Abstract
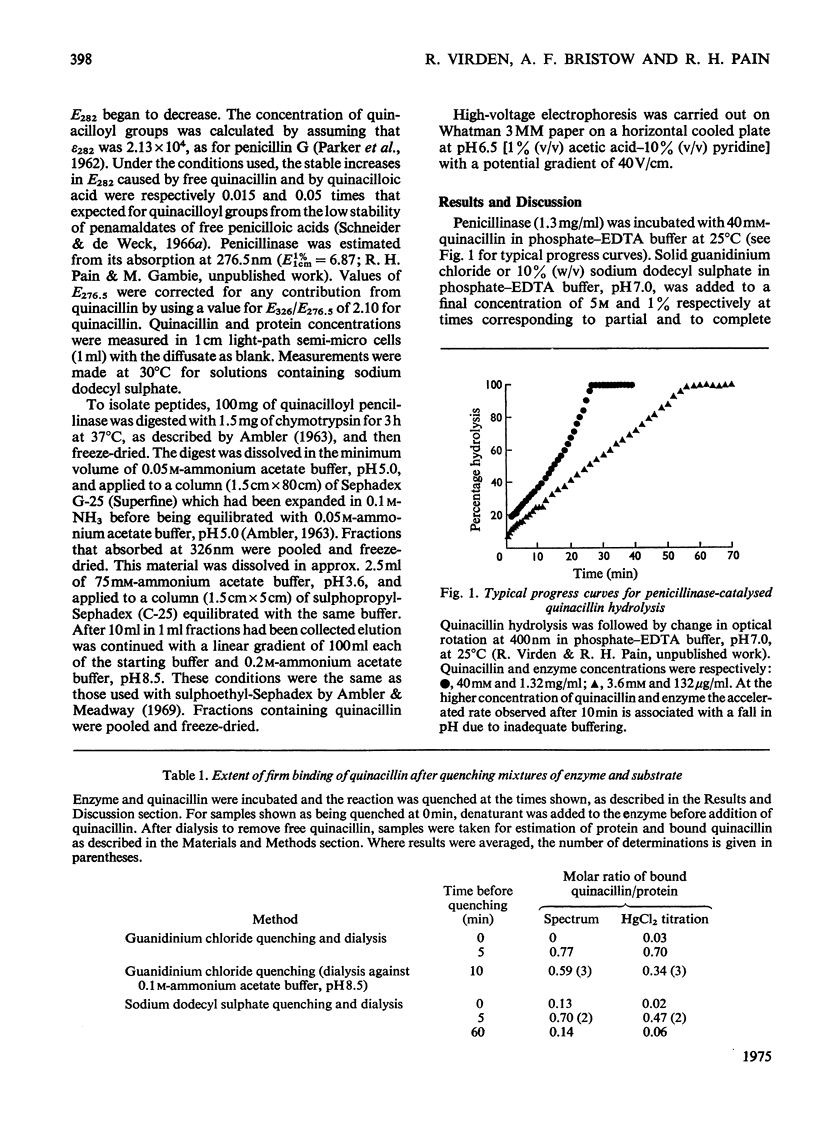
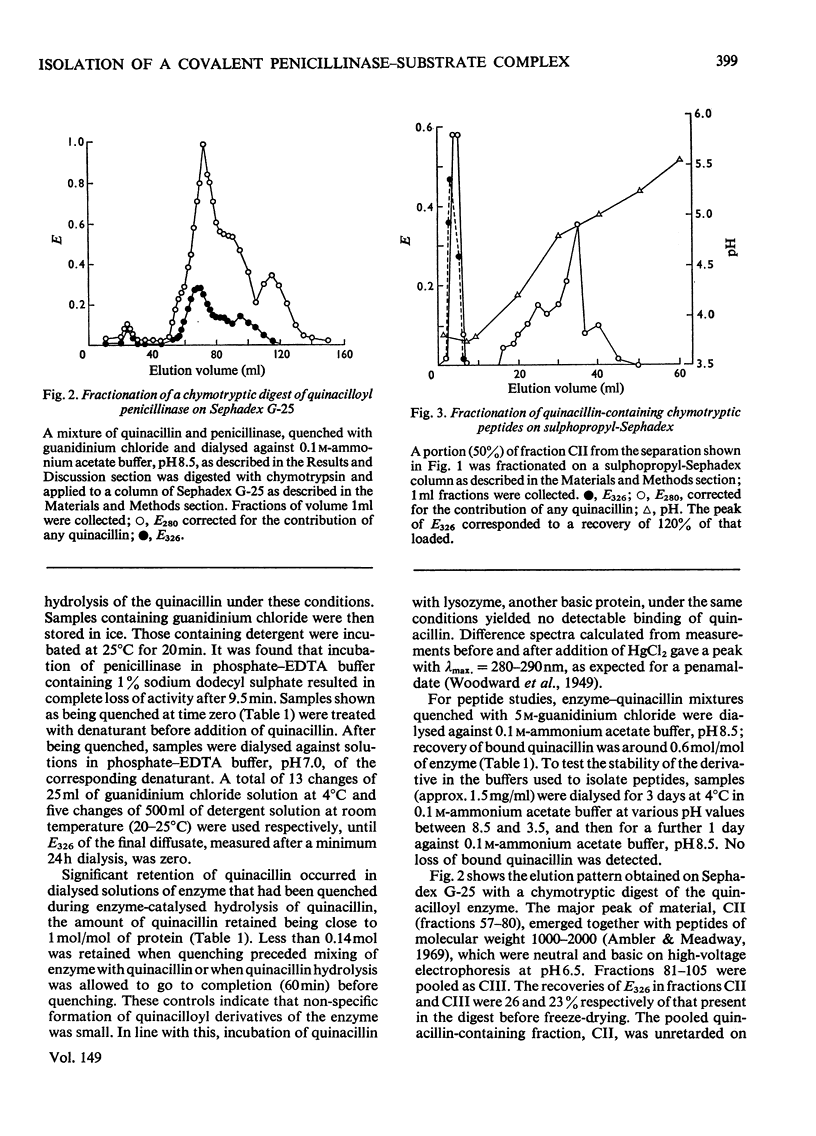
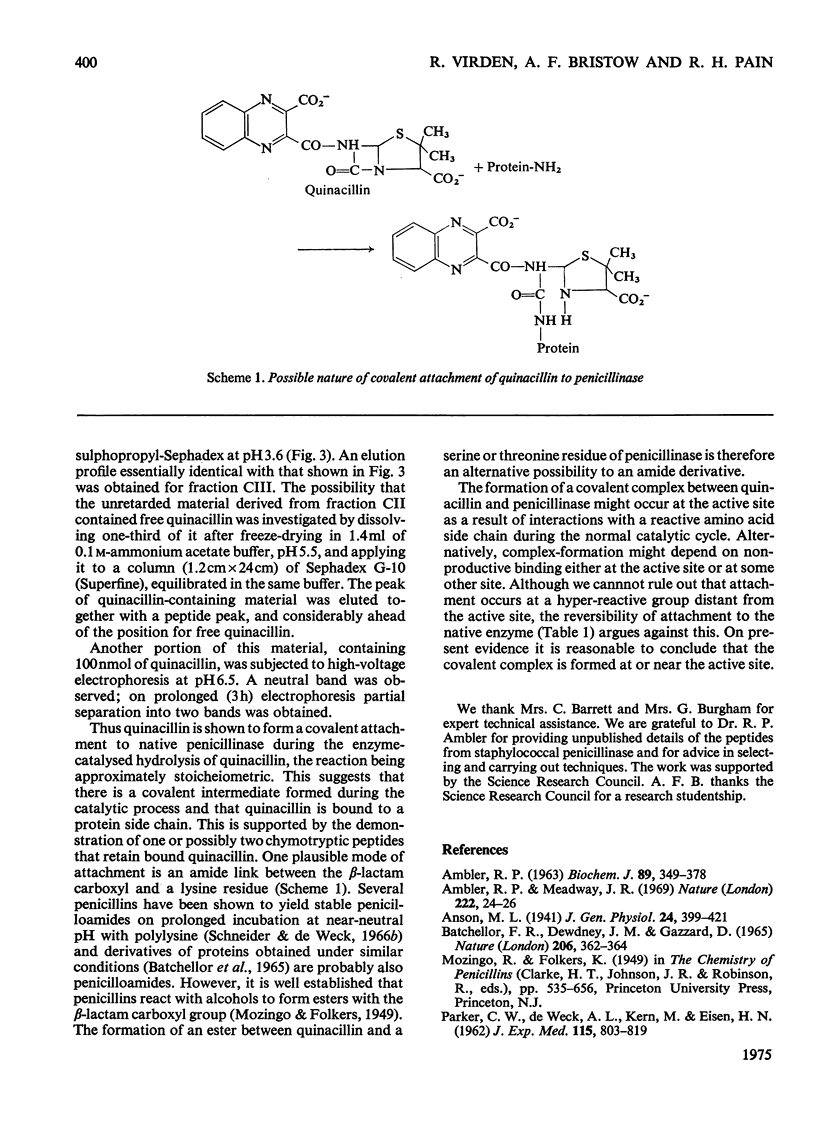
1. The penicillinase-catalysed hydrolysis of quinacillin was quenched by addition of 5 m-guanidinium chloride or 1% (w/v) sodium dodecyl sulphate, and the quenched reaction mixture was dialysed exhaustively against solutions of the denaturant. 2. Irreversibly bound quinacillin was shown by titration with HgCl2 to be covalently attached to the protein by the beta-lactam carboxyl group. 3. The derivative was found to be stable over the pH range 3.5-8.5. 4. Chymotryptic hydrolysis of the product and subsequent fractionation showed that quinacillin was bound to one or possibly two peptides.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMBLER R. P. THE AMINO ACID SEQUENCE OF PSEUDOMONAS CYTOCHROME C-551. Biochem J. 1963 Nov;89:349–378. doi: 10.1042/bj0890349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambler R. P., Meadway R. J. Chemical structure of bacterial penicillinases. Nature. 1969 Apr 5;222(5188):24–26. doi: 10.1038/222024a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batchelor F. R., Dewdney J. M., Gazzard D. Penicillin allergy: the formation of the penicilloyl determinant. Nature. 1965 Apr 24;206(982):362–364. doi: 10.1038/206362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKER C. W., DEWECK A. L., KERN M., EISEN H. N. The preparation and some properties of penicillenic acid derivatives relevant to penicillin hypersensitivity. J Exp Med. 1962 Apr 1;115:803–819. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.4.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDS H. C., HOUSLEY J. R., SPOONER D. F. QUINACILLIN: A NEW PENICILLIN WITH UNUSUAL PROPERTIES. Nature. 1963 Jul 27;199:354–356. doi: 10.1038/199354a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHMOND M. H. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF THE EXOPENICILLINASE FROM STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. Biochem J. 1963 Sep;88:452–459. doi: 10.1042/bj0880452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider C. H., de Weck A. L. Chemische Aspekte der Penicillin-Allergie: Die direkte Penicilloylierung von epsilon-Aminogruppen durch Penicilline bei pH 7,4. Helv Chim Acta. 1966 Jul 11;49(5):1695–1706. doi: 10.1002/hlca.19660490532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipper D. J., Strominger J. L. Mechanism of action of penicillins: a proposal based on their structural similarity to acyl-D-alanyl-D-alanine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Oct;54(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.4.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


