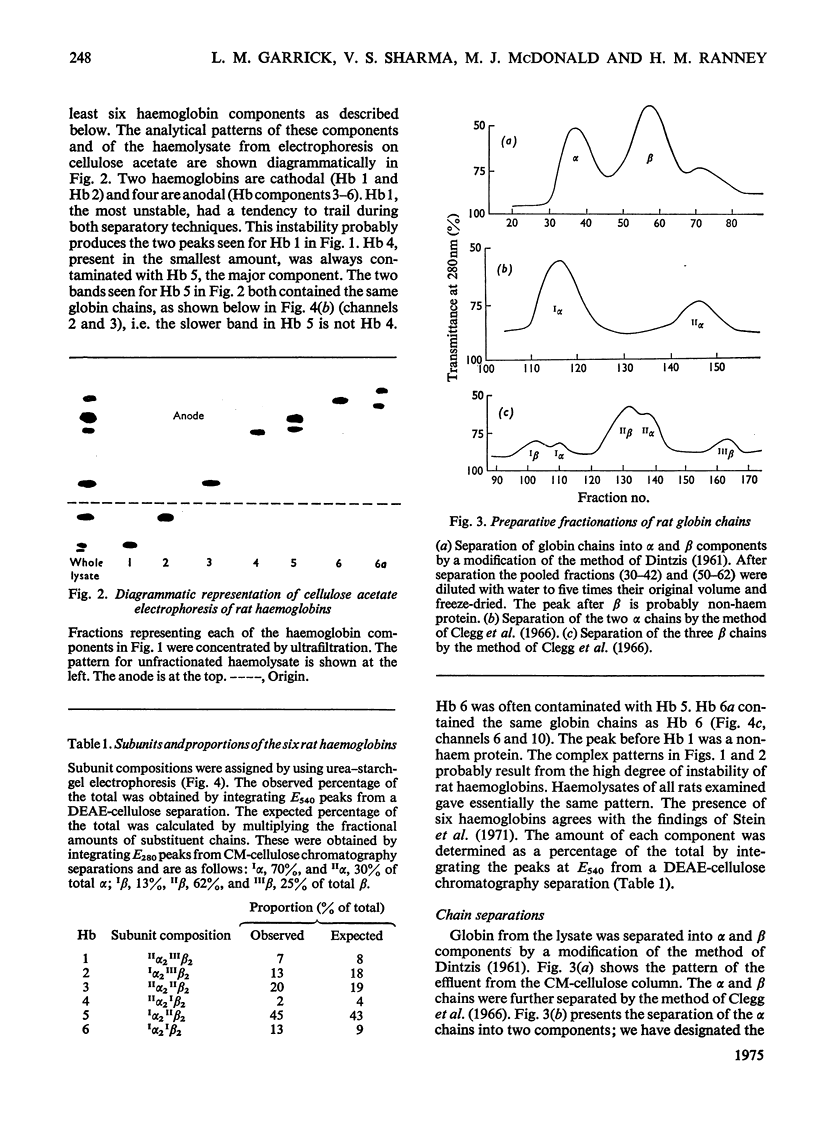
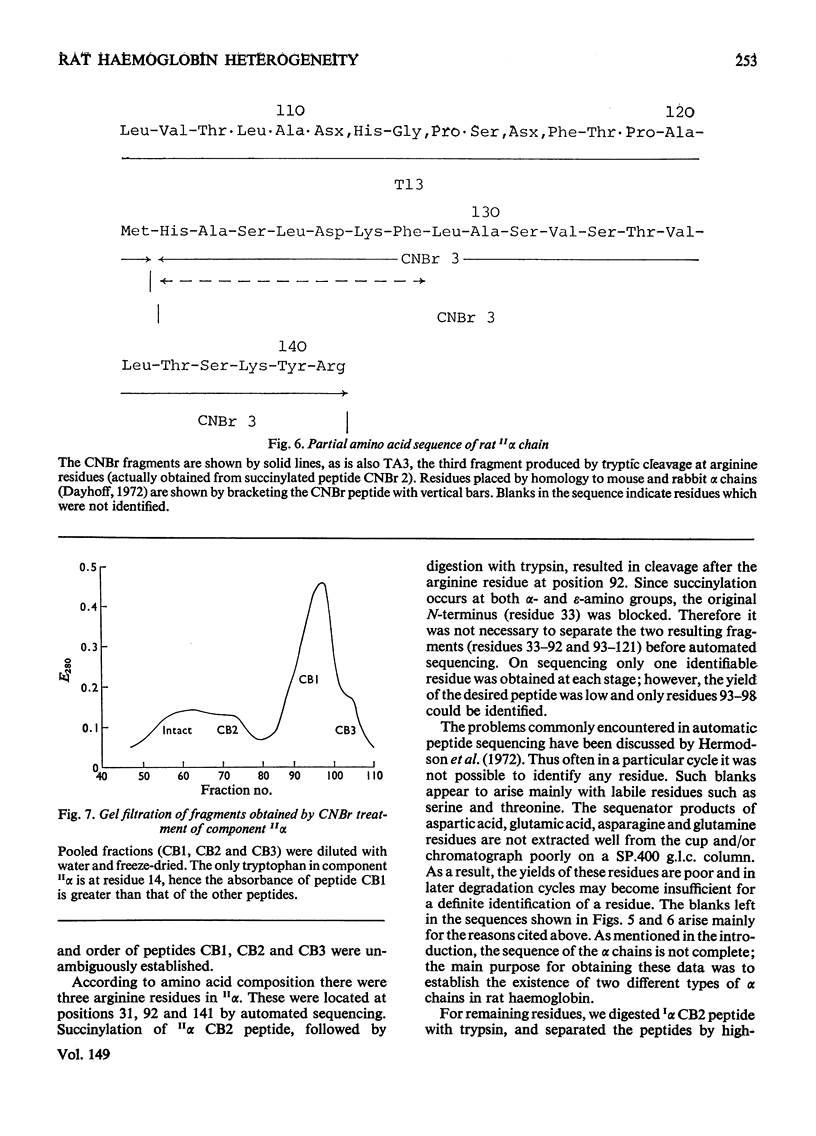
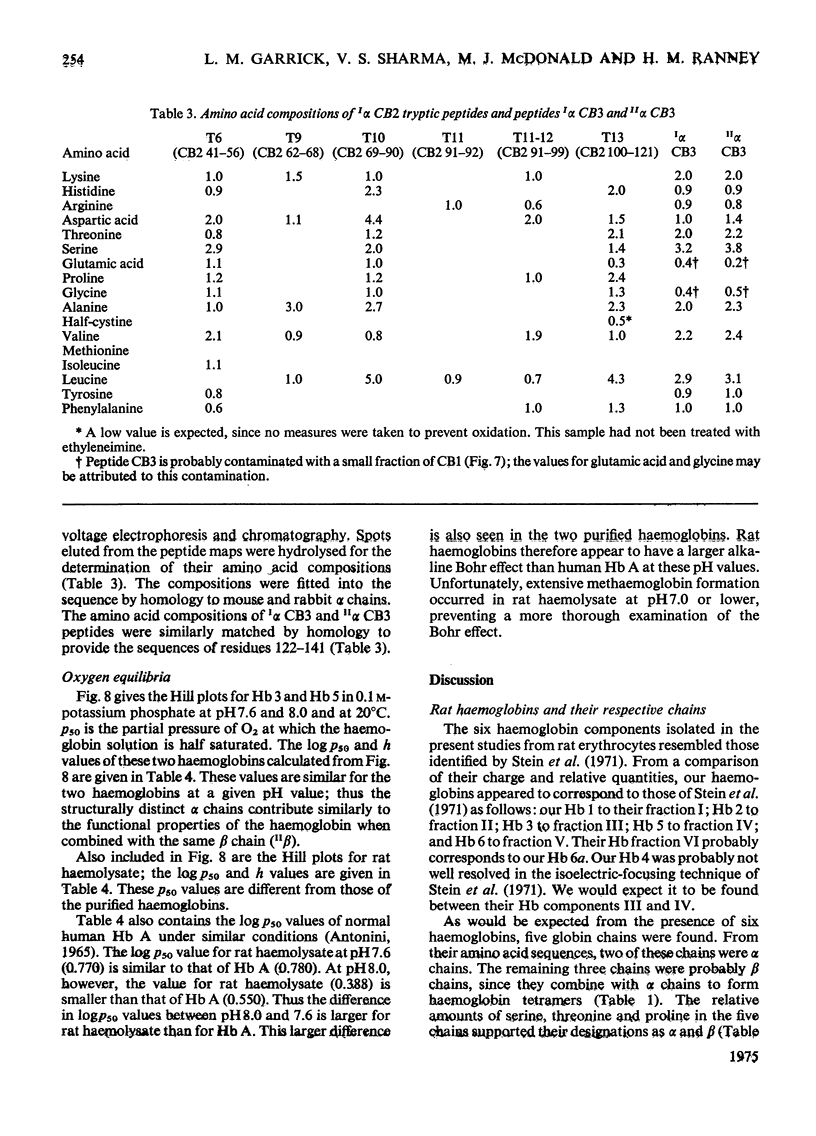
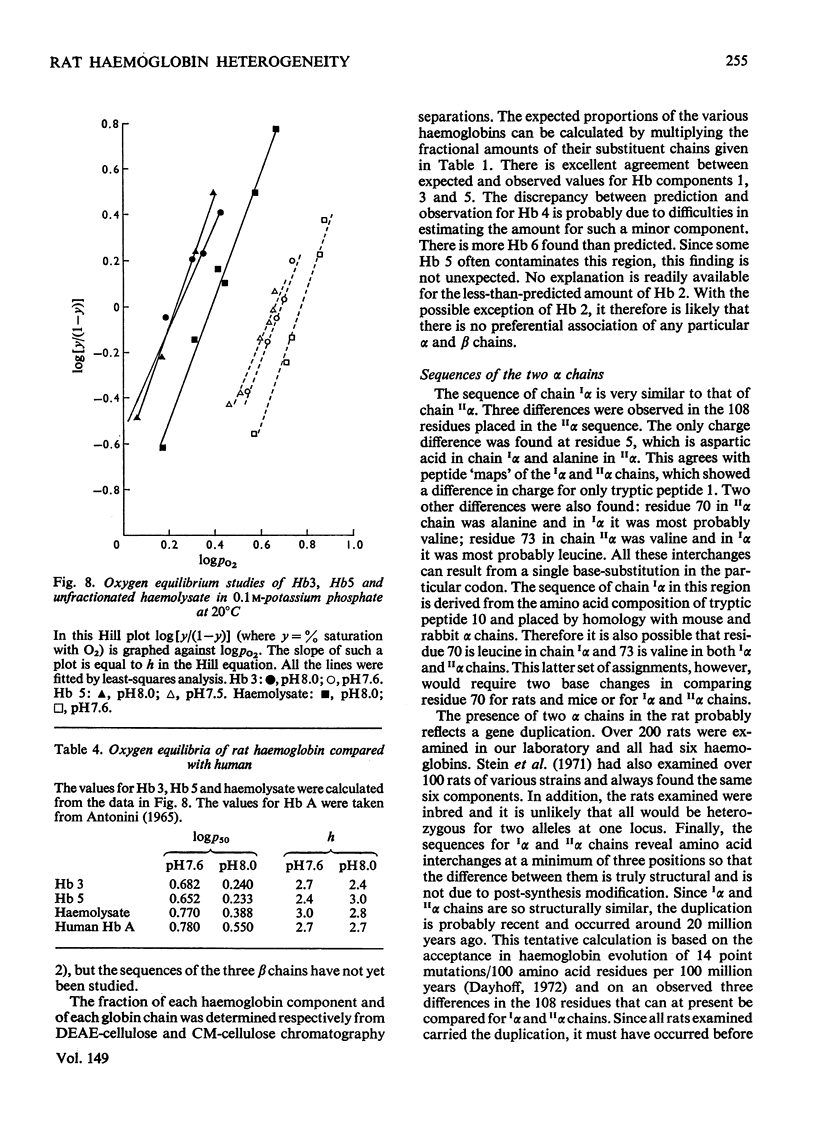
Six haemoglobins were separated analytically from haemolysates of adult Wistar rats (Rattus norvegicus) by cellulose acetate electrophoresis and preparatively by DEAE-cellulose chromatography. The globin chains were separated from unfractionated haemolysates by CM-cellulose chromatography by using a non-linear formic acid-pyridine gradient followed by CM-cellulose chromatography in 8M-urea by using a gradient of increasing Na+ concentration in phosphate buffer, pH 6.7. Two alpha chains and three non-alpha chains were identified. Chains isolated from purified haemoglobins were correlated with chains isolated from unfractionated haemolysates by electrophoresis on urea-starch gels to make presumptive assignments of the subunit composition of the six haemoglobin tetramers. Partial amino acid sequences were determined for the major and minor alpha chains. The oxygen equilibria of two of the major haemoglobin components and of the unfractionated haemolysate were examined at pH 7.5 and 8.0. The two purified haemoglobins exhibited similar oxygen affinities; the haemolysate, however, had a lower oxygen affinity than either of the two purified haemoglobins. Both the haemolysate and the two haemoglobins showed an alkaline Bohr effect larger than that of human haemoglobin A.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANTONINI E. INTERRELATIONSHIP BETWEEN STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION IN HEMOGLOBIN AND MYOGLOBIN. Physiol Rev. 1965 Jan;45:123–170. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1965.45.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams H. R., Wrightstone R. N., Miller A., Huisman T. H. Quantitation of hemoglobin alpha chains in adult and fetal goats; gene duplication and the production of polypeptide chains. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Jun;132(1):223–236. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90356-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
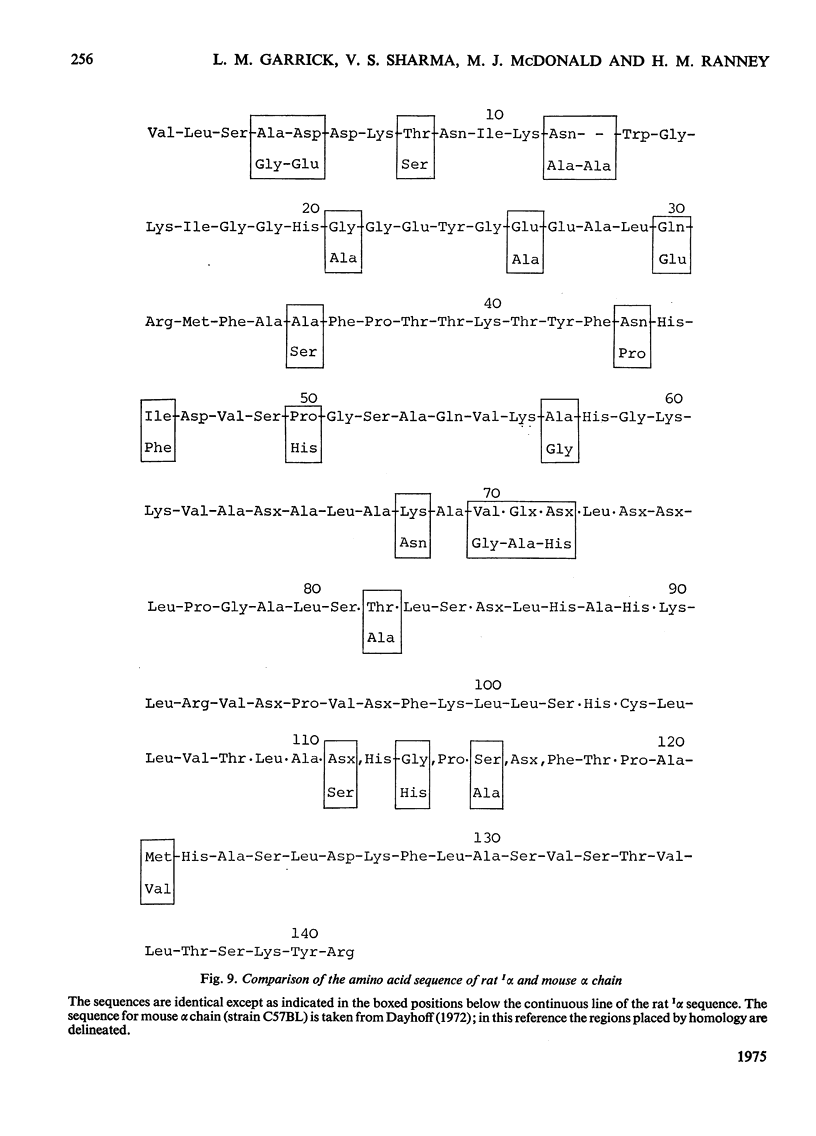
- Chua C. G., Carrell R. W., Howard B. H. The amino acid sequence of the alpha chain of the major haemoglobin of the rat (Rattus norvegicus). Biochem J. 1975 Jul;149(1):259–269. doi: 10.1042/bj1490259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. B., Naughton M. A., Weatherball D. J. Abnormal human haemoglobins. Separation and characterization of the alpha and beta chains by chromatography, and the determination of two new variants, hb Chesapeak and hb J (Bangkok). J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(1):91–108. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80052-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DINTZIS H. M. Assembly of the peptide chains of hemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Mar 15;47:247–261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.3.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman P., Begg G. A protein sequenator. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Mar;1(1):80–91. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrick M. D., Balzer R. H., Jr, Charlton J. P. An improved method for electrophoretic characterization of globin chains from hemolyzates, purified hemoglobins, and fractions selected from chromatographic separations of chains. Anal Biochem. 1970 Apr;34(2):312–330. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90115-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrick M. D., Dembure P., Guthrie R. Sickle-cell anemia and other hemoglobinopathies. Procedures and strategy for screening employing spots of blood on filter paper as specimens. N Engl J Med. 1973 Jun 14;288(24):1265–1268. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197306142882403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermodson M. A., Ericsson L. H., Titani K., Neurath H., Walsh K. A. Application of sequenator analyses to the study of proteins. Biochemistry. 1972 Nov 21;11(24):4493–4502. doi: 10.1021/bi00774a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nute P. E., Sullivan B. Primate hemoglobins: their structure, function and evolution. I. Amino acid compositions of the tryptic peptides from the beta chain of Cebus albifrons. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1971 Aug 15;39(4):797–814. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(71)90104-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perutz M. F., Muirhead H., Cox J. M., Goaman L. C. Three-dimensional Fourier synthesis of horse oxyhaemoglobin at 2.8 A resolution: the atomic model. Nature. 1968 Jul 13;219(5150):131–139. doi: 10.1038/219131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANNEY H. M., BRIEHL R. W., JACOBS A. S. OXYGEN EQUILIBRIA OF HEMOGLOBIN ALPHA-A AND OF HEMOGLOBIN RECONSTITUTED FROM HEMOGLOBINS ALPHA-A AND H. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2442–2447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladic-Simic D., Zivkovic N., Pavic D., Marinkovic D., Martinovic J., Martinovitch P. N. Hereditary hypochromic microcytic anemia in the laboratory rat. Genetics. 1966 Jun;53(6):1079–1089. doi: 10.1093/genetics/53.6.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein S., Cherian M. G., Mazur A. Preparation and properties of six rat hemoglobins. Nonuniform biosynthesis in marrow erythroid cells. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 10;246(17):5287–5293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada S., Itano H. Phenanthrenequinone as an analytical reagent for arginine and other monosubstituted guanidines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 28;130(2):538–540. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90256-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


