Abstract
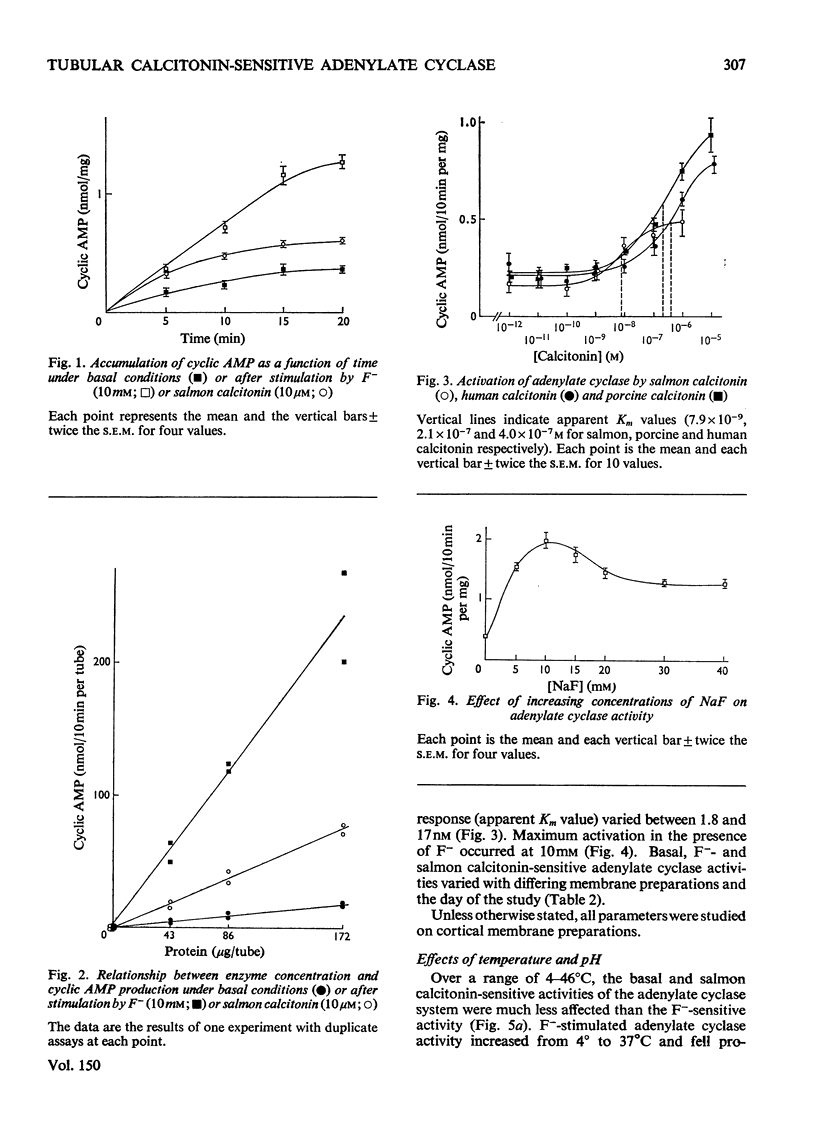
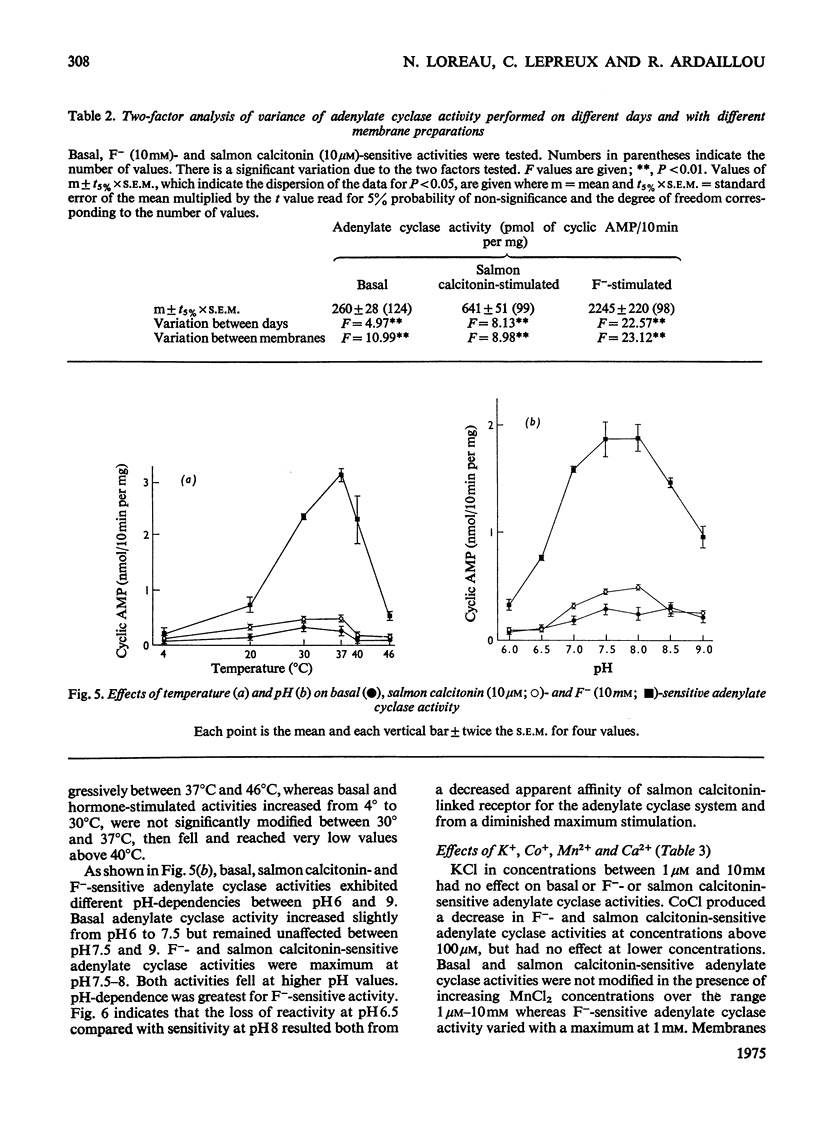
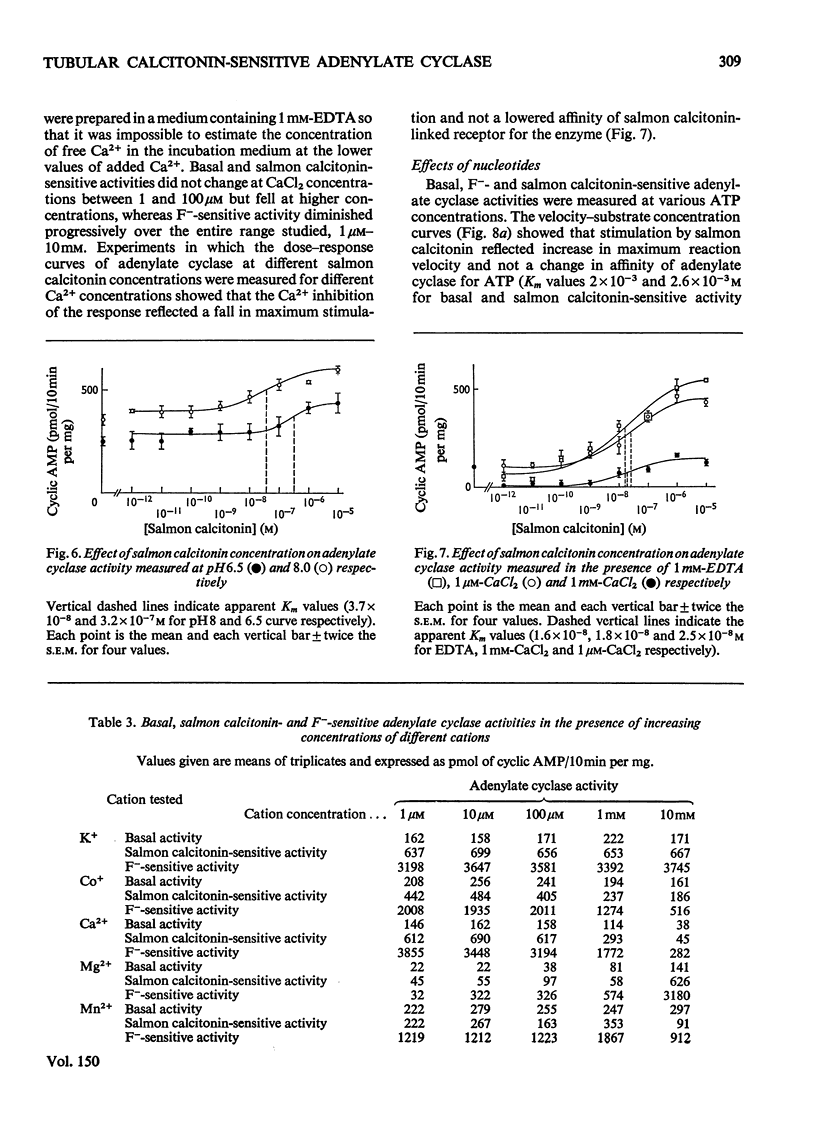
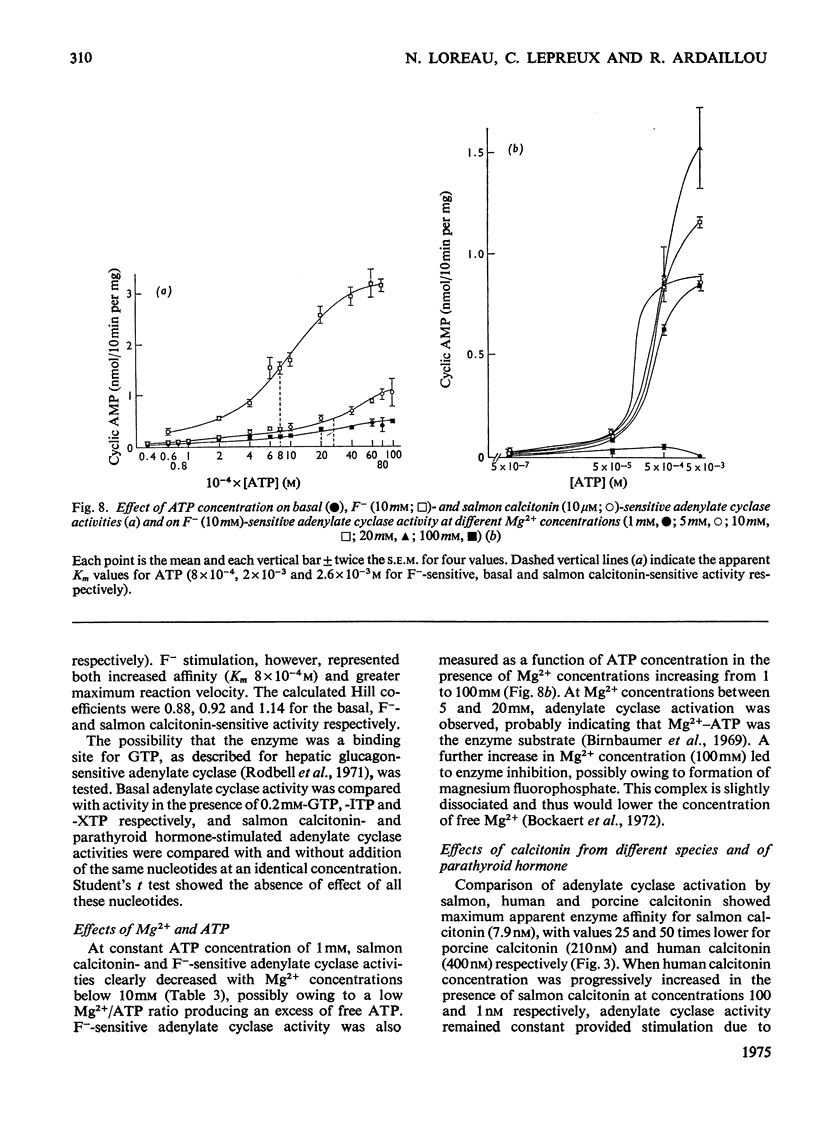
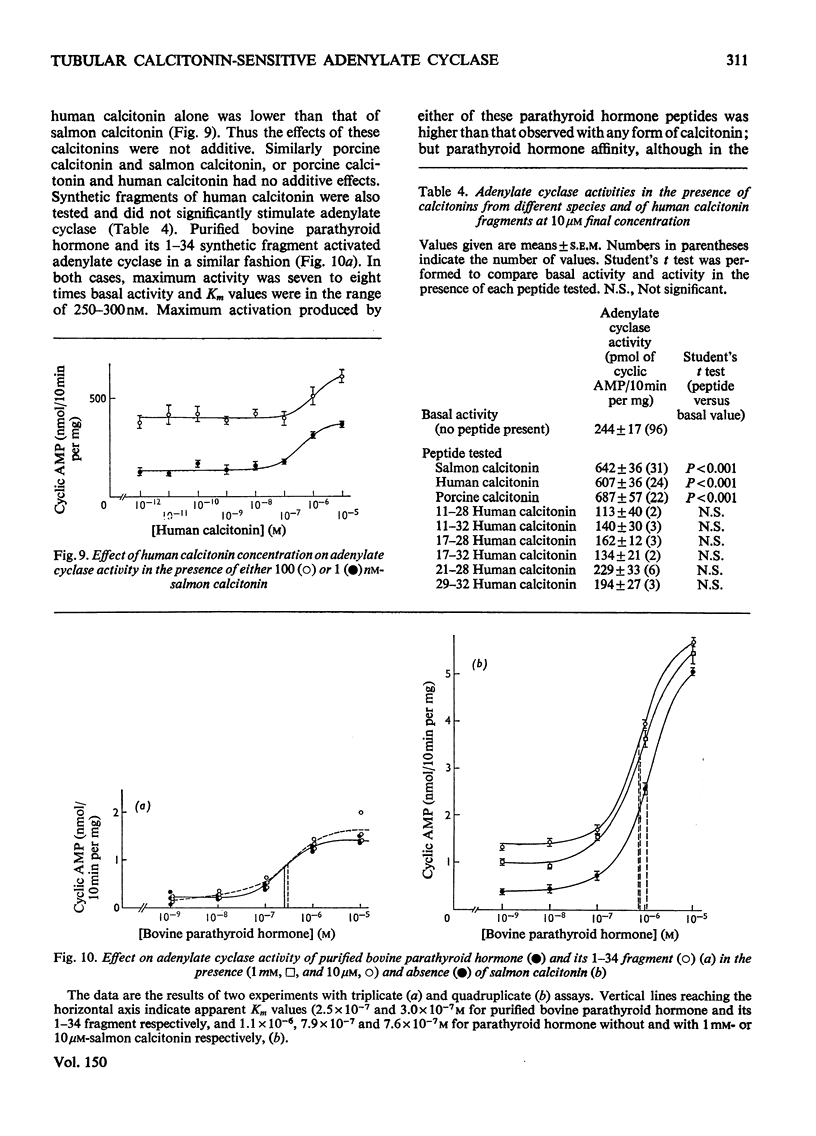
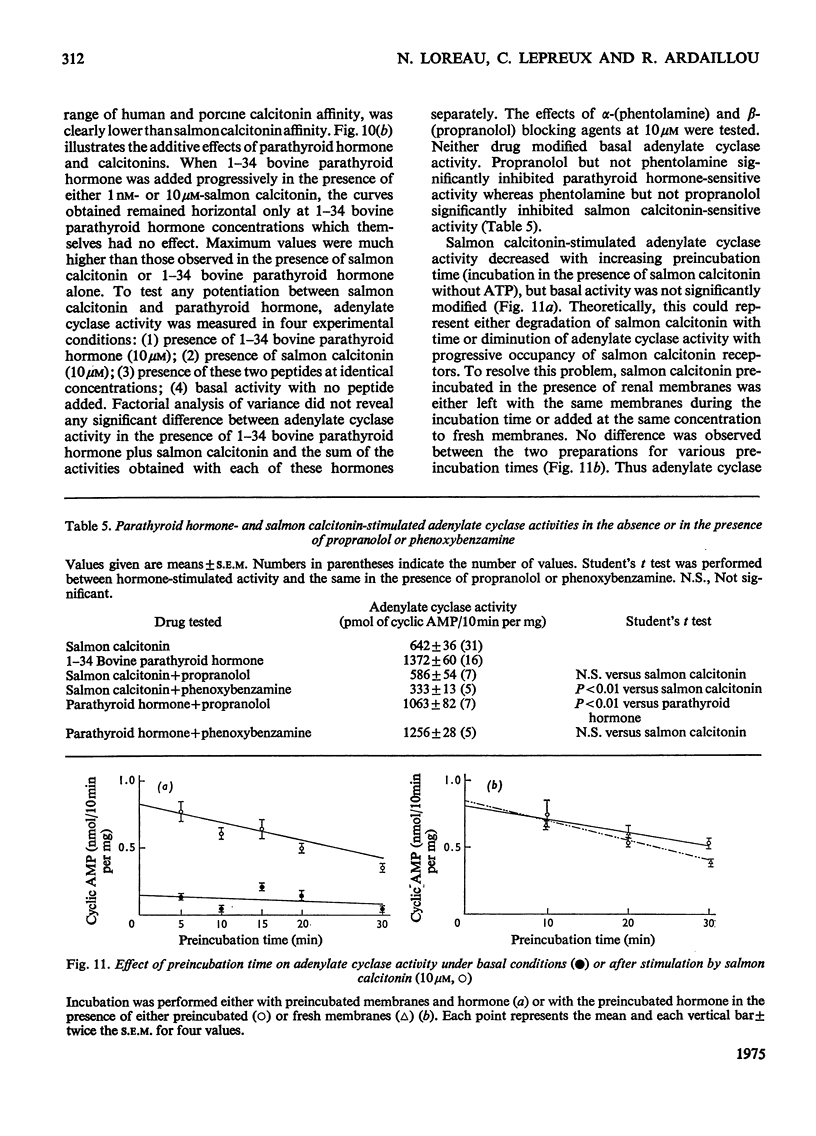
1. Renal tubular membranes from rat kidneys were prepared, and adenylate cyclase activity was measured under basal conditions, after stimulation by NaF or salmon calcitonin. Apparent Km value of the enzyme for hormone-linked receptor was close to 1 x 10(-8) M. 2. The system was sensitive to temperature and pH. pH was found to act both on affinity for salmon calcitonin-linked receptor and maximum stimulation, suggesting an effect of pH on hormone-receptor binding and on a subsequent step. 3. KCl was without effect areas whereas CoCl and CaCl2 above 100 muM and MnCl2 above 1 muM inhibited F- -and salmon calcitonin-sensitive adenylate cyclase activities. The Ca2+ inhibition of the response reflected a fall in maximum stimulation and not a loss of affinity of salmon calcitonin-linked receptor for the enzyme. 4. The measurement of salmon calcitonin-sensitive adenylate cyclase activity as a function of ATP concentration showed that the hormone increases the maximum velocity of the adenylate cyclase. GTP, ITP and XTP at 200 muM did not modify basal, salmon calcitonin- and parathyroid hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase activities. 5. Basal, salmon calcitonin- and F- -sensitive adenylate cyclase activities decreased at Mg2+ concentrations below 10 mM. High concentrations of Mg2+ (100 mM) led to an inhibition of the F- -stimulated enzyme. 6. Salmon calcitonin-linked receptor had a greater affinity for adenylate cyclase than human or porcine calcitonin-linked receptors. There was no additive effect of these three calcitonin peptides whereas parathyroid hormone added to salmon calcitonin increased adenylate cyclase activity, thus showing that both hormones bound to different membrane receptors. Human calcitonin fragments had no effect on adenylate cyclase activity. 7. Salmon calcitonin-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity decreased with the preincubation time. This was due to progressive degradation of the hormone and not to the rate of binding to membrane receptors.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck N. P., DeRubertis F. R., Michelis M. F., Fusco R. D., Field J. B., Davis B. B. Effect of prostaglandin E 1 on certain renal actions of parathyroid hormone. J Clin Invest. 1972 Sep;51(9):2352–2358. doi: 10.1172/JCI107047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L., Pohl S. L., Rodbell M. Adenyl cyclase in fat cells. 1. Properties and the effects of adrenocorticotropin and fluoride. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 10;244(13):3468–3476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockaert J., Roy C., Jard S. Oxytocin-sensitive adenylate cyclase in frog bladder epithelial cells. Role of calcium, nucleotides, and other factors in hormonal stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):7073–7081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase L. R., Aurbach G. D. Renal adenyl cyclase: anatomically separate sites for parathyroid hormone and vasopressin. Science. 1968 Feb 2;159(3814):545–547. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3814.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick D. F., Davenport G. R., Forte L., Landon E. J. Characterization of plasma membrane proteins in mammalian kidney. I. Preparation of a membrane fraction and separation of the protein. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jul 10;244(13):3561–3569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte L. R. Characterization of the adenyl cyclase of rat kidney plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 9;266(2):524–542. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90108-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurokawa K., Massry S. G. Evidence for two separate adenyl cyclase systems responding independently to parathyroid hormone and -adrenergic agents in the renal cortex of the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 May;143(1):123–126. doi: 10.3181/00379727-143-37266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurokawa K., Nagata N., Sasaki M., Nakane K. Effects of calcitonin in the concentration of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in rat kidney in vivo and in vitro. Endocrinology. 1974 Jun;94(6):1514–1518. doi: 10.1210/endo-94-6-1514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., Roth J., Pastan I. Effects of calcium on ACTH stimulation of the adrenal: separation of hormone binding from adenyl cyclase activation. Nature. 1970 Nov 28;228(5274):864–866. doi: 10.1038/228864a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus R., Aurbach G. D. Adenyl cyclase from renal cortex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 20;242(2):410–421. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90232-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx S. J., Fedak S. A., Aurbach G. D. Preparation and characterization of a hormone-responsive renal plasma membrane fraction. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6913–6918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx S. J., Woodward C. J., Aurbach G. D. Calcitonin receptors of kidney and bone. Science. 1972 Dec 1;178(4064):999–1001. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4064.999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx S. J., Woodward C., Aurbach G. D., Glossmann H., Keutmann H. T. Renal receptors for calcitonin. Binding and degradation of hormone. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 10;248(13):4797–4802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melson G. L., Chase L. R., Aurbach G. D. Parathyroid hormone-sensitive adenyl cyclase in isolated renal tubules. Endocrinology. 1970 Mar;86(3):511–518. doi: 10.1210/endo-86-3-511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murad F., Brewer H. B., Jr, Vaughan M. Effect of thyrocalcitonin on adenosine 3':5'-cyclic phosphate formation by rat kidney and bone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Feb;65(2):446–453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.2.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Birnbaumer L., Pohl S. L., Krans H. M. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. V. An obligatory role of guanylnucleotides in glucagon action. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1877–1882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sraer J., Ardaillou R., Couette S. Increased binding of calcitonin to renal receptors in parathyroidectomized rats. Endocrinology. 1974 Aug;95(2):632–637. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-2-632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


